Development of the comprehensive method of situation management of project risks based on big data technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.274473Keywords:
comprehensive method, situational risk management, fuzzy situational graph, goal achievement indexAbstract
Project implementation is often carried out under the influence of negative changes in the environment and circumstances characterized as crisis. Therefore, the processes associated with risk management, which is the object of this study, are becoming important. The topic of this study is to increase the efficiency of projects by adapting the project to crisis conditions, promptly developing and making effective management decisions. For projects, it is necessary not only to identify the current situation as risky but also to determine rational ways to achieve the project goals under crisis conditions. Therefore, a comprehensive method of situational project risk management based on the combined application of situational analysis methods, intelligent and expert methods, as well as Big Data technology, is proposed. Within the framework of the method, a project risk management model has been built in the form of a fuzzy situational graph, which would provide a choice of strategies that could contribute to overcoming a risky situation, as well as reduce the time to make effective management decisions in crisis circumstances. The result of this method is compliance with time constraints, reducing resource overruns and losses in the project, as well as adapting to rapidly changing circumstances and adequate response.
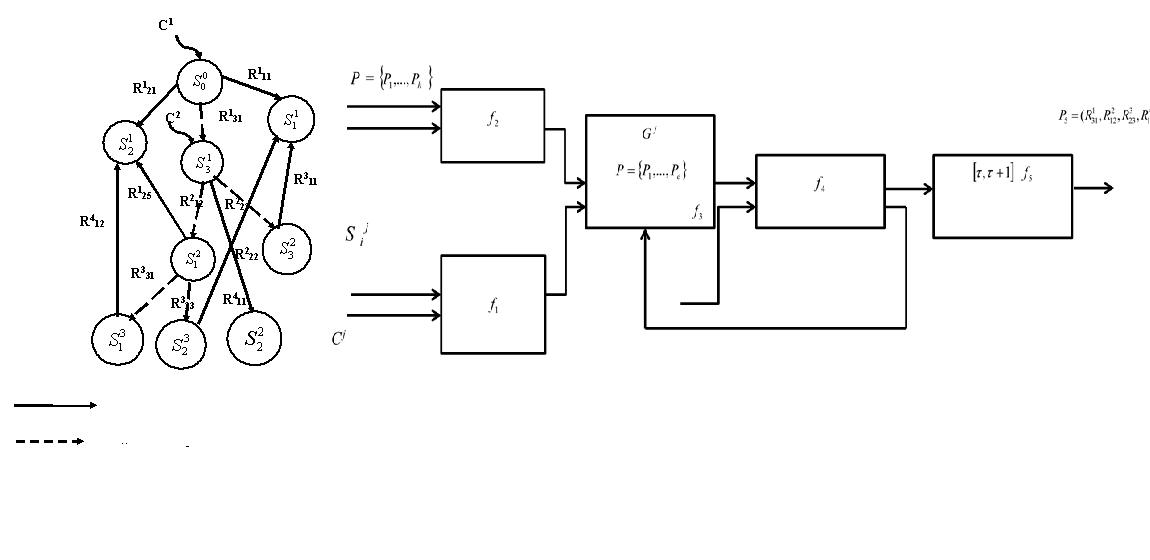
A comprehensive method of situational project risk management is characterized by solving the task toformalize management decision-making procedures and their information support, taking into account the availability of both structured and unstructured data. The proposed procedure for situational project risk management based on the use of Big Data technology can also be the basis of project management information technology and the corresponding decision support system
References
- Prokopenko, T., Grigor, O. (2018). Development of the comprehensive method to manage risks in projects related to information technologies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (3 (92)), 37–43. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.128140
- McCarthy, J., Hayes, P. (1969). Some philosophical problems from the standpoint of artificial intelligence. Available at: https://www-formal.stanford.edu/jmc/mcchay69.pdf
- A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (2013). Project Management Institute, 589. Available at: https://ceulearning.ceu.edu/pluginfile.php/305454/course/overviewfiles/PMBOKGuide_5th_Ed.pdf?forcedownload=1
- Benov, D. M. (2016). The Manhattan Project, the first electronic computer and the Monte Carlo method. Monte Carlo Methods and Applications, 22 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/mcma-2016-0102
- Leha, Yu. H., Prokopenko, T. O., Danchenko, O. B. (2010). Ekspertni protsedury ta metody pryiniattia rishen v investytsiinykh proektakh. Visnyk ChDTU, 2, 69–73.
- Verma, K. K., Ospanova, A. (2022). Risk Management. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science Engineering and Technology, 11 (12), 14315.
- Odubuasi, A. C., Osuagwu, O. V. A., Oby, B. (2021). Effect of Risk Management Committee and Enterprise Risk Management on Performance of Banks in Nigeria. JETMASE, 3 (1), 222–233. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366187232_Effect_of_Risk_Management_Committee_and_Effect_of_Risk_Management_Committee_and_Enterprise_Risk_Management_on_Performance_of_Banks_in_Nigeria
- Petyk, L. O., Baskova, Y. S. (2022). The Problems of Financial Risks Management in the Risk Management System and the Methods for Solving. Business Inform, 10 (537), 181–186. doi: https://doi.org/10.32983/2222-4459-2022-10-181-186
- Hong, Y. (Bright), Ly, M., Lin, H. (2022). RPA Risk Management: Points to Consider. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting. doi: https://doi.org/10.2308/jeta-2022-004
- Ladanyuk, A., Prokopenko, T., Reshetiuk, V. (2014). The model of strategic management of organizational and technical systems, taking into account risk-based cognitive approach. Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences – SGGW Agriculture (Agricultural and Forest Enginweering), 63, 97–104.
- Ladanyuk, A. P., Shumygai, D. A., Boiko, R. O. (2013). Situational Coordination of Continuous Technological Complexes Subsystems. Journal of Automation and Information Sciences, 45 (8), 68–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/jautomatinfscien.v45.i8.70
- Lohani, A. K., Goel, N. K., Bhatia, K. K. S. (2010). Comparative study of neural network, fuzzy logic and linear transfer function techniques in daily rainfall-runoff modelling under different input domains. Hydrological Processes, 25 (2), 175–193. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7831
- Lynch, C. (2008). How do your data grow? Nature, 455 (7209), 28–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/455028a
- Bouchon-Meunier, B., Yager, R. R., Zadeh, L. A. (Eds.) (1991). Uncertainty in Knowledge Bases. Springer. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bfb0028090
- Prokopenko, T. O., Ladaniuk, A. P. (2015). Informatsiyni tekhnolohiyi upravlinnia orhanizatsiyno-tekhnolohichnymy systemamy. Cherkasy: Vertykal, vydavets Kandych S.H., 224.
- Taber, W. R. (1994). Fuzzy Cognitive Maps Model Social Systems. Artificial Intelligence Expert, 9, 18–23.
- Chochowski, I., Chernyshenko, V., Kozyrskyi, V., Kyshenko, A., Ladaniuk, V., Lysenko, V. et at. (2014). Innovative energy-saving technologies in biotechnological objects control. Kyiv: Tsentr Uchbovoii Literatury, 240.
- Zedeh, L. A. (1989). Knowledge representation in fuzzy logic. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 1 (1), 89–100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/69.43406
- Diestel, R. (2005). Graph Theory. Electronic Edition. Springer-Verlag. Available at: https://sites.math.washington.edu/~billey/classes/562.winter.2018/articles/GraphTheory.pdf
- Prokopenko, T., Lavdanska, O., Povolotskyi, Y., Obodovskyi, B., Tarasenko, Y. (2021). Devising an integrated method for evaluating the efficiency of scrum-based projects in the field of information technology. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (3 (113)), 46–53. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.242744
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tetiana Prokopenko, Yevhen Lanskykh, Valentyn Prokopenko, Oleksandr Pidkuiko, Yaroslav Tarasenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









