Оцінка впливу вагової ініціалізації на рекурентні та трансформерні моделі при прогнозуванні цін фінансових активів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326913Ключові слова:
глибоке навчання, фінансове прогнозування активів, ініціалізація ваг, фінансові часові рядиАнотація
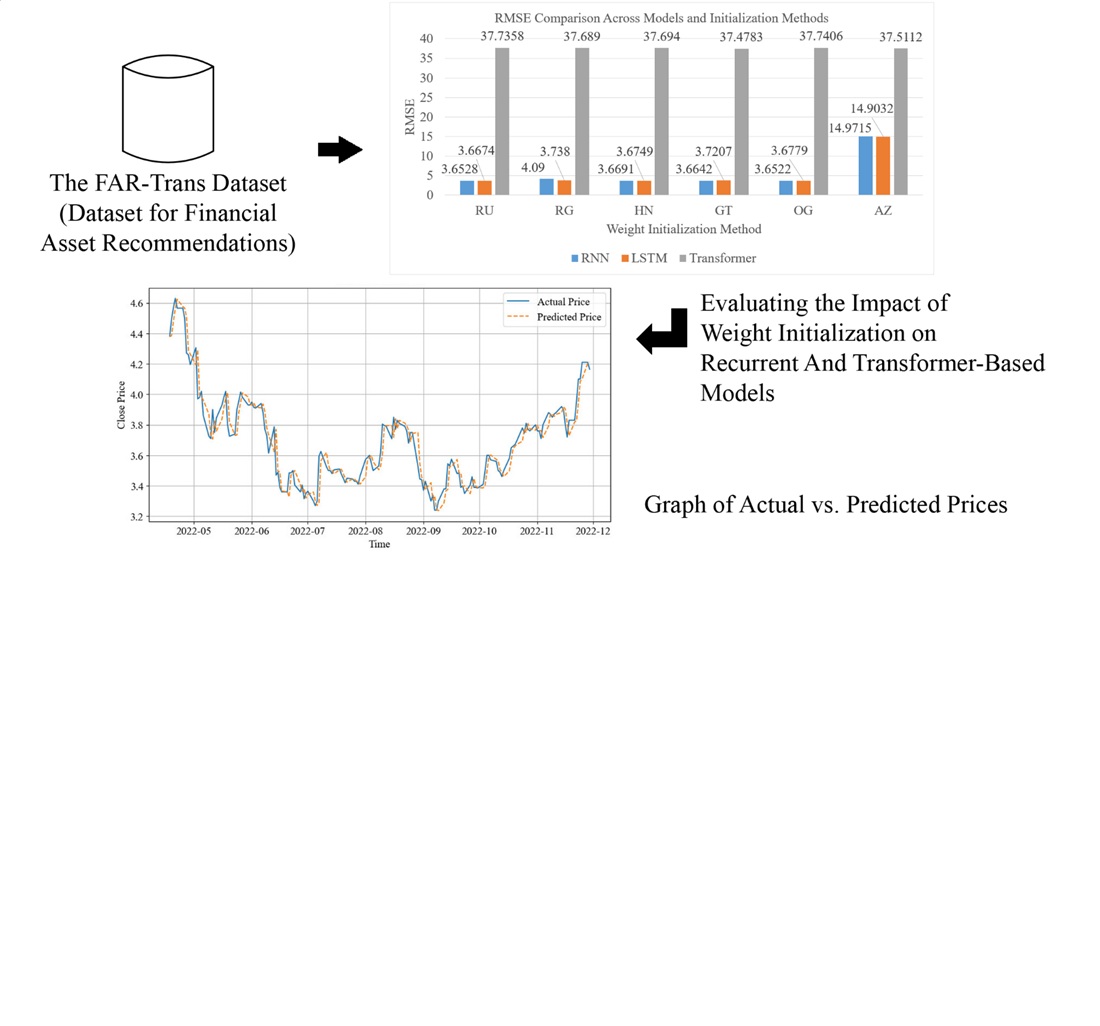
Об’єктом цього дослідження є модель глибокого навчання, заснована на рекурентній нейронній мережі (РНН), довгій короткочасній пам’яті (ДКП) та трансформаторі, що застосовується для прогнозування цін на фінансові активи з використанням історичних даних часових рядів. Основною проблемою, що розглядається, є відсутність систематичного дослідження, що оцінює комбінований вплив методів ініціалізації ваг та функцій активації в моделях прогнозування часових рядів, зокрема щодо швидкості збіжності, точності прогнозування та здатності моделі враховувати мінливість цін. Результати показують, що РНН та ДКП мають кращу стабільність навчання, здатні збігатися в одну епоху та забезпечують високу продуктивність прогнозування (середньоквадратична похибка < 3,7, середня абсолютна відсоткова похибка < 0,015, R2 близько 0,9999). На противагу цьому, трансформер показав нижчу продуктивність прогнозування (середньоквадратична похибка близько 37, середня абсолютна відсоткова похибка близько 0,58, R2 між 0,9884–0,9885) та мав тенденцію до перенавчання для різних комбінацій стратегій. У моделях РНН та ДКП комбінація All-Zeros та ReLU спеціально погіршує стабільність та призводить до перенавчання. Перевага РНН та ДКП пояснюється їхніми послідовними архітектурами, які ефективніше навчаються короткостроковим часовим патернам та стійкіші до неоптимальної ініціалізації ваг. Тому вибір відповідної комбінації ініціалізації ваг та функції активації відіграє ключову роль у підвищенні продуктивності моделі. Ці результати надають емпіричні докази важливості вибору конфігурації в глибокому навчанні для прогнозування часових рядів. Результати можуть бути застосовані при розробці систем прогнозування та рекомендацій щодо фінансових активів на основі глибокого навчання, особливо для активів з тривалою історією та волатильними ринковими умовами
Посилання
- Achury-Calderón, F., Arredondo, J. A., Sánchez Ascanio, L. C. (2025). A novel predictive analytics model for forecasting short-term trends in equity assets prices. Decision Analytics Journal, 14, 100534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2024.100534
- Tan, J., Deveci, M., Li, J., Zhong, K. (2024). Asset pricing via fused deep learning with visual clues. Information Fusion, 102, 102049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102049
- Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Xie, Z., Zhang, W., Li, Q. (2025). Unraveling asset pricing with AI: A systematic literature review. Applied Soft Computing, 175, 112978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2025.112978
- Harumy, H. F., Hardi, S. M., Al Banna, M. F. (2024). EarlyStage Diabetes Risk Detection Using Comparison of Xgboost, Lightgbm, and Catboost Algorithms. Advanced Information Networking and Applications, 12–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57931-8_2
- Al-Selwi, S. M., Hassan, M. F., Abdulkadir, S. J., Muneer, A., Sumiea, E. H., Alqushaibi, A., Ragab, M. G. (2024). RNN-LSTM: From applications to modeling techniques and beyond – Systematic review. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 36 (5), 102068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2024.102068
- Kim, D.-K., Kim, K. (2022). A Convolutional Transformer Model for Multivariate Time Series Prediction. IEEE Access, 10, 101319–101329. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3203416
- Ahmed, S., Nielsen, I. E., Tripathi, A., Siddiqui, S., Ramachandran, R. P., Rasool, G. (2023). Transformers in Time-Series Analysis: A Tutorial. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 42 (12), 7433–7466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02454-8
- Ahn, J. Y., Kim, Y., Park, H., Park, S. H., Suh, H. K. (2024). Evaluating Time-Series Prediction of Temperature, Relative Humidity, and CO2 in the Greenhouse with Transformer-Based and RNN-Based Models. Agronomy, 14 (3), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030417
- de Pater, I., Mitici, M. (2023). A mathematical framework for improved weight initialization of neural networks using Lagrange multipliers. Neural Networks, 166, 579–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2023.07.035
- Harumy, T., Ginting, D. S. Br. (2021). Neural Network Enhancement Forecast of Dengue Fever Outbreaks in Coastal Region. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1898 (1), 012027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1898/1/012027
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Lydia, M. S., Efendi, S. (2023). A novel approach to the development of neural network architecture based on metaheuristic protis approach. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (124)), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281986
- Ghallabi, F., Souissi, B., Du, A. M., Ali, S. (2025). ESG stock markets and clean energy prices prediction: Insights from advanced machine learning. International Review of Financial Analysis, 97, 103889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2024.103889
- Xu, F., Tan, S. (2021). Deep learning with multiple scale attention and direction regularization for asset price prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 186, 115796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115796
- Abolmakarem, S., Abdi, F., Khalili-Damghani, K., Didehkhani, H. (2022). A Multi-Stage Machine Learning Approach for Stock Price Prediction: Engineered and Derivative Indices. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4074883
- Pan, S., Long, S., Wang, Y., Xie, Y. (2023). Nonlinear asset pricing in Chinese stock market: A deep learning approach. International Review of Financial Analysis, 87, 102627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102627
- Gülmez, B. (2025). GA-Attention-Fuzzy-Stock-Net: An optimized neuro-fuzzy system for stock market price prediction with genetic algorithm and attention mechanism. Heliyon, 11 (3), e42393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42393
- Islam, B. ul, Ahmed, S. F. (2022). Short-Term Electrical Load Demand Forecasting Based on LSTM and RNN Deep Neural Networks. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2022, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2316474
- Rahman, N. H. A., Yin, C. H., Zulkafli, H. S. (2024). Activation functions performance in multilayer perceptron for time series forecasting. Proceedings of the 38th International Conference of the Polymer Processing Society (PPS-38), 3158, 070001. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0223864
- Sinanc Terzi, D. (2024). Effect of different weight initialization strategies on transfer learning for plant disease detection. Plant Pathology, 73 (9), 2325–2343. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13997
- Srivastava, G., Vashisth, S., Dhall, I., Saraswat, S. (2020). Behavior Analysis of a Deep Feedforward Neural Network by Varying the Weight Initialization Methods. Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences, 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5345-5_15
- Alhlffee, M. H. B., Ahmad Abuirbaiha, R. A. (2024). The Effects of Dropout and Weight Initialization on Human Face Classification Accuracy Using Multiple-agent Generative Adversarial Network. 2024 7th International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1109/icict62343.2024.00050
- Rajaraman, S., Zamzmi, G., Yang, F., Liang, Z., Xue, Z., Antani, S. (2024). Uncovering the effects of model initialization on deep model generalization: A study with adult and pediatric chest X-ray images. PLOS Digital Health, 3 (1), e0000286. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pdig.0000286
- Berghout, T., Bentrcia, T., Lim, W. H., Benbouzid, M. (2023). A Neural Network Weights Initialization Approach for Diagnosing Real Aircraft Engine Inter-Shaft Bearing Faults. Machines, 11 (12), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11121089
- Boulila, W., Alshanqiti, E., Alzahem, A., Koubaa, A., Mlaiki, N. (2024). An effective weight initialization method for deep learning: Application to satellite image classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 254, 124344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124344
- Wong, K., Dornberger, R., Hanne, T. (2022). An analysis of weight initialization methods in connection with different activation functions for feedforward neural networks. Evolutionary Intelligence, 17 (3), 2081–2089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-022-00795-y
- Mojtahedi, F. F., Yousefpour, N., Chow, S. H., Cassidy, M. (2025). Deep Learning for Time Series Forecasting: Review and Applications in Geotechnics and Geosciences. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-025-10244-5
- Mienye, I. D., Swart, T. G., Obaido, G. (2024). Recurrent Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Review of Architectures, Variants, and Applications. Information, 15 (9), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15090517
- Huang, H., Wang, Z., Liao, Y., Gao, W., Lai, C., Wu, X., Zeng, Z. (2024). Improving the explainability of CNN-LSTM-based flood prediction with integrating SHAP technique. Ecological Informatics, 84, 102904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102904
- Sanz-Cruzado, J., Droukas, N., McCreadie, R. (2024). FAR-Trans: An Investment Dataset for Financial Asset Recommendation. IJCAI-2024 Workshop on Recommender Systems in Finance (Fin-RecSys). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.08692
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Andri Andri, Tengku Henny Febriana Harumy, Syahril Efendi

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









