Цифрові технології відстеження та супроводження суден на внутрішніх водних шляхах
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31498/2225-6733.50.2025.336406Ключові слова:
цифрові технології, внутрішні водні шляхи, навігаційна безпека, відстеження суден, супроводження суден, інформаційні системи, безпека судноплавства, транспортна логістикаАнотація
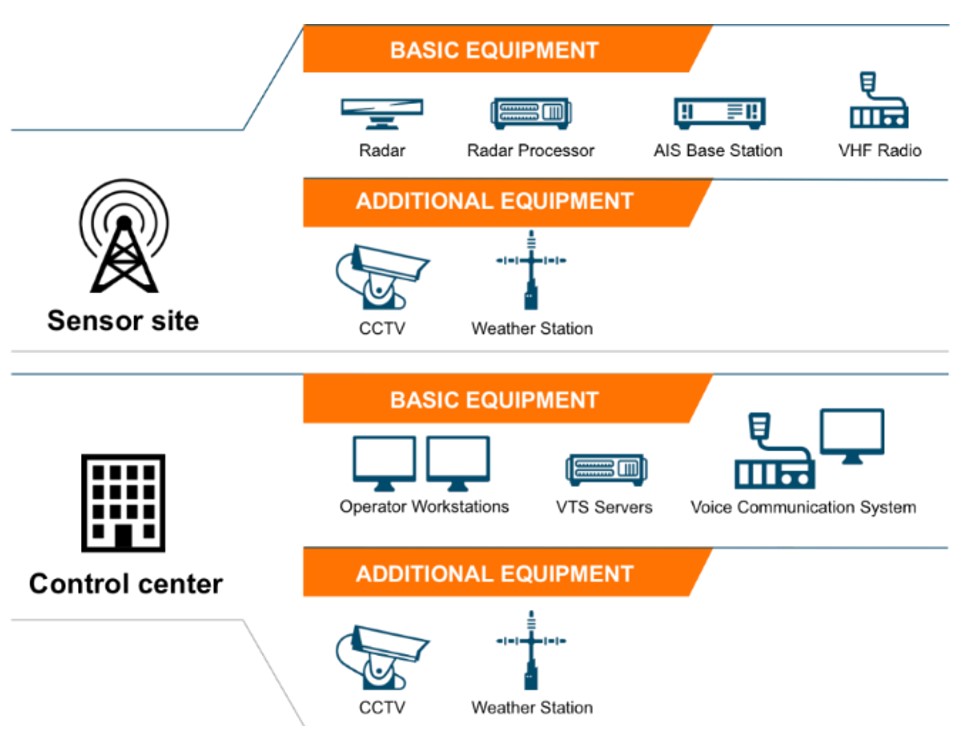
У статті досліджено можливості застосування сучасних цифрових технологій для вирішення проблем забезпечення належного рівня безпеки судноплавства. Зокрема, розглянуто використання систем автоматичної ідентифікації суден, річкових інформаційних служб, геоінформаційних систем, технологій обробки великих даних, а також інструментів Індустрії 4.0. Акцентовано увагу на необхідності інтеграції цифрових технологій для створення єдиного інформаційного середовища, що дозволяє забезпечити повноцінний обмін навігаційною, гідрографічною та метеорологічною інформацією між усіма учасниками транспортного процесу. У межах дослідження проведено класифікацію інформаційних потреб користувачів систем моніторингу суден залежно від типів інформації (динамічна, напівдинамічна та статична), а також визначено функціональні вимоги до цифрових систем супроводження та відстеження суден. Встановлено, що для підвищення ефективності таких систем необхідно забезпечити високу швидкість оновлення інформації в реальному часі, сумісність форматів обміну даними, інтеграцію з існуючими системами управління судноплавством і можливість використання прогнозних моделей для прийняття оптимальних управлінських рішень. Результати дослідження підтверджують доцільність впровадження комплексних цифрових платформ, які поєднують можливості сучасних інформаційних технологій для покращення якості управління судноплавством на внутрішніх водних шляхах. У статті сформульовано рекомендації щодо подальшого розвитку інтелектуальних систем моніторингу та супроводження суден, які передбачають інтеграцію цифрових рішень на основі технологій штучного інтелекту та обробки великих даних, розробку єдиної цифрової архітектури для управління рухом суден, а також впровадження сучасних методів прогнозування та аналізу навігаційних ризиків. Отримані результати мають практичне значення для проєктування та впровадження сучасних інформаційних систем у сфері внутрішнього водного транспорту, сприяючи підвищенню конкурентоспроможності та сталому розвитку транспортної галузі України та Європейського Союзу
Посилання
Bazylev A.V., Plyushchaev V.I. Digital information system for inland water transport vessels based on AIS. Journal of Physics Conference Se-ries. 2021. Vol. 2131(3). Article 032031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2131/3/032031.
Pfliegl R., Bäck A. Increasing the Attractiveness of Inland Waterway Transport with E-Transport River Information Services. Transportation Research Record. 2006. Vol. 1963(1). Pp. 15-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198106196300103.
Watanabe S., Hasegawa K., Rigo P. Inland Waterway Traffic Simulator. Computer Applications and Information Technology in the Maritime Industries: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference, Liege, Belgium, 21-23 April 2008. Pp. 578-588.
Industry 4.0 Technologies Applied to Inland Waterway Transport: Systematic Literature Review / J.F. Restrepo-Arias et al. Sensors. 2022. Vol. 22(10). Article 3708. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22103708.
Broeke I.T., Willems C., Glansdorp C. River Information Services: a joint European effort to enhance safety and usability of the inland waterway. Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems ITSC 2001, Oakland, California, USA, 25-29 August 2001. Pp. 1108-1115. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/itsc.2001.948817.
A maritime big data framework integration in a common information sharing environment / Z. Paladin et al. Proceedings of the 45th Jubilee International Convention on Information, Communication and Electronic Technology (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 23-27 May 2022. Pp. 1161-1166. DOI: https://doi.org/10.23919/mipro55190.2022.9803777.
Maritime Transport And Logistics Digital Solutions Optimization Using Advanced Data Sharing Platforms: ePIcenter Projects’ Case / Z. Paladin et al. Proceedings of the 37th Bled eConference – Resilience Through Digital Innovation: Enabling the Twin Transition, Bled, Slovenia, 9-12 June 2024. Pp. 403-420. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18690/um.fov.4.2024.23.
Buravtsova J. Implementation of river electronic navigation systems and onshore information services on the inland waterways of Ukraine. Shipping & Navigation. 2021. Vol. 32(2). Pp. 10-17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31653/2306-5761.32.2021.10-17.
Skocibusic M.B., Brnardic M. Integrated vessel traffic management systems in the function of inland waterway traffic optimization. Telematics in the Transport Environment. TST 2012. Communications in Computer and Information Science. 2012. Vol. 329. Pp. 117-123. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34050-5_14.
A systematic literature review of technological developments and challenges for inland waterways freight transport in intermodal supply chain management / S. Gbako et al. Benchmarking an International Journal. 2024. Vol. 32, no. 1. Pp. 398-431. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-03-2023-0164.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Журнал "Вісник Приазовського державного технічного університету. Серія: Технічні науки" видається під ліцензією СС-BY (Ліцензія «Із зазначенням авторства»).
Дана ліцензія дозволяє поширювати, редагувати, поправляти і брати твір за основу для похідних навіть на комерційній основі із зазначенням авторства. Це найзручніша з усіх пропонованих ліцензій. Рекомендується для максимального поширення і використання неліцензійних матеріалів.
Автори, які публікуються в цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:
1. Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons Attribution License, яка дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.
2. Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди, які стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи в тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.








