Development of a method for inactivating lipoxygenases in linseed using chemical reagents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.309079Keywords:
oxidative stability, endogenous lipoxygenase, lipid component, linseed, chemical reagentsAbstract
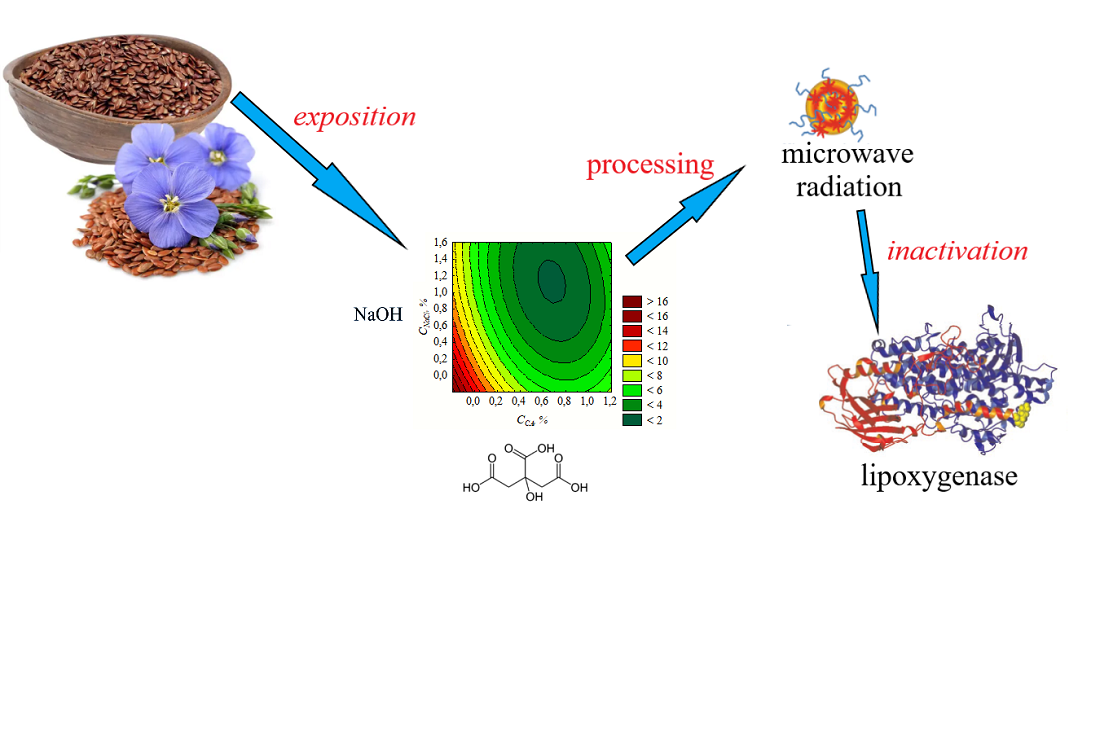
The object of the study is the oxidative stability of the lipid component of linseed treated with a citric acid and sodium chloride solution. The rational composition of chemical reagents for inactivating linseed lipoxygenases was determined in the work. The obtained results make it possible to develop an effective linseed treatment method for increasing stability to oxidative spoilage. The proposed composition of the linseed treatment solution (citric acid – 1.0...1.3 %; sodium chloride – 0.6...0.8 %) significantly reduces the peroxide and anisidine numbers of the lipid component. This helps reduce oxidative spoilage during accelerated oxidation and storage under normal conditions. Rational treatment conditions were determined based on the approximate dependency of these indicators on the concentrations of chemical reagents. The data obtained in the work are explained by chemical interactions between the solution components and the enzyme complex of linseed, leading to enzyme denaturation and, accordingly, increased oxidative stability of the lipid component. A feature of the obtained results is the competitiveness of treated linseed, characterized by increased nutritional value due to improved technological properties. The results of the study allow minimizing the loss of nutritional value and increasing the shelf life of linseed products. The results are important for developing new oilseed processing technologies. This makes it possible not only to increase the stability of products against oxidative spoilage, but also to preserve their high nutritional value. Further research in this area will contribute to improving oilseed processing technologies, in particular linseed, which is an important contribution to the development of the food industry
References
- Rashid, F., Ahmed, Z., Hussain, S., Huang, J.-Y., Ahmad, A. (2019). Linum usitatissimum L. seeds: Flax gum extraction, physicochemical and functional characterization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 215, 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.054
- Belinska, A., Bochkarev, S., Varankina, O., Rudniev, V., Zviahintseva, O., Rudnieva, K. et al. (2019). Research on oxidative stability of protein-fat mixture based on sesame and flax seeds for use in halva technology. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (11 (101)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.178908
- Kajla, P., Sharma, A., Sood, D. R. (2014). Flaxseed – a potential functional food source. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52 (4), 1857–1871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1293-y
- Dunford, N. T. (2022). Enzyme-aided oil and oilseed processing: opportunities and challenges. Current Opinion in Food Science, 48, 100943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100943
- Rozhmina, T., Bankin, M., Samsonova, A., Kanapin, A., Samsonova, M. (2021). A comprehensive dataset of flax (Linum uitatissimum L.) phenotypes. Data in Brief, 37, 107224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2021.107224
- Jandali, R., Agha, M. I. H. (2022). Lipoxygenase Inhibitory Activity of Some Extracts Prepared from Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimumv L.). Current Bioactive Compounds, 18 (3). https://doi.org/10.2174/1574893616666211012091140
- Belinska, A., Bliznjuk, O., Masalitina, N., Bielykh, I., Zviahintseva, O., Gontar, T. et al. (2023). Development of biotechnologically transesterified three-component fat systems stable to oxidation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (6 (125)), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287326
- Chakraborty, S., Pulivarthi, M. K., Raj, A. S., Prakash, S. D., Bommina, H., Siliveru, K. (2024). Inactivation of lipase and lipoxygenase in whole wheat flour using atmospheric cold plasma and steam treatments: Kinetics, mechanism, and impact on its compositional properties. Journal of Cereal Science, 117, 103889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2024.103889
- Farag, M. A., Elimam, D. M., Afifi, S. M. (2021). Outgoing and potential trends of the omega-3 rich linseed oil quality characteristics and rancidity management: A comprehensive review for maximizing its food and nutraceutical applications. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 114, 292–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.041
- Pointner, T., Rauh, K., Auñon-Lopez, A., Kostadinović Veličkovska, S., Mitrev, S., Arsov, E., Pignitter, M. (2024). Comprehensive analysis of oxidative stability and nutritional values of germinated linseed and sunflower seed oil. Food Chemistry, 454, 139790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.139790
- Sytnik, N., Korchak, M., Nekrasov, S., Herasymenko, V., Mylostyvyi, R., Ovsiannikova, T. et al. (2023). Increasing the oxidative stability of linseed oil. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (6 (124)), 35–44. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.284314
- Dun, Q., Yao, L., Deng, Z., Li, H., Li, J., Fan, Y., Zhang, B. (2019). Effects of hot and cold-pressed processes on volatile compounds of peanut oil and corresponding analysis of characteristic flavor components. LWT, 112, 107648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.11.084
- Al-Haidari, A. M. Dh., Alsaadawi, I. S., Khudhair, S. H. (2021). Determination the Optimum Conditions of the Activity and Stability of Lipase Extracted from Sunflower Germinated Seeds. Iraqi Journal of Science, 62 (2), 431–440. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2021.62.2.8
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. (2020). Effect of lipoxygenase-3 on storage characteristics of peanut seeds. Journal of Stored Products Research, 87, 101589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2020.101589
- Machado, S. A., Da Rós, P. C. M., de Castro, H. F., Giordani, D. S. (2021). Hydrolysis of vegetable and microbial oils catalyzed by a solid preparation of castor bean lipase. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 37, 102188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102188
- Zhang, Y., Li, X., Lu, X., Sun, H., Wang, F. (2021). Effect of oilseed roasting on the quality, flavor and safety of oil: A comprehensive review. Food Research International, 150, 110791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110791
- Szydłowska-Czerniak, A., Tymczewska, A., Momot, M., Włodarczyk, K. (2020). Optimization of the microwave treatment of linseed for cold-pressing linseed oil - Changes in its chemical and sensory qualities. LWT, 126, 109317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109317
- Bochkarev, S., Krichkovska, L., Petrova, I., Petrov, S., Varankina, O., Belinska, A. (2017). Research of influence of technological processing parameters of protein-fat base for supply of sportsmen on activity of protease inhibitors. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 4 (3 (36)), 27–30. https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2017.108376
- Belinska, A., Petik, I., Bliznjuk, O., Bochkarev, S., Khareba, O. (2022). Bioengineering studies of inactivation of sesame proteolitic enzyme inhibitors in sports nutrition. Food Resources, 10 (19), 38–46. https://doi.org/10.31073/foodresources2022-19-04
- Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Lutsenko, M., Derevianko, І., Zhukova, L., Filenko, O. et al. (2023). Use of thistle seeds of modified composition in chocolate mass technology. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (11 (126)), 83–91. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.291042
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Anna Belinska, Igor Ryshchenko, Olga Bliznjuk, Nataliia Masalitina, Kostiantyn Siedykh, Svitlana Zolotarova, Natalia Fedak, Olena Petrova, Natalia Shevchuk, Galyna Danylchuk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








