Design and implementation of disk-based graph feature preprocessor for terrorist financing detection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340033Keywords:
terrorism-financing, graph processing, external-memory algorithms, anomaly detection, complianceAbstract
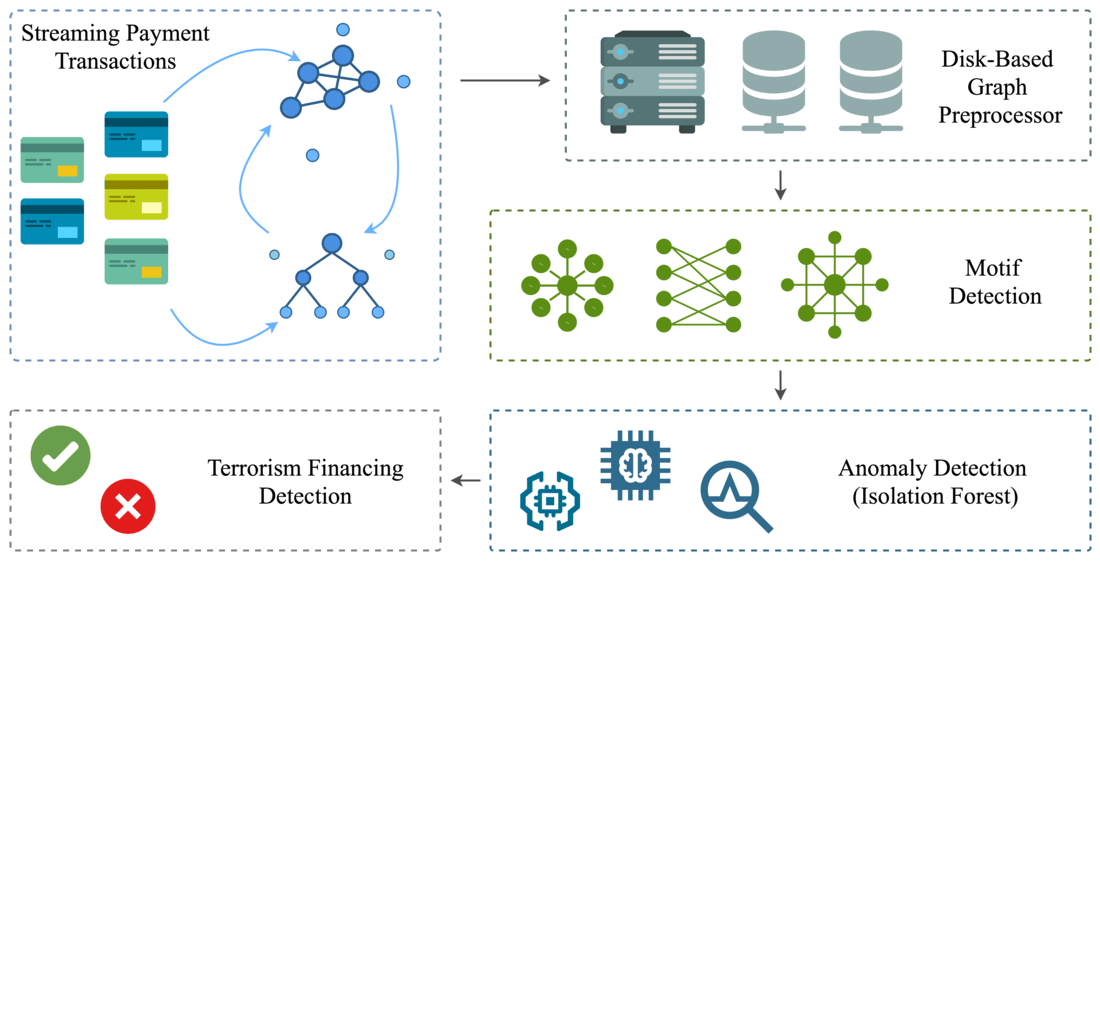
The object of the study is streaming payment transactions modeled as directed multigraphs. This study investigates terrorism-financing detection in payment transaction networks using disk-based graph processing and anomaly detection. The key problem addressed is the high memory consumption of graph-based detectors, which prevents analysis on systems with limited Random Access Memory, typical of small and mid-sized financial institutions.
A disk-based graph feature preprocessor (DGFP) was made to get around this problem. During stream processing, DGFP dynamically labels connected components and identifies eight graph patterns characteristic of terrorist financing, including fan-in/fan-out stars and multi-hop chains. The system persists component descriptors to a columnar store on an SSD and uses an LRU-managed hot cache to serve the features, enabling real-time transaction scoring with sub-second latency.
On a two-million-transaction AMLSim stream, the system integrates with a lightweight Isolation Forest and achieves an F1-score of 0.76 while reducing peak RAM from 18.3 GB to 9.8 GB and maintaining 410 ± 15 ms mean latency for 10 000 transactions. Per-motif computation remains ≤ 28.4 ms (median < 24 ms), supporting real-time scoring on commodity hardware.
DGFP produces model-agnostic graph features that interoperate with standard anomaly detectors without retraining GNNs.
Contributions of this research include an external memory architecture for streaming graph feature extraction; a motif-aware feature labeling scheme stored on SSD and cached by LRU; and an empirical evaluation demonstrating real-time performance and memory efficiency improvements on anti-money laundering data
References
- Money Laundering. Terrorist Financing. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Available at: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/money-laundering/overview.html
- Crowdfunding for terrorism financing (2023). Financial Action Task Force. Available at: https://www.fatf-gafi.org/content/dam/fatf-gafi/reports/Crowdfunding-Terrorism-Financing.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf
- U.S. Department of the Treasury. Available at: https://home.treasury.gov/
- Opportunities and Challenges of New Technologies for AML/CFT (2021). Financial Action Task Force. Available at: https://www.fatf-gafi.org/content/dam/fatf-gafi/guidance/Opportunities-Challenges-of-New-Technologies-for-AML-CFT.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf
- Anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism at EU level. European Commission. Available at: https://finance.ec.europa.eu/financial-crime/anti-money-laundering-and-countering-financing-terrorism-eu-level_en
- Thakkar, H., Datta, S., Bhadra, P., Dabhade, S. B., Barot, H., Junare, S. O. (2024). Mapping the Knowledge Landscape of Money Laundering for Terrorism Financing: A Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 17 (10), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17100428
- Altman, J., Blanuša, J., von Niederhäusern, L., Egressy, B., Anghel, A., Atasu, K. (2023). Realistic Synthetic Financial Transactions for Anti-Money Laundering Models. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.16424
- Alarab, I., Prakoonwit, S., Nacer, M. I. (2020). Competence of Graph Convolutional Networks for Anti-Money Laundering in Bitcoin Blockchain. Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Machine Learning Technologies, 23–27. https://doi.org/10.1145/3409073.3409080
- Cardoso, M., Saleiro, P., Bizarro, P. (2022). LaundroGraph: Self-Supervised Graph Representation Learning for Anti-Money Laundering. Proceedings of the Third ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1145/3533271.3561727
- Deprez, B., Vanderschueren, T., Baesens, B., Verdonck, T., Verbeke, W. (2024). Network Analytics for Anti-Money Laundering -- A Systematic Literature Review and Experimental Evaluation. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2405.19383
- Egressy, B., Von Niederhäusern, L., Blanuša, J., Altman, E., Wattenhofer, R., Atasu, K. (2024). Provably Powerful Graph Neural Networks for Directed Multigraphs. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 38 (10), 11838–11846. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v38i10.29069
- Mohan, A., P.V., K., Sankar, P., Maya Manohar, K., Peter, A. (2022). Improving anti-money laundering in bitcoin using evolving graph convolutions and deep neural decision forest. Data Technologies and Applications, 57 (3), 313–329. https://doi.org/10.1108/dta-06-2021-0167
- Lo, W. W., Kulatilleke, G. K., Sarhan, M., Layeghy, S., Portmann, M. (2023). Inspection-L: self-supervised GNN node embeddings for money laundering detection in bitcoin. Applied Intelligence, 53 (16), 19406–19417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04504-9
- Motie, S., Raahemi, B. (2024). Financial fraud detection using graph neural networks: A systematic review. Expert Systems with Applications, 240, 122156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122156
- Weber, M., Domeniconi, G., Chen, J., Weidele, D. K. I., Bellei, C., Robinson, T., Leiserson, C. E. (2019). Anti-money laundering in Bitcoin: Experimenting with graph convolutional networks for financial forensics. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.02591
- Asiri, A., Somasundaram, K. (2025). Graph convolution network for fraud detection in bitcoin transactions. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-95672-w
- Soria Quijaite, J. J., Segura Peña, L. V., Loayza Abal, R. I. (2024). Machine Learning Models for Money Laundering Detection in Financial Institutions. A Systematic Literature Review. Proceedings of the 22nd LACCEI International Multi-Conference for Engineering, Education and Technology (LACCEI 2024): “Sustainable Engineering for a Diverse, Equitable, and Inclusive Future at the Service of Education, Research, and Industry for a Society 5.0.” https://doi.org/10.18687/laccei2024.1.1.1682
- Zhu, X., Ao, X., Qin, Z., Chang, Y., Liu, Y., He, Q., Li, J. (2021). Intelligent financial fraud detection practices in post-pandemic era. The Innovation, 2 (4), 100176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100176
- Anti-money laundering and combating financing of terrorism framework (2020). European Investment Bank. https://doi.org/10.2867/941947
- AI Fraud Detection in Banking. IBM. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-fraud-detection-in-banking
- Bhatia, S., Liu, R., Hooi, B., Yoon, M., Shin, K., Faloutsos, C. (2022). Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Edge Streams. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 16 (4), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1145/3494564
- Oztas, B., Cetinkaya, D., Adedoyin, F., Budka, M., Dogan, H., Aksu, G. (2023). Enhancing Anti-Money Laundering: Development of a Synthetic Transaction Monitoring Dataset. 2023 IEEE International Conference on E-Business Engineering (ICEBE), 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1109/icebe59045.2023.00028
- Altman, E. (2019). IBM Transactions for Anti Money Laundering (AML). Available at: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/ealtman2019/ibm-transactions-for-anti-money-laundering-aml
- Li, M., Jia, L., Su, X. (2025). Global-local graph attention with cyclic pseudo-labels for bitcoin anti-money laundering detection. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-08365-9
- Rakhmetulayeva, S., Kulbayeva, A., Bolshibayeva, A., Serbin, V. (2025). Identifying the graph-based typology features for machine learning models in financial fraud detection. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (9 (135)), 40–54. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327410
- Urmashev, B., Buribayev, Z., Amirgaliyeva, Z., Ataniyazova, A., Zhassuzak, M., Turegali, A. (2021). Development of a weed detection system using machine learning and neural network algorithms. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (114)), 70–85. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.246706
- Isolauri, E. A., Ameer, I. (2022). Money laundering as a transnational business phenomenon: a systematic review and future agenda. Critical Perspectives on International Business, 19 (3), 426–468. https://doi.org/10.1108/cpoib-10-2021-0088
- Gaviyau, W., Sibindi, A. B. (2023). Global Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorism Financing Regulatory Framework: A Critique. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 16 (7), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16070313
- Ercanbrack, J. G. (2024). Hawala in criminal court: the role of law and commercial culture in informal financial exchange. Crime, Law and Social Change, 82 (3), 659–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10611-024-10162-w
- Farber, S., Yehezkel, S. A. (2024). Financial Extremism: The Dark Side of Crowdfunding and Terrorism. Terrorism and Political Violence, 37 (5), 651–670. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546553.2024.2362665
- Rocha-Salazar, J.-J., Segovia-Vargas, M.-J., Camacho-Miñano, M.-M. (2021). Money laundering and terrorism financing detection using neural networks and an abnormality indicator. Expert Systems with Applications, 169, 114470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114470
- Akartuna, E. A., Johnson, S. D., Thornton, A. (2024). Motivating a standardised approach to financial intelligence: a typological scoping review of money laundering methods and trends. Journal of Experimental Criminology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11292-024-09623-y
- Bolshibayeva, A., Rakhmetulayeva, S., Ukibassov, B., Zhanabekov, Z. (2024). Advancing real-time echocardiographic diagnosis with a hybrid deep learning model. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (132)), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.314845
- Rakhmetulayeva, S., Ukibassov, B., Zhanabekov, Z., Bolshibayeva, A. (2024). Development of data-efficient training techniques for detection and segmentation models in atrial septum defect analysis. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (2 (131)), 13–23. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.312621
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Aigerim Bolshibayeva, Sabina Rakhmetulayeva, Aliya Kulbayeva, Ansar-Ul-Haque Yasar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








