Enhanced identification of illicit bitcoin transactions through genetic algorithm-based feature selection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.335630Keywords:
bitcoin, illicit transactions, machine learning, genetic algorithms, cryptocurrency forensicsAbstract
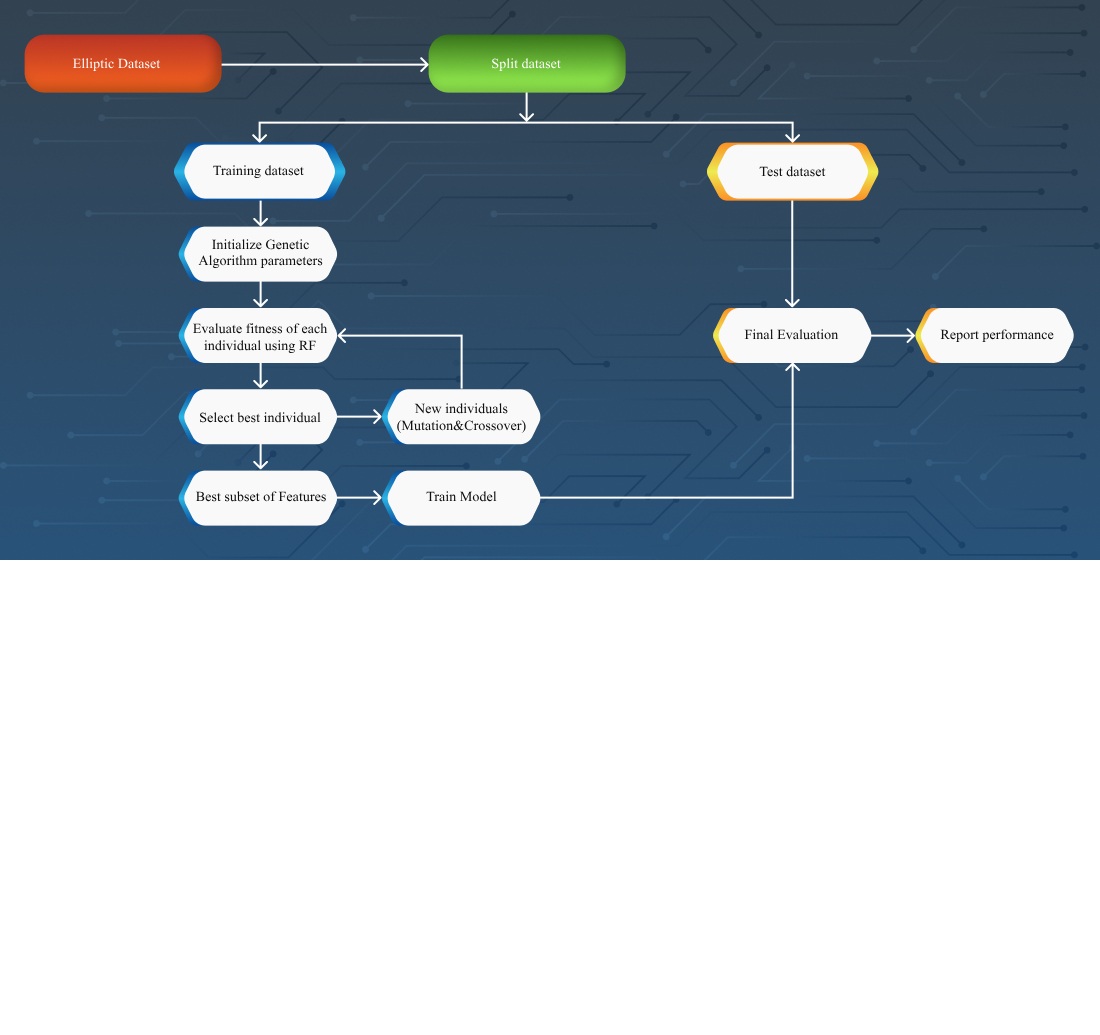
The object of this study is the process of classifying illicit Bitcoin transactions in blockchain datasets. The problem addressed in this work is the difficulty of detecting suspicious activity in cryptocurrency networks due to the high dimensionality of transaction data and the lack of semantic labels, which limits the effectiveness of conventional manual feature engineering. The proposed method combines domain-specific indicators of illicit behavior with a Genetic Algorithm-driven selection mechanism that dynamically evolves informative feature subsets. The developed framework was implemented and evaluated on the Elliptic and Elliptic++ datasets using random forest. The results obtained demonstrate that the GA-based method significantly increases model performance: the best-performing configuration achieved an F1-score of 84.3%, a precision of 99.4%, and a recall of 73.1%. Compared to baseline approaches on the same dataset, this method provides relative improvements of 0.9% in F1-score, 0.3% in precision, and 1.2% in recall. The effectiveness of the proposed solution is explained by its ability to detect hidden patterns in transactional data with many potential attributes without resorting to manual heuristics, as well as an optimized setting of Genetic Algorithm parameters. A distinctive feature of this method is the combination of heuristic search with domain-informed feature categories, which improves classification accuracy and reduces model complexity. The obtained results can be applied in practical scenarios such forensic analysis of cryptocurrency transactions. However, successful implementation requires access to historical transaction records and sufficient computing resources to process large, feature-rich datasets
References
- Berentsen, A., Schar, F. (2018). The Case for Central Bank Electronic Money and the Non-case for Central Bank Cryptocurrencies. Review, 100 (2), 97–106. https://doi.org/10.20955/r.2018.97-106
- Gajdek, S., Kozak, S. (2019). Bitcoin as an Electronic Payment Tool. Zeszyty Naukowe Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczo-Humanistycznego w Siedlcach. Seria: Administracja i Zarządzanie, 47 (120), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.34739/zn.2019.47.04
- Bunjaku, F., Gjorgieva-Trajkovska, O., Kacarski, E. M. (2017). Cryptocurrencies – advantages and disadvantages. Journal of Economics, 2 (1), 31–39.
- Sicignano, G. J. (2021). Money Laundering using Cryptocurrency: The Case of Bitcoin! Athens Journal of Law, 7 (2), 253–264. https://doi.org/10.30958/ajl.7-2-7
- How terrorist groups are exploiting crypto to raise funds and evade detection. Elliptic. Available at: https://www.elliptic.co/blog/how-terrorist-organizations-are-exploiting-crypto-to-raise-funds-and-evade-detection Last accessed: 18.03.2024
- Crypto crime mid-year update: Crime down 65% overall, but ransomware headed for huge year thanks to return of big game hunting (2023). Chainalysis Team. Available at: https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/crypto-crime-midyear-2023-update-ransomware-scams/ Last accessed: 18.03.2024
- Crypto Crime Trends: Illicit Volumes Portend Record Year as On-Chain Crime Becomes Increasingly Diverse and Professionalized (2025). Chainalysis Team. Available at: https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/2025-crypto-crime-report-introduction/ Last accessed: 15.02.2025
- Chuen, D. L. K. (2015). Handbook of Digital Currency: Bitcoin, Innovation, Financial Instruments, and Big Data. London: Academic Press. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286223926_Handbook_of_Digital_Currency_Bitcoin_Innovation_Financial_Instruments_and_Big_Data Last accessed: 01.03.2024
- Weber, M., Domeniconi, G., Chen, J., Weidele, D. K. I., Bellei, C., Robinson, T., Leiserson, C. E. (2019). Anti-Money Laundering in Bitcoin: Experimenting with Graph Convolutional Networks for Financial Forensics. Proceedings of the Workshop on Anomaly Detection in Finance (KDD ’19). Anchorage. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.02591
- Alarab, I., Prakoonwit, S., Nacer, M. I. (2020). Comparative Analysis Using Supervised Learning Methods for Anti-Money Laundering in Bitcoin. Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning Technologies, 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1145/3409073.3409078
- Alarab, I., Prakoonwit, S., Nacer, M. I. (2020). Competence of Graph Convolutional Networks for Anti-Money Laundering in Bitcoin Blockchain. Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Machine Learning Technologies, 23–27. https://doi.org/10.1145/3409073.3409080
- Elmougy, Y., Liu, L. (2023). Demystifying Fraudulent Transactions and Illicit Nodes in the Bitcoin Network for Financial Forensics. Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Long Beach, 3979–3990. https://doi.org/10.1145/3580305.3599803
- Pham, T. B., Lee, S. (2016). Anomaly detection in bitcoin network using unsupervised learning methods. arXiv, arXiv:1611.03941. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.02591
- Lorenz, J., Silva, M. I., Aparício, D., Ascensão, J. T., Bizarro, P. (2020). Machine learning methods to detect money laundering in the bitcoin blockchain in the presence of label scarcity. Proceedings of the First ACM International Conference on AI in Finance. New York, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1145/3383455.3422549
- Nerurkar, P., Bhirud, S., Patel, D., Ludinard, R., Busnel, Y., & Kumari, S. (2020). Supervised learning model for identifying illegal activities in Bitcoin. Applied Intelligence, 51 (6), 3824–3843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02048-w
- Tayebi, M., El Kafhali, S. (2022). Performance analysis of metaheuristics based hyperparameters optimization for fraud transactions detection. Evolutionary Intelligence, 17 (2), 921–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-022-00764-5
- Bouchlaghem, Y., Akhiat, Y., Amjad, S. (2022). Feature Selection: A Review and Comparative Study. E3S Web of Conferences, 351, 01046. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202235101046
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45 (1), 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010933404324
- Katoch, S., Chauhan, S. S., Kumar, V. (2020). A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80 (5), 8091–8126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6
- Contreras, R. C., Xavier da Silva, V. T., Xavier da Silva, I. T., Viana, M. S., Santos, F. L. dos, Zanin, R. B. et al. (2024). Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection Applied to Financial Time Series Monotonicity Prediction: Experimental Cases in Cryptocurrencies and Brazilian Assets. Entropy, 26 (3), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26030177
- Taha, A. A., Malebary, S. J. (2020). An Intelligent Approach to Credit Card Fraud Detection Using an Optimized Light Gradient Boosting Machine. IEEE Access, 8, 25579–25587. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2971354
- Howcroft, E. (2023). Crypto ransom attacks rise in first half of 2023, chainalysis says. Available at: https://www.reuters.com/technology/crypto-ransom-attacks-rise-first-half-2023-chainalysis-2023-07-12/ Last accessed: 15.02.2025
- Aziz, R. M., Baluch, M. F., Patel, S., Ganie, A. H. (2022). LGBM: a machine learning approach for Ethereum fraud detection. International Journal of Information Technology, 14 (7), 3321–3331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-022-00864-6
- Kute, D. V., Pradhan, B., Shukla, N., Alamri, A. (2021). Deep Learning and Explainable Artificial Intelligence Techniques Applied for Detecting Money Laundering–A Critical Review. IEEE Access, 9, 82300–82317. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3086230
- Černevičienė, J., Kabašinskas, A. (2024). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in finance: a systematic literature review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 57 (8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10854-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Medet Shaizat, Shynar Mussiraliyeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








