Identification of the influence ofgas metal arc welding methods on the mechanical characteristics of duplex stainless steel
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327278Keywords:
gas metal, duplex, mechanical, impact, welding, material, tensile strength, corrosionAbstract
This study evaluates the effect of various Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) methods on the mechanical properties of duplex stainless steel. The main objective is to identify the most effective GMAW process parameters in improving the mechanical properties of the material, including tensile strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
The results of this study provide valuable insights into improving the weld quality, mechanical properties, and durability of duplex stainless steels in high-performance environments and corrosive conditions. Industries such as oil and gas, shipbuilding and chemical processing can greatly benefit from these findings by adopting optimized GMAW parameters to produce stronger and more durable weld joints.
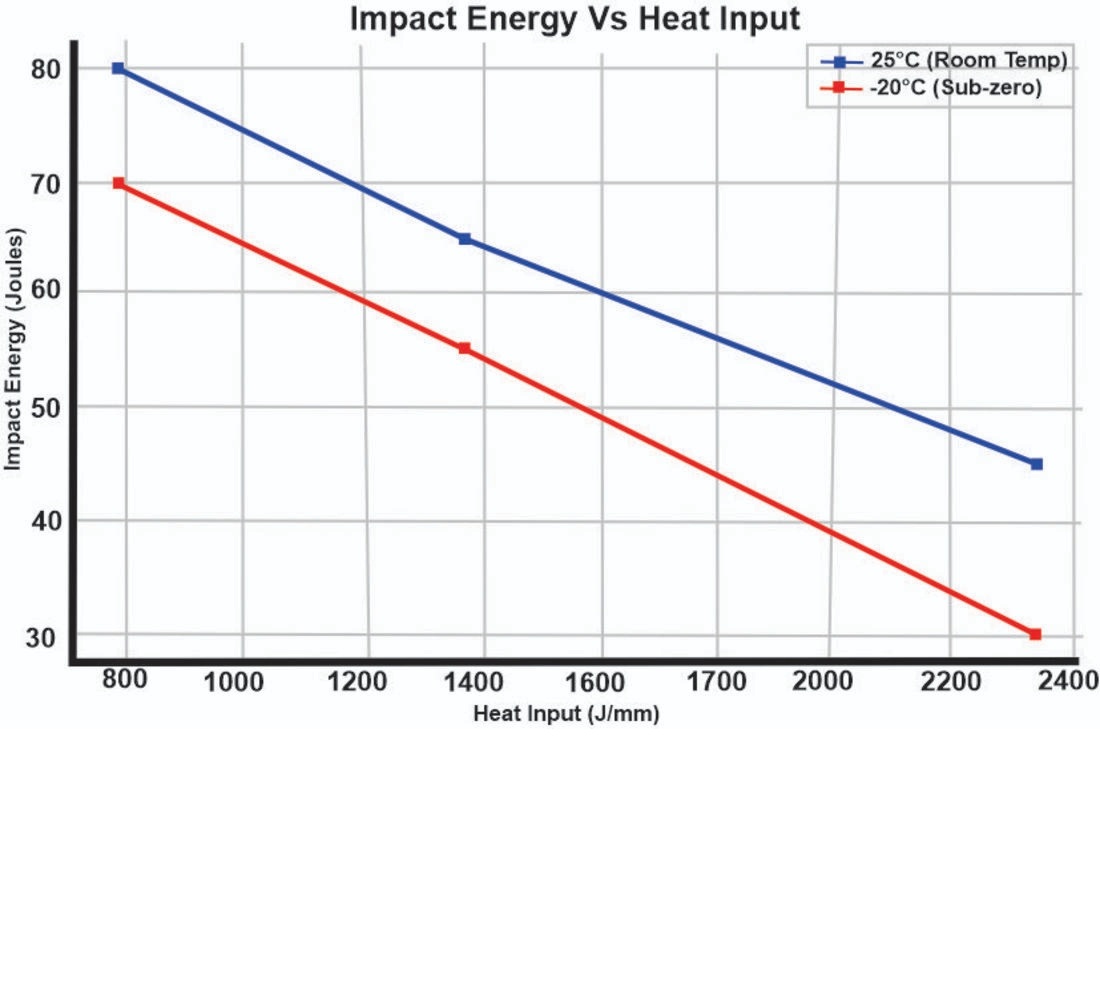
The findings also highlight the significant impact of welding and heat treatment on the alloy’s mechanical properties. The strength of the control material was recorded at 811.47 MN/m2, whereas the welded samples exhibited strengths between 177.07 and 257.32 MN/m2. The impact energy of the control material was 162.70 J, while the welded samples showed values ranging from 38.64 J to 56.20 J.
Additionally, the study reveals that stress relief heat treatment resulted in the highest strength (A3=331 MN/m2) compared to quenching in lubricating oil (A2=329 MN/m2) and neem oil (A1=222 MN/m2), although variations in material toughness were observed. The uniqueness of this research lies in its systematic approach in correlating GMAW parameters with changes in microstructure and mechanical properties. The distinctiveness of this research stems from its structured methodology in linking GMAW parameters to variations in microstructure and mechanical properties, facilitating the identification of optimal welding conditions
References
- Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Sabzi, M. (2018). The Effect of Heat Treatment Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties, Precipitation, Fatigue Life, and Fracture Mode of an Austenitic Mn Hadfield Steel. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 27 (10), 5246–5253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3625-y
- Aguirre, H. V. M., Teixeira, F. R., Mota, C. A. M. da, Nascimento, A. S. do. (2021). Evaluation of Dissimilar Welds with the Temper-bead Technique Using ER 316L and ER NiCrMo-3 Electrodes on ASTM A182 F22 Steel. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro), 26 (3). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-707620210003.13000
- Alvarães, C. P., Madalena, F. C. A., Souza, L. F. G. de, Jorge, J. C. F., Araújo, L. S., Mendes, M. C. (2019). Performance of the INCONEL 625 alloy weld overlay obtained by FCAW process. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro), 24 (1). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-707620190001.0627
- Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Sabzi, M., Ghobeiti-Hasab, M., Roshan-Ghiyas, A. (2018). Optimization of spot welding process parameters in dissimilar joint of dual phase steel DP600 and AISI 304 stainless steel to achieve the highest level of shear-tensile strength. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 726, 120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.072
- Chagas de Souza, G., da Silva, A. L., Tavares, S. S. M., Pardal, J. M., Ferreira, M. L. R., Filho, I. C. (2016). Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance evaluation of superduplex stainless steel UNS S32760 repaired by GTAW process. Welding International, 30 (6), 432–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507116.2015.1096527
- Giarollo, D. F., Mazzaferro, C. C. P., Mazzaferro, J. A. E. (2019). Effect of filler material on sliding wear resistance of a structural steel welded by GMAW. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro), 24 (3). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-707620190003.0780
- Hosseini, V. A., Valiente Bermejo, M. A., Gårdstam, J., Hurtig, K., Karlsson, L. (2016). Influence of multiple thermal cycles on microstructure of heat-affected zone in TIG-welded super duplex stainless steel. Welding in the World, 60 (2), 233–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-016-0300-5
- Jafarian, H. R., Sabzi, M., Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Eivani, A. R., Park, N. (2021). The influence of austenitization temperature on microstructural developments, mechanical properties, fracture mode and wear mechanism of Hadfield high manganese steel. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 10, 819–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.003
- Kangazian, J., Shamanian, M. (2019). Effect of Pulsed Current on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Based Alloy/Super Duplex Stainless Steel Dissimilar Welds. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 72 (9), 2403–2416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01693-1
- Muthusamy, C., Karuppiah, L., Paulraj, S., Kandasami, D., Kandhasamy, R. (2016). Effect of Heat Input on Mechanical and Metallurgical Properties of Gas Tungsten Arc Welded Lean Super Martensitic Stainless Steel. Materials Research, 19 (3), 572–579. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2015-0538
- Mosa, E. S., Morsy, M. A., Atlam, A. (2017). Effect of heat input and shielding gas on microstructure and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel 304L. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4 (12), 370–377.
- Sabzi, M., Dezfuli, S. M. (2018). Drastic improvement in mechanical properties and weldability of 316L stainless steel weld joints by using electromagnetic vibration during GTAW process. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 33, 74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.05.002
- Shamanian, M., Kangazian, J., Szpunar, J. A. (2021). Insights into the microstructure evolution and crystallographic texture of API X-65 steel/UNS S32750 stainless steel dissimilar welds by EBSD analysis. Welding in the World, 65 (5), 973–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-01062-3
- Sabzi, M., Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Eivani, A. R., Park, N., Jafarian, H. R. (2021). The effect of pulse current changes in PCGTAW on microstructural evolution, drastic improvement in mechanical properties, and fracture mode of dissimilar welded joint of AISI 316L-AISI 310S stainless steels. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 823, 141700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141700
- Zhang, Y., Yang, H., Huang, R., Sun, P., Zheng, S., Li, M. et al. (2024). Investigation of microstructure and corrosion resistance of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy under various ageing conditions. Corrosion Science, 227, 111719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2023.111719
- Karakulov, V. V., Smolin, I., Kulkov, S. N. (2020). About mechanical behaviour of metal matrix composites under shock wave loading. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1527 (1), 012020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1527/1/012020
- Yetgin, Ş., Çavdar, Ö., Çavdar, A. (2008). The effects of the fiber contents on the mechanic properties of the adobes. Construction and Building Materials, 22 (3), 222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2006.08.022
- Madugu, I. A., Abdulwahab, M., Aigbodion, V. S. (2009). Effect of iron fillings on the properties and microstructure of cast fiber–polyester/iron filings particulate composite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 476 (1-2), 807–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.09.165
- Zhang, Z., Jing, H., Xu, L., Han, Y., Zhao, L., Lv, X., Zhang, J. (2018). Influence of heat input in electron beam process on microstructure and properties of duplex stainless steel welded interface. Applied Surface Science, 435, 352–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.125
- Reza Tabrizi, T., Sabzi, M., Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Eivani, A. R., Park, N., Jafarian, H. R. (2021). Comparing the effect of continuous and pulsed current in the GTAW process of AISI 316L stainless steel welded joint: microstructural evolution, phase equilibrium, mechanical properties and fracture mode. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 15, 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.154
- Fonseca, G. S. da, Oliveira, P. M. de, Diniz, M. G., Bubnoff, D. V., Castro, J. A. de. (2017). Sigma Phase in Superduplex Stainless Steel: Formation, Kinetics and Microstructural Path. Materials Research, 20 (1), 249–255. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0436
- Wang, Y., Xu, L., Han, Y., Zhao, L., Li, H., Hao, K., Ren, W. (2023). Super duplex stainless steel with balance ratio produced by laser directed energy deposition (L-DED). Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 105, 213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.09.023
- Maslak, M., Stankiewicz, M., Slazak, B. (2021). Duplex Steels Used in Building Structures and Their Resistance to Chloride Corrosion. Materials, 14 (19), 5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195666
- Hutchinson, B., Komenda, J., Rohrer, G. S., Beladi, H. (2015). Heat affected zone microstructures and their influence on toughness in two microalloyed HSLA steels. Acta Materialia, 97, 380–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.05.055
- Cao, Y., Zhang, Y. (2025). Control of DE-GMAW through human–robot collaboration. Welding in the World, 69 (5), 1459–1468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-025-01954-2
- Xu, B., Liu, F., Lin, D., Han, X., Chen, X., Wu, L. et al. (2022). Investigation of weld formation and porosity in 5052 aluminium alloy laser-GMA hybrid welding assisted by magnetic field with different orientations. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 27 (8), 672–682. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2022.2106022
- Yuan, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Wang, C., Li, Z. (2025). Bond Characteristic-Dependent Viscosity Variations in CaF₂-SiO₂-Al₂O₃-MgO Welding Fluxes. Welding Journal, 104 (04), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.29391/2025.104.009
- Ibrahim, T., Yawas, D. S., Aku, S. Y. (2013). Effects of Gas Metal Arc Welding Techniques on the Mechanical Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 01 (05), 222–230. https://doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2013.15035
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahmad Bakhori, Muhammad Rafiq Yanhar, Suhardi Napid

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








