Development of image encryption method using surjective finite automata and custom S-box within the advanced encryption standard framework
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.348368Keywords:
image encryption, surjective finite automaton, custom S-box, AESAbstract
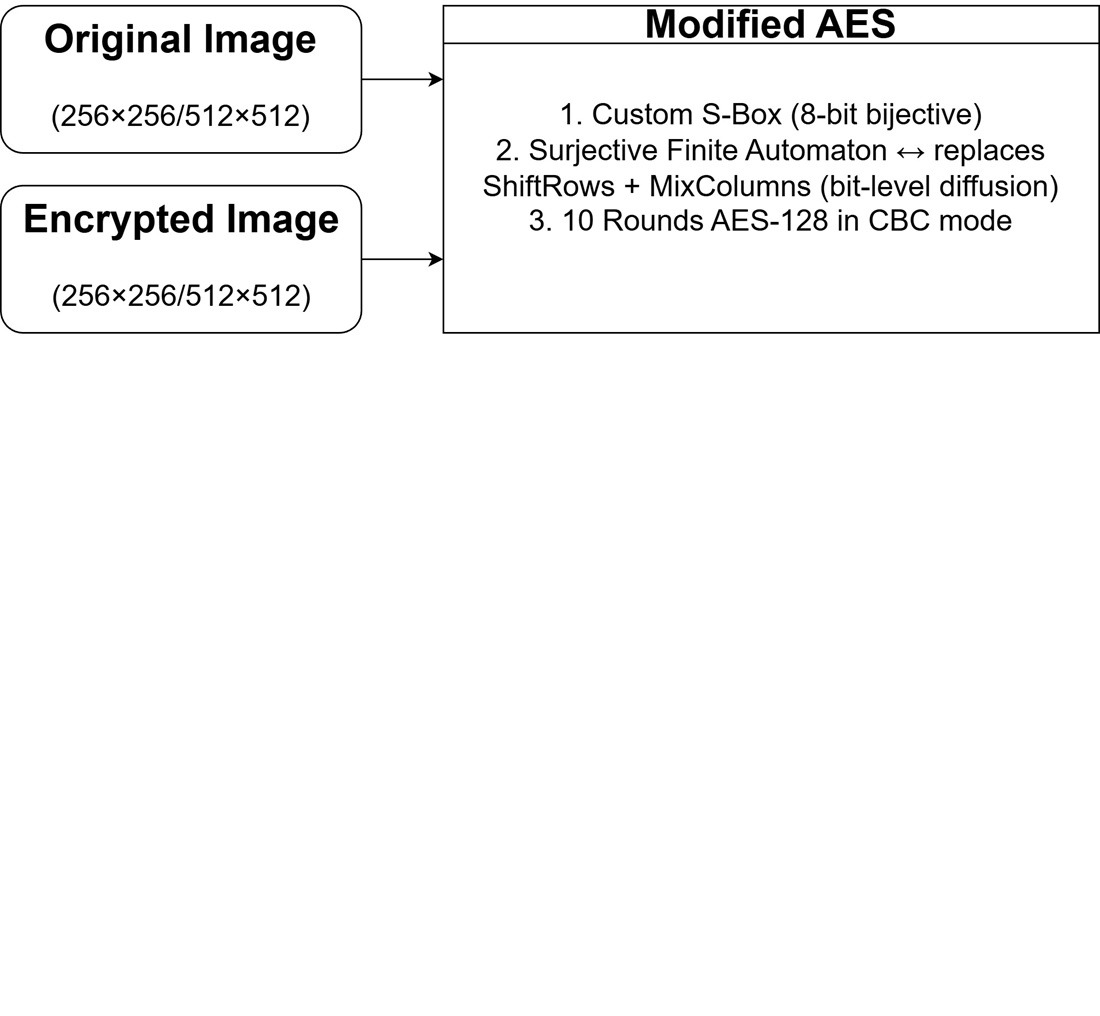
The object of the study is the AES-128 (Advanced Encryption Standard) – based image-encryption scheme. The problem solved is the persistence of residual image structure and sub-ideal statistical security when classical AES is naively applied to visual data. The generated cipher images yield near-maximal entropy with low pixel correlations and uniform histograms. Encrypted-image Chi-square values concentrate around 200–310 (close to a uniform distribution), the NPCR (Number Of Changing Pixel Rate) consistently 99.623–99.657% with a best case 99.6547%, and the UACI (Unified Averaged Changed Intensity) ≈ 33.64% per channel (RGB combined ≈ 22%). Robustness tests show ≈ 30.7 dB at 50% cropping and ≈ 39.5–39.7 dB at 0.01 salt-and-pepper noise and 6.25% cropping. These outcomes are explained by the bit-level, state-dependent permutations introduced by the surjective automaton (boosting diffusion) and by the nonlinear S-box synthesized under strict criteria (e. g., bounded differential uniformity, high nonlinearity) that heighten confusion, and operation in CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) mode supplies semantic security. Other unique features that facilitate the solution are the substituting of ShiftRows/MixColumns with surjective finite automata; a custom, criteria-optimized S-box; and a 10-round AES-128 CBC pipeline with a random. Taking all of this together yielding observed statistical uniformity, a high NPCR/UACI, and stable robustness under degradation. Lastly, the findings demonstrate the applicability to secure multimedia transmission and storage in channels prone to noise or partial data loss, and being data-agnostic, that the transformations can generalize to text and generic binary data when carefully managed
References
- Chahar, S. (2024). Exploring the future trends of cryptography. Next Generation Mechanisms for Data Encryption, 234–257. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003508632-16
- Kong, J. H., Ang, L.-M., Seng, K. P. (2015). A comprehensive survey of modern symmetric cryptographic solutions for resource constrained environments. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 49, 15–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2014.09.006
- Sharipbay, A., Saukhanova, Z., Shakhmetova, G., Barlybayev, A. (2023). Development of Reliable and Effective Methods of Cryptographic Protection of Information Based on the Finite Automata Theory. The Eurasia Proceedings of Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics, 26, 19–25. https://doi.org/10.55549/epstem.1409285
- Shakhmetova, G., Barlybayev, A., Saukhanova, Z., Sharipbay, A., Raykul, S., Khassenov, A. (2024). Enhancing Visual Data Security: A Novel FSM-Based Image Encryption and Decryption Methodology. Applied Sciences, 14 (11), 4341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114341
- Salami, Y., Khajevand, V., Zeinali, E. (2023). Cryptographic algorithms: A review of the literature, weaknesses and open challenges. Journal of Computer & Robotics, 2 (16), 63–115. http://dx.doi.org/10.22094/JCR.2023.1983496.1298
- Hospodár, M., Jirásková, G. (2024). Conversions Between Six Models of Finite Automata. International Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, 36 (03), 321–344. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129054124430020
- Lotfi, Z., Khalifi, H., Ouardi, F. (2023). Efficient Algebraic Method for Testing the Invertibility of Finite State Machines. Computation, 11 (7), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11070125
- Abubaker, S., Wu, K. (2013). DAFA - A Lightweight DES Augmented Finite Automaton Cryptosystem. Security and Privacy in Communication Networks, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36883-7_1
- Kodada, B. (2022). FSAaCIT: Finite State Automata based One-Key Cryptosystem and Chunk-based Indexing Technique for Secure Data De-duplication in Cloud Computing. https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.20443653.v1
- Salas Pena, P. I., Ernesto Gonzalez Torres, R. (2016). Authenticated Encryption based on finite automata cryptosystems. 2016 13th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/iceee.2016.7751254
- Khatua, K., Chattopadhyay, S., Dhar, A. S. (2025). Performance evaluation for accelerated and efficient prediction of different regression models aggravated with BPSO for enhancing area efficiency through state encoding in sequential circuits. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 95, 101919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2025.101919
- Srilakshmi, S. (2012). On finite state machines and recursive functions application to cryptosystems. Anantapuram. Available at: https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/handle/10603/11436
- Meskanen, T. (2001). On finite automaton public key cryptosystems. Turku Centre for Computer Science. Available at: https://www.finna.fi/Record/utu.998871095405971
- Tao, R., Chen, S., Chen, X. (1997). FAPKC3: A new finite automaton public key cryptosystem. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 12 (4), 289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02943149
- Tao, R., Chen, S. (1999). The generalization of public key cryptosystem FAPKC4. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44 (9), 784–790. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02885019
- Kodada, B. B., D’Mello, D. A. (2021). Symmetric Key Cryptosystem based on Sequential State Machine. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1187 (1), 012026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1187/1/012026
- Seitkulov, Y., Ospanov, R., Tashatov, N., Eraliyeva, B., Sisenov, N. (2023). Software tool for analysis and synthesis of cryptographic S-boxes. KazATC Bulletin, 126 (3), 257–266. https://doi.org/10.52167/1609-1817-2023-126-3-257-266
- Ospanov, R., Seitkulov, Y., Eraliyeva, B. (2022). Generalized algebraic method for constructing 8-bit Rijndael S-block. KazATC Bulletin, 120 (1), 156–163. https://doi.org/10.52167/1609-1817-2022-120-1-156-163
- Zheng, D., Alkawaz, M. H., Johar, M. G. M. (2025). Privacy protection and data security in intelligent recommendation systems. Neural Computing and Applications, 37 (34), 28431–28448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-025-11189-3
- Xu, X., Song, X., Liu, S., Zhou, N., Wang, M. (2025). New 2D hyperchaotic Cubic-Tent map and improved 3D Hilbert diffusion for image encryption. Applied Intelligence, 55 (7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-025-06414-4
- Dougherty, S. T., Klobusicky, J., Şahinkaya, S., Ustun, D. (2023). An S-Box construction from exponentiation in finite fields and its application in RGB color image encryption. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83 (14), 41213–41241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17046-6
- Norouzi, B., Mirzakuchaki, S., Seyedzadeh, S. M., Mosavi, M. R. (2012). A simple, sensitive and secure image encryption algorithm based on hyper-chaotic system with only one round diffusion process. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 71 (3), 1469–1497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-012-1292-9
- Dokku, N. S., David Amar Raj, R., Bodapati, S. K., Pallakonda, A., Reddy, Y. R. M., Krishna Prakasha, K. (2025). Resilient cybersecurity in smart grid ICS communication using BLAKE3-driven dynamic key rotation and intrusion detection. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-17530-z
- Khan, M. A., Sharif, M., Akram, T., Raza, M., Saba, T., Rehman, A. (2020). Hand-crafted and deep convolutional neural network features fusion and selection strategy: An application to intelligent human action recognition. Applied Soft Computing, 87, 105986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105986
- Zhang, H., Wu, Q. J., Nguyen, T. M. (2013). Incorporating Mean Template Into Finite Mixture Model for Image Segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 24 (2), 328–335. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2012.2228227
- Pareschi, F., Rovatti, R., Setti, G. (2012). On Statistical Tests for Randomness Included in the NIST SP800-22 Test Suite and Based on the Binomial Distribution. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7 (2), 491–505. https://doi.org/10.1109/tifs.2012.2185227
- Ullah, A., Jamal, S. S., Shah, T. (2017). A novel scheme for image encryption using substitution box and chaotic system. Nonlinear Dynamics, 91 (1), 359–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3874-6
- Abdul, Y., Ramasamy, V., Kukaram, G., Boulaaras, S., Alharbi, A. (2025). A dynamic image encryption scheme through 2-D cellular automata and chaotic logistic map. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-21225-w
- Sharmila, S., Bhuvaneswaran, R. S., Vaithiyanathan, D. (2025). Secure image encryption using Rubik’s Cube-based scrambling with chaos-driven diffusion and circular shifts. Optik, 339, 172533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2025.172533
- Hadžic, V., Bloem, R. (2024). Efficient and Composable Masked AES S-Box Designs Using Optimized Inverters. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2025 (1), 656–683. https://doi.org/10.46586/tches.v2025.i1.656-683
- Sharma, P. L., Gupta, S., Nayyar, A., Harish, M., Gupta, K., Sharma, A. K. (2024). ECC based novel color image encryption methodology using primitive polynomial. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83 (31), 76301–76340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18245-5
- Kaushik, P., Attkan, A. (2021). A Chaotic and Hyperchaotic Map based Image Encryption Protocol for High-End Colour density Images using enhanced S-box pixel permutator. 2021 2nd International Conference on Computational Methods in Science & Technology (ICCMST), 174–180. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccmst54943.2021.00045
- Hermassi, H., Rhouma, R., Belghith, S. (2011). Improvement of an image encryption algorithm based on hyper-chaos. Telecommunication Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9459-7
- Ye, G., Wong, K.-W. (2012). An efficient chaotic image encryption algorithm based on a generalized Arnold map. Nonlinear Dynamics, 69 (4), 2079–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0409-z
- Song, C.-Y., Qiao, Y.-L., Zhang, X.-Z. (2013). An image encryption scheme based on new spatiotemporal chaos. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 124 (18), 3329–3334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.11.002
- Zeng, J., Wang, C. (2021). A Novel Hyperchaotic Image Encryption System Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and Cellular Automata. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6675565
- Liu, H., Wang, X. (2011). Color image encryption using spatial bit-level permutation and high-dimension chaotic system. Optics Communications, 284 (16-17), 3895–3903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2011.04.001
- Su, Y., Tang, C., Chen, X., Li, B., Xu, W., Lei, Z. (2017). Cascaded Fresnel holographic image encryption scheme based on a constrained optimization algorithm and Henon map. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 88, 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.07.012
- Abdullah, A. H., Enayatifar, R., Lee, M. (2012). A hybrid genetic algorithm and chaotic function model for image encryption. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 66 (10), 806–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2012.01.015
- Abbasi, A. A., Mazinani, M., Hosseini, R. (2020). Evolutionary-based image encryption using biomolecules operators and non-coupled map lattice. Optik, 219, 164949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164949
- Mahmud, M., Atta-ur-Rahman, Lee, M., Choi, J.-Y. (2020). Evolutionary-based image encryption using RNA codons truth table. Optics & Laser Technology, 121, 105818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105818
- Ghaz, A., Seddiki, A., Nouioua, N. (2022). Comparative Study of Encryption Algorithms Applied to the IOT. The Eurasia Proceedings of Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics, 21, 469–476. https://doi.org/10.55549/epstem.1226679
- Ahmad, M., Alam, M. Z., Umayya, Z., Khan, S., Ahmad, F. (2018). An image encryption approach using particle swarm optimization and chaotic map. International Journal of Information Technology, 10 (3), 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-018-0099-y
- Kaur, M., Kumar, V. (2018). Beta Chaotic Map Based Image Encryption Using Genetic Algorithm. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 28 (11), 1850132. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127418501328
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Alibek Barlybayev, Zhanat Saukhanova, Gulmira Shakhmetova, Altynbek Sharipbay, Sayat Raykul, Altay Khassenov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








