Розробка моделі прогнозування раціональності фінансових рішень в умовах діджиталізації фінансових ринків
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325518Ключові слова:
полівекторна модель прогнозування, діджиталізація фінансових ринків, фінансовий менеджмент, фінанси, ризикиАнотація
Об’єктом цього дослідження є прогнозування раціональності фінансових рішень в умовах діджиталізації фінансових ринків. В умовах діджиталізації фінансових ринків близько ¼ фінансових рішень виявляються не раціональними для суб’єктів фінансових ринків. У цьому контексті проблемою є нездатність суб’єктів фінансових ринків прогнозувати раціональність фінансових рішень.
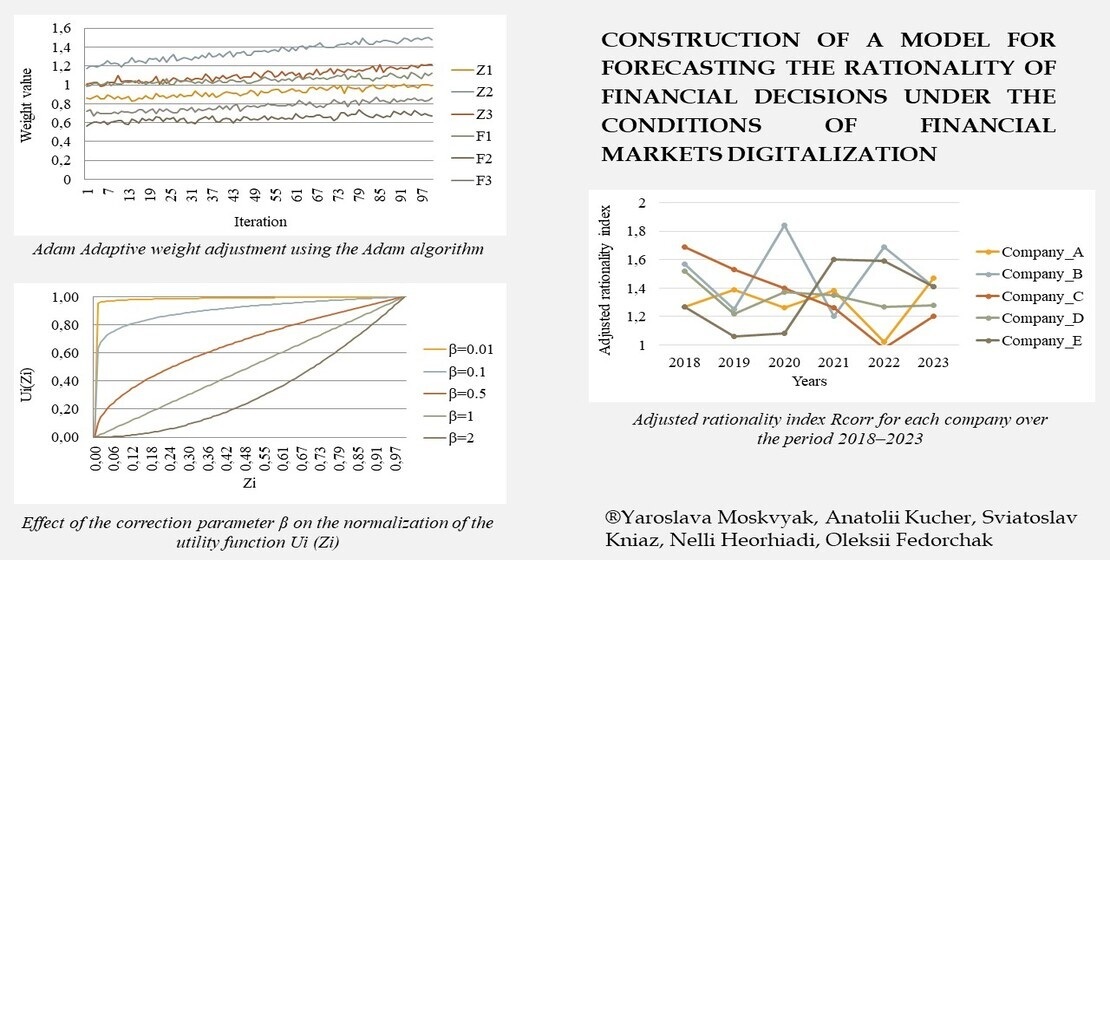
Розроблена полівекторна модель прогнозування раціональності фінансових рішень в умовах діджиталізації фінансових ринків дозволяє оцінювати ключові показники ефективності прийняття рішень та мінімізувати ризики. Установлено, що застосування адаптивного алгоритму оптимізації Adam забезпечує зниження середньої похибки прогнозування на 18,7% порівняно з традиційними методами, такими як градієнтний спуск. Використання функції корисності з коригувальним параметром β дозволило згладити ринкові флуктуації, зменшуючи відхилення прогнозованих значень від фактичних у середньому на 12,3%. Проведене сценарне моделювання методом Монте-Карло продемонструвало, що в умовах високої волатильності ринку точність прогнозів залишається стабільною та перевищує 85%. Апробація моделі на прикладі п’яти українських фінансових компаній (Moneyveo, Леогеймінг Пей, Укрфінжитло, Європейський мікрофінансовий альянс, Смарт Пей) за період 2018–2023 років показала, що рівень нераціональних фінансових рішень знизився в середньому з 24,6% до 15,2%, що еквівалентно економії фінансових ресурсів у розмірі 37,8 млн грн на кожну компанію. Це свідчить про значний потенціал моделі у підвищенні якості фінансового менеджменту та забезпеченні стійкого розвитку фінансових ринків.
Практична цінність розробленої полівекторної прогностичної моделі раціональності фінансових рішень полягає у її здатності оптимізувати процес оцінки ризиків та доходності інвестицій із урахуванням багатофакторності сучасного ринкового середовища. Результати можуть бути інструментом для стратегічного планування та оцінки інвестиційної привабливості
Посилання
- Fama, E. F. (1970). Efficient Capital Markets: A Review of Theory and Empirical Work. The Journal of Finance, 25 (2), 383. https://doi.org/10.2307/2325486
- Merton, R. C. (1973). Theory of Rational Option Pricing. The Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science, 4 (1), 141. https://doi.org/10.2307/3003143
- Box, G. E. P., Jenkins, G. M. (1976). Time series analysis: Forecasting and control. Holden-Day, 575. Available at: https://archive.org/details/timeseriesanalys0000boxg_p2r1/page/n5/mode/2up
- Makridakis, S., Spiliotis, E., Assimakopoulos, V. (2018). Statistical and Machine Learning forecasting methods: Concerns and ways forward. PLOS ONE, 13 (3), e0194889. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194889
- Kahneman, D., Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect Theory: An Analysis of Decision under Risk. Econometrica, 47 (2), 263. https://doi.org/10.2307/1914185
- Grinblatt, M., Han, B. (2005). Prospect theory, mental accounting, and momentum. Journal of Financial Economics, 78 (2), 311–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2004.10.006
- Aaker, D. A. (1991). Managing brand equity: Capitalizing on the value of a brand name. Free Press. Available at: https://archive.org/details/managingbrandequ00aake
- Kaplan, R. S., Norton, D. P. (1996). The balanced scorecard: Translating strategy into action. Harvard Business School Press. Available at: https://archive.org/details/balancedscorecar00kapl
- Shiller, R. J. (2000). Irrational exuberance. Princeton University Press. Available at: https://archive.org/details/irrationalexuber00shil
- Taleb, N. N. (2007). The black swan: The impact of the highly improbable. Random House. Available at: https://archive.org/details/10.1.1.695.4305
- de Frutos, M. Á., Manzano, C. (2014). Market transparency, market quality, and sunshine trading. Journal of Financial Markets, 17, 174–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finmar.2013.06.001
- Kolodiziev, O., Gontar, D. (2014). Scenario modeling of the bank’s market value strategic management. Economic Annals-XXI, 9-10 (2), 19–23. Available at: https://ea21journal.world/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/ea-V145-05.pdf
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45 (1), 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010933404324
- Bidyuk, P., Prosyankina-Zharova, T., Terentiev, O., Medvedieva, M. (2018). Adaptive modelling for forecasting economic and financial risks under uncertainty in terms of the economic crisis and social threats. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 4 (2 (42)), 4–10. https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2018.135483
- Costello, S., François, G., Bonvin, D. (2016). A Directional Modifier-Adaptation Algorithm for Real-Time Optimization. Journal of Process Control, 39, 64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2015.11.008
- Chachuat, B., Marchetti, A., Bonvin, D. (2008). Process optimization via constraints adaptation. Journal of Process Control, 18 (3-4), 244–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2007.07.001
- Papasavvas, A., de Avila Ferreira, T., Marchetti, A. G., Bonvin, D. (2019). Analysis of output modifier adaptation for real-time optimization. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 121, 285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.09.028
- Marchetti, A., Chachuat, B., Bonvin, D. (2010). A dual modifier-adaptation approach for real-time optimization. Journal of Process Control, 20 (9), 1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.06.006
- Liu, X.-F., Zhan, Z.-H., Gu, T.-L., Kwong, S., Lu, Z., Duh, H. B.-L., Zhang, J. (2020). Neural Network-Based Information Transfer for Dynamic Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31 (5), 1557–1570. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2019.2920887
- Kniaz, S., Brych, V., Heorhiadi, N., Shevchenko, S., Dzvonyk, R., Skrynkovskyy, R. (2024). Enhancing the Informativeness of Managing Mentoring Activities based on Simulation Modeling. 2024 14th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), 8, 384–388. https://doi.org/10.1109/acit62333.2024.10712547
- Kniaz, S., Brych, V., Heorhiadi, N., Shevchenko, S., Dzvonyk, R., Skrynkovskyy, R. (2024). Informational-Reflective Management of Mentoring Activities Development in the Enterprise. 2024 14th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), 13, 389–392. https://doi.org/10.1109/acit62333.2024.10712601
- Kniaz, S., Heorhiadi, N., Kucher, L., Tyrkalo, Y., Bovsunivska, A. (2023). Development of a customer service system in electronic commerce. Business Management, 2. https://doi.org/10.58861/tae.bm.2023.2.04
- Meziane, M. T., Bouguetaia, S. (2023). Impact of financial technology on Algerian bank performance. Journal of Innovations and Sustainability, 7 (4), 07. https://doi.org/10.51599/is.2023.07.04.07
- Paltrinieri, N., Comfort, L., Reniers, G. (2019). Learning about risk: Machine learning for risk assessment. Safety Science, 118, 475–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.06.001
- Mashrur, A., Luo, W., Zaidi, N. A., Robles-Kelly, A. (2020). Machine Learning for Financial Risk Management: A Survey. IEEE Access, 8, 203203–203223. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3036322
- Chandrinos, S. K., Sakkas, G., Lagaros, N. D. (2018). AIRMS: A risk management tool using machine learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 105, 34–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.044
- Toromade, A. S., Chiekezie, N. R. (2024). Forecasting stock prices and market trends using historical data to aid investment decisions. Finance & Accounting Research Journal, 6 (8), 1472–1484. https://doi.org/10.51594/farj.v6i8.1434
- Sun, B., Zhang, Y., Zhu, K., Mao, H., Liang, T. (2024). Is faster really better? The impact of digital transformation speed on firm financial distress: Based on the cost-benefit perspective. Journal of Business Research, 179, 114703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2024.114703
- Wang, D., Shao, X. (2024). Research on the impact of digital transformation on the production efficiency of manufacturing enterprises: Institution-based analysis of the threshold effect. International Review of Economics & Finance, 91, 883–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iref.2024.01.046
- Do Thi, M., Le Huyen, T., Le Thi, L. (2024). The impact of policies on the digital transformation capability of Vietnamese agricultural enterprises: the moderating role of policy accessibility. Agricultural and Resource Economics: International Scientific E-Journal, 10 (4). https://doi.org/10.51599/are.2024.10.04.05
- Dakalbab, F., Talib, M. A., Nasir, Q., Saroufil, T. (2024). Artificial intelligence techniques in financial trading: A systematic literature review. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 36 (3), 102015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2024.102015
- Ragazou, K., Passas, I., Garefalakis, A., Galariotis, E., Zopounidis, C. (2023). Big Data Analytics Applications in Information Management Driving Operational Efficiencies and Decision-Making: Mapping the Field of Knowledge with Bibliometric Analysis Using R. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 7 (1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010013
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Yaroslava Moskvyak, Anatolii Kucher, Sviatoslav Kniaz, Nelli Heorhiadi, Oleksii Fedorchak

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









