Синтез спостерігача швидкості ротора в складі векторної системи керування машиною подвійного живлення
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31498/2225-6733.51.2025.344825Ключові слова:
машина подвійного живлення, еталонна модель, вектор потокозчеплення статора, алгоритм адаптації, характеристичне рівняння, критерій стійкості, параметри регулятораАнотація
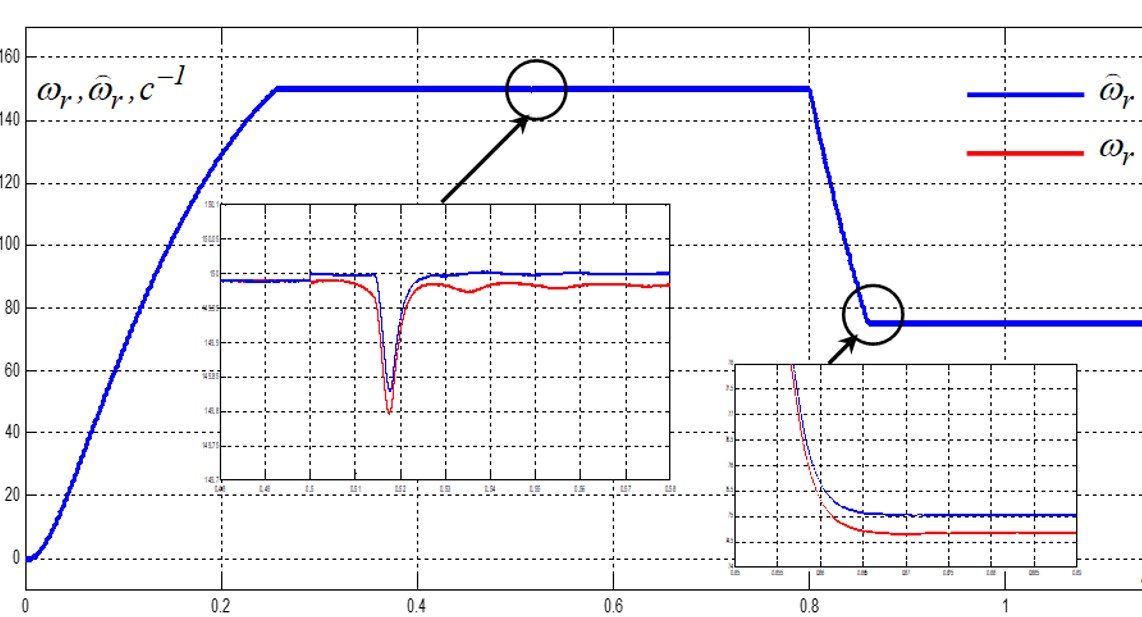
У статті використано відомі рівняння спостерігача швидкості машини подвійного живлення (МПЖ), складені при керуванні за ротором за аналогією з адаптивним спостерігачем швидкості з еталонною моделлю для асинхронних машин (АМ) з керуванням за статором. Для розв’язання задачі параметричного синтезу спостерігача швидкості МПЖ запропоновано оригінальну методику, що базується на аналізі стійкості лінеаризованої моделі спостерігача за її характеристичним рівнянням. Усі аналітичні викладки перевірено методом математичного моделювання динамічних режимів бездатчикової релейно-векторної системи керування МПЖ
Посилання
Клюєв О. В., Садовой О. В., Сохіна Ю. В. Спос-терігач швидкості обертання ротора асинхронного вентильного каскаду. Збірник наукових праць Дніпровського державного технічного університету (технічні науки). 2022. Вип. 1(40). С. 89-99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31319/2519-2884.40.2022.11.
Клюєв О. В., Садовой О. В., Сохіна Ю. В. Системи керування асинхронними вентильними каскадами: монографія. Кам’янське: ДДТУ, 2018. 294 с. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16887109.
Karlovsky P., Lettl J. Application of MRAS algorithm to replace the speed sensor in induction motor drive system. Procedia Engineering. 2017. Vol. 192. Pp. 421-426. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.06.073.
Montanari M., Peresada S., Tilli A. Speed-sensorless indirect field-oriented control for induction motors based on high gain speed estimation. Automatica. 2006. Vol. 41, iss. 10. Pp. 1637-1650. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2006.05.021.
Ren X., Wang M., Chen J. Rotor Speed and Rotor Position Estimation Based on MRAS. Proceedings of the 2018 international conference on mechanical, electrical, electronic engineering science (MEEES 2018), Chongqing, China, 26-27 May 2018. Vol. 154. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2991/meees-18.2018.1.
Mousavi Gazafroodi S. M., Dashti A. A Novel MRAS Based Estimator for Speed-Sensorless Induction Motor Drive. Iranian Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering. 2014. Vol. 10, no. 4. Pp. 304-313.
Thieli Gabbi S., Hilton Gründling A., Rodrigo Vieira P. Sliding mode MRAS speed observer applied to Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with decoupled current control. IECON 2016 – 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23-26 October 2016. Pp. 2929-2934. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2016.7793641.
An MRAS speed observer based on dq-axis power winding flux for sensorless control of standalone BDFIGs / A. Ebraheem et al. Journal of advanced industrial technology and application. 2022. Vol. 3, no. 2. Pp. 34-48. DOI: https://doi.org/10.30880/jaita.2022.03.02.005.
Pattnaik M., Kastha D. Reactive power based MRAS observer for speed sensorless control of double output induction generator. 5th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, ICIIS 2010, Mangalore, India, 29 July - 01 August 2010. Pp. 556-561. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIINFS.2010.5578644.
Ben Regaya C., Zaafouri A., Chaari A. Electric drive control with rotor resistance and rotor speed observers based on fuzzy logic. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. 2014. Article 207826. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/207826.
Issaouni S., Boulkroune A., Chekireb H. MRAS speed observer for sensorless adaptive intelligent backstepping controller of induction machines. International Journal of Digital Signals and Smart Systems. 2019. Vol. 3, no. 1. Pp. 121-136. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1504/IJDSSS.2019.10024903.
Giribabu D., Srivastava S. P., Pathak M. K. Modified reference model for rotor flux-based MRAS speed observer using neural network controller. IETE Journal of Research. 2018. Vol. 65. Pp. 1-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2017.1407267.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Журнал "Вісник Приазовського державного технічного університету. Серія: Технічні науки" видається під ліцензією СС-BY (Ліцензія «Із зазначенням авторства»).
Дана ліцензія дозволяє поширювати, редагувати, поправляти і брати твір за основу для похідних навіть на комерційній основі із зазначенням авторства. Це найзручніша з усіх пропонованих ліцензій. Рекомендується для максимального поширення і використання неліцензійних матеріалів.
Автори, які публікуються в цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:
1. Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons Attribution License, яка дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.
2. Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди, які стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи в тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи в цьому журналі.








