Лабораторні дослідження динамічного стану жорсткої сіячої поверхні, діючої в вібраційно-ударному полі
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31498/2225-6733.49.1.2024.321237Ключові слова:
коливання, вібраційно-ударне поле, сіяча поверхня, вільно укладена поверхня, голопування, режимАнотація
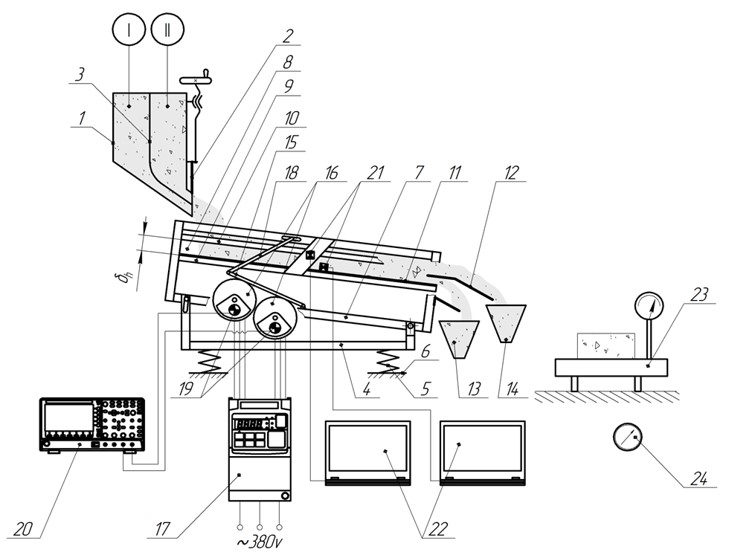
У статті досліджується динамічний стан жорсткої сіячої поверхні, яка працює у вібраційно-ударному полі. Проведені лабораторні дослідження дозволили отримати емпіричну залежність часу несталого руху від прискорень коливань коробу в діапазоні 18…47 м/с². Встановлено, що зі збільшенням прискорення коливань швидкість руху та амплітуда переміщення матеріальної точки сіячої поверхні зростають до певного діапазону, після якого спостерігається уповільнення змін досліджуваних параметрів. Також виявлено, що точки сіячої поверхні в завантажувальній та
розвантажувальній частинах знаходяться в протифазі, що свідчить про поворотне-обертальний характер її руху. Отримані результати підтверджують адекватність розробленої розрахункової моделі та дозволяють зробити висновки щодо оптимізації процесу грохочення
Посилання
Товаровский И. Г. Нормативная оценка влияния параметров доменной плавки на расход кокса и производительность. Фундаментальные и прикладные проблемы черной металлургии. 2014. № 28. С. 117-131.
Теория и практика подготовки металлургического кокса к доменной плавке: монография / В.Г. Гусак та ін. Киев : Наукова думка, 2011. 216 с.
Учитель С. А., Лялюк В. П., Пополов Д. В. Сортировка металлургических шихт на вибрационных грохотах. Саарбрюккен: Palmarium Academic Publishing, 2014. 413 с.
Бергеман Г. В., Пелых И. В., Петренко В. А. Проблемы калибровки металлургического минерального сырья – известняка. Металл и литье Украины. 2008. № 5. С. 5-8.
Берник П. С., Омельянов О. Н., Паламарчук И. П. Разработка виброгрохота с пространственными колебаниями рабочих органов. Вибрации в технике и в технологиях. 1998. № 2(6). С. 8-13.
Складоновский Е. Н., Баланов В. Г., Нехаев Г. Е. Коксовый грохот с резиновыми ситами. Металлургическая и горнорудная промышленность. 1990. № 4. С. 68-69.
Dynamic Characteristics of a Vibrating Flip-Flow Screen and Analysis for Screening 3 mm Iron Ore / C. Yu et al. Shock and Vibration. 2020. Vol. 2020. P. 1-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1031659.
Slepyan L. I., Slepyan V. I. Coupled mode parametric resonance in a vibrating screen model. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 2014. Vol. 43, no. 1-2. P. 295–304. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.10.001.
Засельский В. И., Зайцев Г. Л., Китач Е. И. Промышленные исследования работы резонирующих просеивающих поверхностей. Теория и практика металлургии. 2009. № 5-6. С. 15-18.
Повышение эффективности классификации кокса за счет использования активных рабочих поверхностей виброгрохотов / Потураев В. Н., Надутый В. П., Гольдин А. А., Бараненко В. Д. Металлургическая и горнорудная промышленность. 1991. № 2. С. 48-49.
Longo S.G. Principles and Applications of Dimensional Analysis and Similarity. Parma: Springer Cham, 2021. 428 р. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79217-6.
Upton G., Cook I. Understanding statistics. Oxford University Press, 2003. 657 p.
Moore D. S. Introduction to the practice of statistics. 6th ed. New York : W. H. Freeman and Company, 2009. 166 p.
Maxfield B. Engineering with mathcad. Great Britain: Elsevier, 2006. 494 p.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Журнал "Вісник Приазовського державного технічного університету. Серія: Технічні науки" видається під ліцензією СС-BY (Ліцензія «Із зазначенням авторства»).
Дана ліцензія дозволяє поширювати, редагувати, поправляти і брати твір за основу для похідних навіть на комерційній основі із зазначенням авторства. Це найзручніша з усіх пропонованих ліцензій. Рекомендується для максимального поширення і використання неліцензійних матеріалів.
Автори, які публікуються в цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:
1. Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons Attribution License, яка дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.
2. Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди, які стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи в тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.








