Дослідження алгоритмів стиснення зображень із використанням нейронних мереж
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31498/2225-6733.49.1.2024.321212Ключові слова:
автокодувальник, стиснення зображень, нейронні мережі, JPEG, алгоритми стисненняАнотація
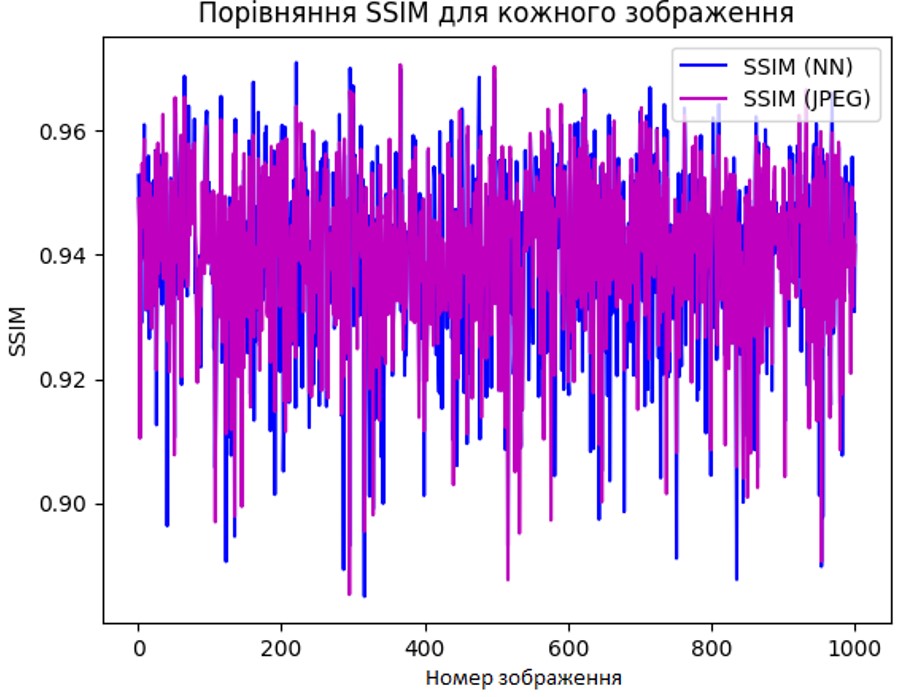
У статті наведено результати дослідження алгоритмів стиснення зображень на основі нейронних мереж. Проаналізовано класичні методи стиснення, такі як JPEG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, а також виокремлено переваги нейромережевих методів, зокрема використання автокодувальника, варіаційного автокодувальника, генеративних змагальних мереж. Зроблено висновок, що основними перевагами нейромережевих методів є збереження високого рівня текстур та деталей при низьких бітрейтах, а також можливість роботи з високоякісними зображеннями, хоча це вимагає значних обчислювальних ресурсів. Проведено порівняльний аналіз класичних алгоритмів стиснення, таких як JPEG, з новими підходами на основі нейронних мереж на прикладі автокодувальника, а також оцінено перспективи нейронних мереж у вирішенні проблеми стиснення даних. Головний акцент зосереджено на аналізі якості відновлення зображень та рівня стиснення з використанням різних налаштувань нейронної мережі. Наведено математичну модель, яка описує принцип роботи автокодувальника та показує, як нейронна мережа кодує та відновлює зображення, використовуючи латентний простір. Для досягнення найкращої якості реконструкції використано гібридну функцію втрат, яка складається з трьох компонентів: перцептивної втрати на основі VGG16, SSIM-втрати та MSE-втрати. Для проведення експериментів розроблено модульну програмну систему за допомогою мови програмування Python. Програмне забезпечення включає в себе графічний інтерфейс, модуль стиснення для виконання операцій кодування та декодування зображення за допомогою моделі автокодувальника, а також модуль оцінки якості для розрахунку основних метрик якості (PSNR та SSIM). Встановлено, що традиційні методи стиснення зображень демонструють високу ефективність, але при цьому більше схильні до генерації артефактів, особливо при високих рівнях стиснення, ніж нейромережеві методи. У результаті проведених досліджень встановлено, що модель автокодувальника може кодувати та декодувати зображення з мінімальною втратою якості, на рівні з JPEG, проте поступається класичним алгоритмам у швидкості (1,6 секунди на зображення проти 0,02 для JPEG) та ступені стиснення (модель забезпечує зменшення розміру файлу на 11-18%). Зроблено висновок, що без зменшення потреби в обчислювальних ресурсах нейромережеві методи стиснення не зможуть замінити класичні методи
Посилання
Li X., Ji S. Neural Image Compression and Explanation. IEEE Access. 2020. Vol. 8. Pp. 214605-214615. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041416.
Ballé J., Laparra V., Simoncelli E.P. End-to-end Optimized Image Compression. ICLR 2017 : 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24-26 April 2017. Pp. 1-27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1611.01704.
Autoencoders and their applications in machine learning: a survey / K. Berahmand Fet al. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2024. Vol. 57(2). Pp. 1-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10662-6.
Kingma D.P., Welling M. An introduction to variational autoencoders. Foundations and trends in machine learning. 2019. Vol. 12(4). Pp. 307-392. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1312.6114.
Generative Adversarial Nets / I. Goodfellow et al. Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 8-13 December 2014. Vol. 3(11). Pp. 2672-2680. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2969033.2969125.
High-Fidelity Generative Image Compression / Mentzer F., Toderici G., Tschannen M., Agustsson E. NeurIPS 2020 : Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 6-12 December 2020. Pp. 11913-11924. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/3495724.3496723.
Bank D., Koenigstein N., Giryes R. Autoencoders. Machine Learning for Data Science Handbook / ed. by Rokach L., Maimon O., Shmueli E. Springer, Cham, 2023. Pp. 353-374. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-24628-9_16.
Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity / Wang Zh., Bovik A. C. , Sheikh H. R., Simoncelli E. P. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 2004. Vol.13. No. 4. Pp. 600-612. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Журнал "Вісник Приазовського державного технічного університету. Серія: Технічні науки" видається під ліцензією СС-BY (Ліцензія «Із зазначенням авторства»).
Дана ліцензія дозволяє поширювати, редагувати, поправляти і брати твір за основу для похідних навіть на комерційній основі із зазначенням авторства. Це найзручніша з усіх пропонованих ліцензій. Рекомендується для максимального поширення і використання неліцензійних матеріалів.
Автори, які публікуються в цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:
1. Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons Attribution License, яка дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.
2. Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди, які стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи в тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.








