Development of lentil malt production technology using plasma-chemically activated aqueous solutions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.308298Keywords:
lentil malt, plasma-chemical activation, aqueous solutions, hydrogen peroxideAbstract
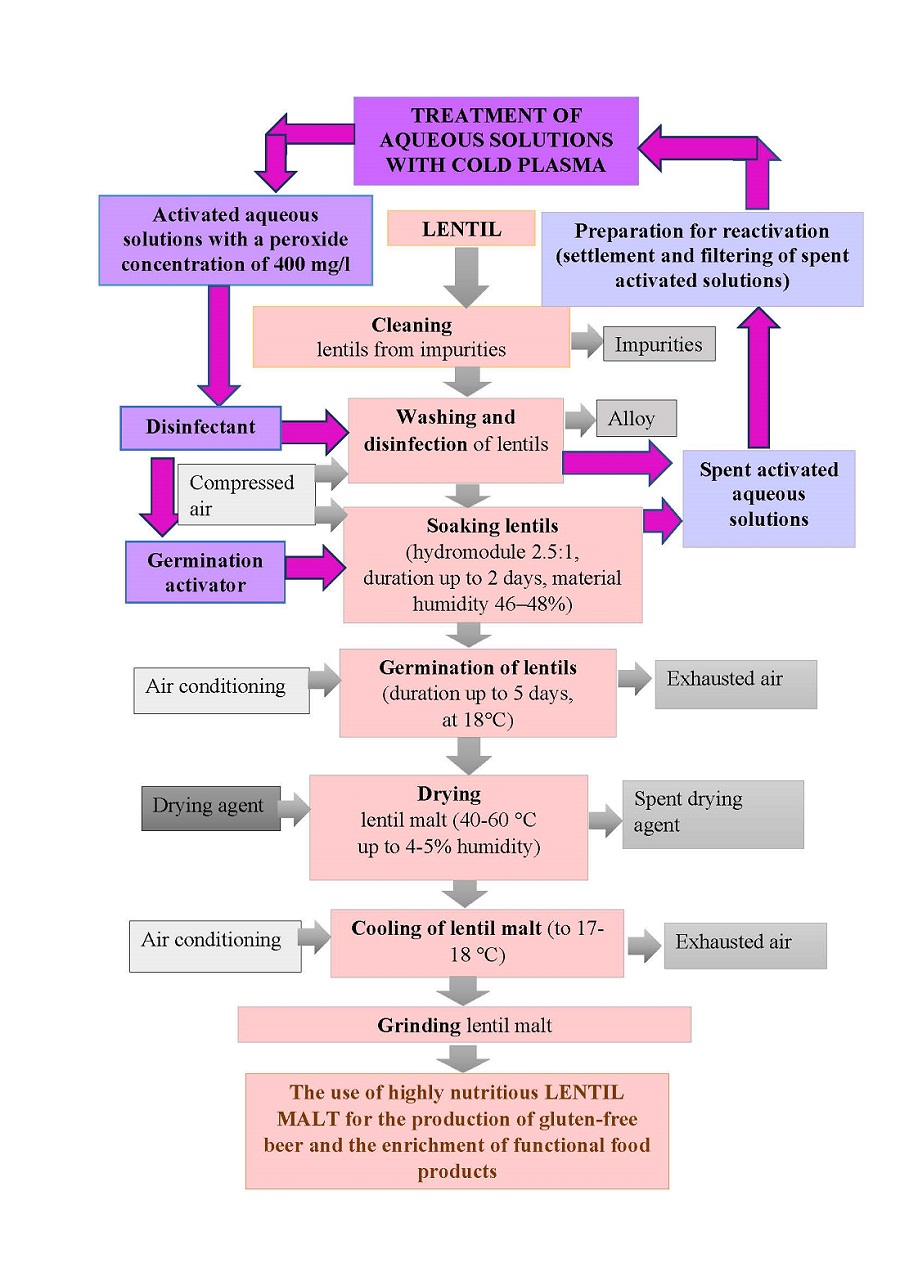
The result of the implemented research is the development of a technology for sprouted lentil (lentil malt) production using cold plasma-treated aqueous solutions. The object of the study was lentil grain. The main technological task is to obtain high-quality lentil malt suitable for producing gluten-free beer and highly nutritious foods. The rationality of using cold plasma-treated aqueous solutions as an intensifier of lentil grain germination process and high-quality lentil malt disinfectant is experimentally proven. It is confirmed that using cold plasma-treated aqueous solutions can accelerate the process of lentil bean moistening by 2 times. The germination indicators of lentils also experienced positive changes, with germination energy increased by 8–16 %, germination capacity by 3–10 %, and sprout length by 12–29 %. An analysis of the amino acid composition of lentil grain and lentil malt was carried out. Thus, the experimental samples had an increased content of amino acids: non-essential by 2.7 %, essential by 3.6 %. There was also an increase in the content of B vitamins (B1, B2, B5, B9), as well as PP and C, which indicates an increased biological value of lentil malt obtained by the presented technologies. In addition, the work noted the steady antiseptic properties of activated aqueous solutions in relation to lentil malt.
The intensive technology of obtaining lentil malt can be implemented in the industrial production of malt for the brewing industry. In addition, sprouted lentil beans have health-improving properties and can be used in the production of functional products. The presented technology of lentil bean malting will be in demand in the production of highly nutritious and healthy grain products and fermented beverages
References
- Dewan, Md. F., Shams, S., Haque, M. A. (2024). A Review of the Health Benefits of Processed Lentils (Lens culinaris L.). Legume Science, 6 (2). https://doi.org/10.1002/leg3.232
- Gasiński, A., Kawa-Rygielska, J. (2023). Malting – A method for modifying volatile composition of black, brown and green lentil seeds. PLOS ONE, 18 (9), e0290616. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290616
- Ispiryan, L., Kuktaite, R., Zannini, E., Arendt, E. K. (2021). Fundamental study on changes in the FODMAP profile of cereals, pseudo-cereals, and pulses during the malting process. Food Chemistry, 343, 128549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128549
- Gasiński, A., Kawa-Rygielska, J., Mikulski, D., Kłosowski, G. (2022). Changes in the raffinose family oligosaccharides content in the lentil and common bean seeds during malting and mashing processes. Scientific Reports, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-22943-1
- Cimini, A., Poliziani, A., Morgante, L., Moresi, M. (2023). Antinutrient removal in yellow lentils by malting. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 104 (1), 508–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12950
- Cimini, A., Poliziani, A., Moresi, M. (2023). Decorticated lentil malt flour: production process and use. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 102, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET23102021
- Lucas-Aguirre, J. C., Quintero-Castaño, V. D., Beltrán-Bueno, M., Rodríguez-García, M. E. (2024). Study of the changes on the physicochemical properties of isolated lentil starch during germination. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 267, 131468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131468
- Gasiński, A., Kawa-Rygielska, J. (2024). Assessment of green lentil malt as a substrate for gluten-free beer brewing. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-50724-x
- Gasiński, A., Kawa-Rygielska, J. (2022). Mashing quality and nutritional content of lentil and bean malts. LWT, 169, 113927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113927
- Trummer, J., Watson, H., De Clippeleer, J., Poreda, A. (2021). Brewing with 10% and 20% Malted Lentils – Trials on Laboratory and Pilot Scales. Applied Sciences, 11 (21), 9817. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219817
- Gasiński, A., Błażewicz, J., Kawa-Rygielska, J., Śniegowska, J., Zarzecki, M. (2021). Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters of Congress Worts Prepared from Special Legume Seed Malts, Acquired with and without Use of Enzyme Preparations. Foods, 10 (2), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020304
- Cichońska, P., Kostyra, E., Piotrowska, A., Ścibisz, I., Roszko, M., Ziarno, M. (2024). Enhancing the sensory and nutritional properties of bean-based and lentil-based beverages through fermentation and germination. LWT, 199, 116140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116140
- Horstmann, S. W., Atzler, J. J., Heitmann, M., Zannini, E., Lynch, K. M., Arendt, E. K. (2018). A comparative study of gluten-free sprouts in the gluten-free bread-making process. European Food Research and Technology, 245 (3), 617–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-018-3185-2
- Liberal, Â., Fernandes, Â., Ferreira, I. C. F. R., Vivar-Quintana, A. M., Barros, L. (2024). Effect of different physical pre-treatments on physicochemical and techno-functional properties, and on the antinutritional factors of lentils (Lens culinaris spp). Food Chemistry, 450, 139293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139293
- Kovalova, O., Vasylieva, N., Haliasnyi, I., Gavrish, T., Dikhtyar, A., Andrieieva, S. et al. (2023). Development of buckwheat groats production technology using plasma-chemically activated aqueous solutions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (11 (126)), 59–72. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.290584
- Kovalova, O., Vasylieva, N., Haliasnyi, I., Gavrish, T., Dikhtyar, A., Andrieieva, S. et al. (2024). Development of technology for the production of all-purpose buckwheat malt using plasmochemically activated aqueous solutions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (11 (127)), 38–51. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.298797
- Kovaliova, O., Pivovarov, O., Kalyna, V., Tchoursinov, Y., Kunitsia, E., Chernukha, A. et al. (2020). Implementation of the plasmochemical activation of technological solutions in the process of ecologization of malt production. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (10 (107)), 26–35. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.215160
- Pivovarov, O., Kovaliova, O., Koshulko, V. (2020). Effect of plasmochemically activated aqueous solution on process of food sprouts production. Ukrainian Food Journal, 9 (3), 576–587. https://doi.org/10.24263/2304-974x-2020-9-3-7
- Kovaliova, O., Vasylieva, N., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Mandych, O., Hontar, T. et al. (2023). Development of a technology for the production of germinated flaxseed using plasma-chemically activated aqueous solutions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (11 (124)), 6–19. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.284810
- Kovalova, O., Vasylieva, N., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Haliasnyi, I., Gontar, T. et al. (2023). Determining the effect of plasmochemically activated aqueous solutions on the bioactivation process of sea buckthorn seeds. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (122)), 99–111. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.275548
- Cetinkaya-Rundel, R., Hardin, J. (2021). Introduction to Modern Statistics. OpenIntro, 549.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Olena Kovalova, Natalia Vasylieva, Oksana Zhulinska, Iryna Balandina, Liubov Zhukova, Valentyna Bezpal'ko, Viktoriia Horiainova, Ruslan Trybrat, Oleksandr Zazymko, Yevhen Barkar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








