Comparison of solutions to the task of IT product configuration items early identification using hierarchical clusterization methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.303526Keywords:
information system, configuration item, hierarchical clustering, Chameleon method, Chebyshev distanceAbstract
The object of this study is the IT project configuration management process.
During the research, the problem of early identification of configuration items (CI) in the information system (IS) of enterprise management was solved. Research in this field is mainly aimed at solving the task of early identification of services and microservices during the refactoring of software systems. The issue of the application of artificial intelligence methods for the detection of CI has not been sufficiently investigated.
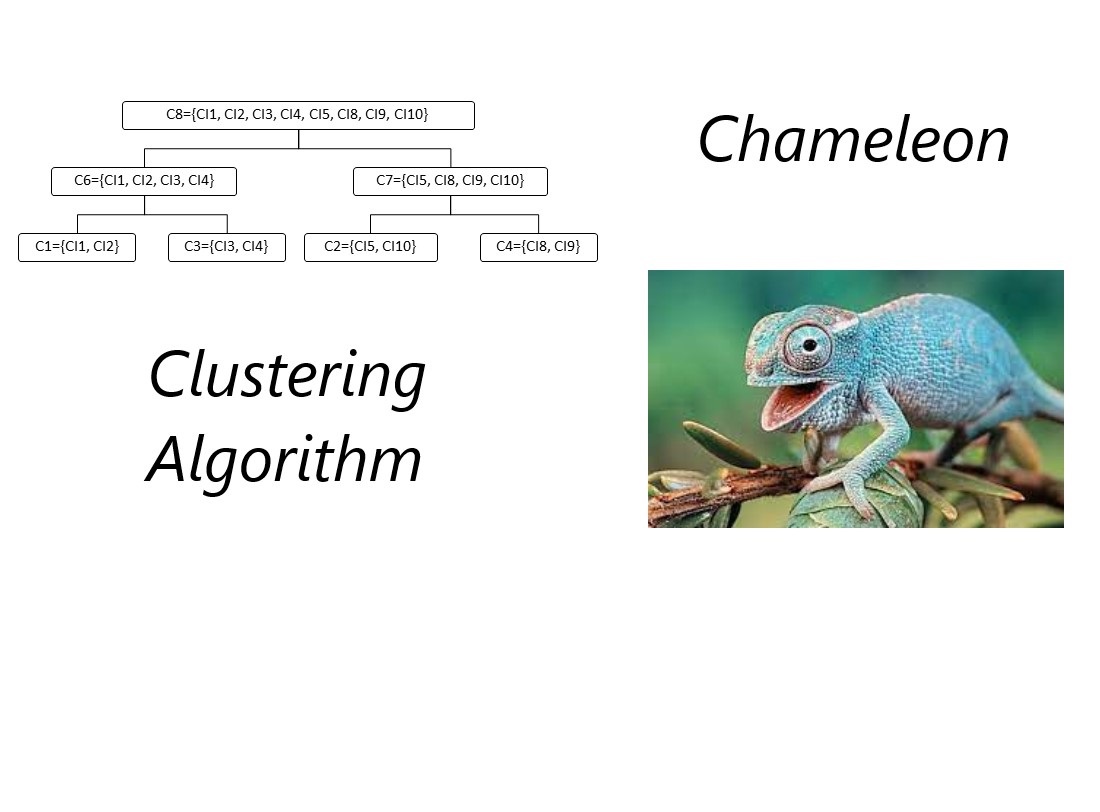
During the study, the Chameleon hierarchical clustering method was adapted to solve the problem of early identification of CI IS. This method takes into account both the internal similarity and the connectivity of individual functions of the studied IS.
The adapted Chameleon method was used when solving the task of early identification of CI in the functional task "Formation and maintenance of an individual plan of a scientific and pedagogical employee of the department". 10 functions and 12 essences of the problem database were considered as the initial CIs. The result of the solution is a dendrogram with all possible options for decomposition of the description of the task architecture into individual CIs.
Based on the results, a comparative analysis of the use of Chameleon, DIANA, and AGNES methods for solving the problem of early identification was carried out. According to the criteria "Number of vertices of the dendrogram", "Number of levels of decomposition of the dendrogram", and "Evenness of filling the elements of the dendrogram", the results from using the Chameleon method are the best.
Using the research results allows automating the procedure of forming backlogs of IT project implementation teams. This makes it possible to improve the quality of IS development by assigning IS containing similar functions to the same IT project executor
References
- Bourque, P., Fairley, R. E. (Eds.) (2014). Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge. Version 3.0. IEEE Computer Society, 335. Available at: https://cs.fit.edu/~kgallagher/Schtick/Serious/SWEBOKv3.pdf
- Quigley, J. M., Robertson, K. L. (2019). Configuration Management. Auerbach Publications. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429318337
- -2015 - ISO/IEC/IEEE International Standard - Systems and software engineering -- System life cycle processes. https://doi.org/10.1109/ieeestd.2015.7106435
- Farayola, O. A., Hassan, A. O., Adaramodu, O. R., Fakeyede, O. G., Oladeinde, M. (2023). Configuration management in the modern era: best practices, innovations, and challenges. Computer Science & IT Research Journal, 4 (2), 140–157. https://doi.org/10.51594/csitrj.v4i2.613
- Reiff-Marganiec, S., Tilly, M. (Eds.) (2012). Handbook of Research on Service-Oriented Systems and Non-Functional Properties. IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-61350-432-1
- Cadavid, H., Andrikopoulos, V., Avgeriou, P., Broekema, P. C. (2022). System and software architecting harmonization practices in ultra-large-scale systems of systems: A confirmatory case study. Information and Software Technology, 150, 106984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2022.106984
- Faitelson, D., Heinrich, R., Tyszberowicz, S. (2017). Supporting Software Architecture Evolution by Functional Decomposition. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006206204350442
- Shahin, R. (2021). Towards Assurance-Driven Architectural Decomposition of Software Systems. Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security. SAFECOMP 2021 Workshops, 187–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-83906-2_15
- Suljkanović, A., Milosavljević, B., Inđić, V., Dejanović, I. (2022). Developing Microservice-Based Applications Using the Silvera Domain-Specific Language. Applied Sciences, 12 (13), 6679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136679
- Felfernig, A., Le, V.-M., Popescu, A., Uta, M., Tran, T. N. T., Atas, M. (2021). An Overview of Recommender Systems and Machine Learning in Feature Modeling and Configuration. Proceedings of the 15th International Working Conference on Variability Modelling of Software-Intensive Systems. https://doi.org/10.1145/3442391.3442408
- Abolfazli, A., Spiegelberg, J., Palmer, G., Anand, A. (2023). A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach to Configuration Sampling Problem. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). https://doi.org/10.1109/icdm58522.2023.00009
- Sellami, K., Saied, M. A., Ouni, A. (2022). A Hierarchical DBSCAN Method for Extracting Microservices from Monolithic Applications. The International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering 2022. https://doi.org/10.1145/3530019.3530040
- Krause, A., Zirkelbach, C., Hasselbring, W., Lenga, S., Kroger, D. (2020). Microservice Decomposition via Static and Dynamic Analysis of the Monolith. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture Companion (ICSA-C). https://doi.org/10.1109/icsa-c50368.2020.00011
- Ievlanov, M., Vasiltcova, N., Neumyvakina, O., Panforova, I. (2022). Development of a method for solving the problem of it product configuration analysis. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (120)), 6–19. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269133
- Karypis, G., Han, E.-H., Kumar, V. (1999). Chameleon: hierarchical clustering using dynamic modeling. Computer, 32 (8), 68–75. https://doi.org/10.1109/2.781637
- Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J. (2012). Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2009-0-61819-5
- Vasyltsova, N. V., Panforova, I. Yu. (2022). Doslidzhennia vykorystannia metodiv ierarkhichnoi klasteryzatsiyi pid chas vyrishennia zadachi analizu konfihuratsiyi IT-produktu. ASU ta prylady avtomatyky, 178, 37–49. Available at: https://www.ewdtest.com/asu/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/ASUiPA_178_37_49.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Maksym Ievlanov, Nataliya Vasiltcova, Iryna Panforova, Borys Moroz, Andrii Martynenko, Dmytro Moroz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








