Synthesis of recursive-type neural elements with parallel vertical-group data processing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329139Keywords:
model of a neural element, real-time calculations, hardware implementation of a neural elementAbstract
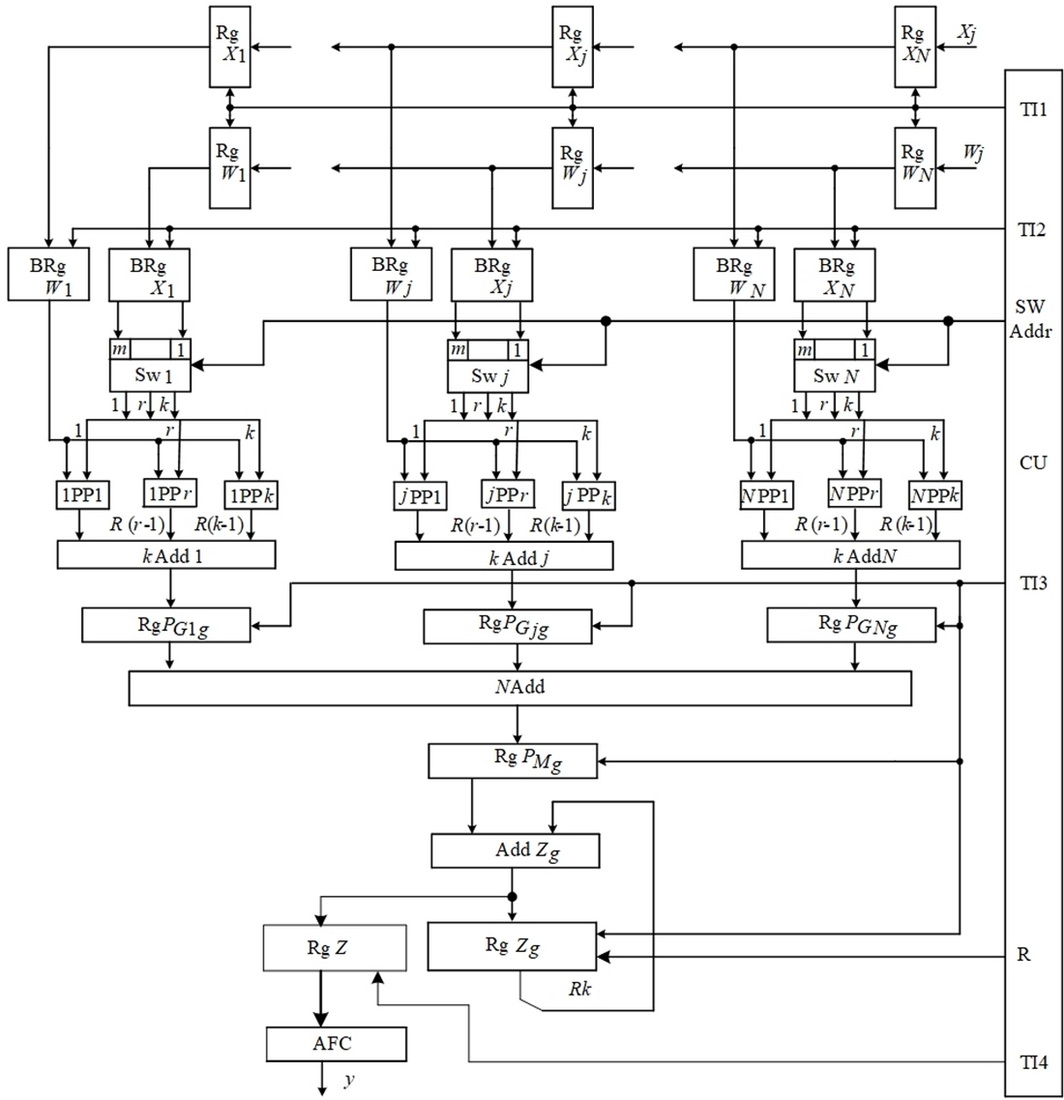
The object of this study is the processes of parallel vertical-group data processing and minimization of equipment costs, which enable the synthesis of real-time recursive neural elements with high efficiency of equipment use. A model of a recursive-type neural element has been built, which, through the use of a parallel vertical-group method for calculating the scalar product and the ability to choose the number of bits in the group for the formation of partial products, coordinates the time of receipt of weights and input data with the time of calculating the result at the output of the neural element. This approach provides a hardware implementation of the neural element with minimal use of equipment.
The basic structure of the neural element has been designed, which, through the use of hardware mapping of the constructed graph model, regularity, and modularity of the structure, provides the synthesis of hardware for a specific application. The application of pipelines and spatial parallelism of data processing, as well as the organization of the process of calculating the scalar product, as the performance of a single operation, enables the implementation of a neural element for real-time operation.
Analytical expressions have been built to estimate the parameters of a neural element depending on the bit depth of operands, the number of data inputs, and the number of bits in the group. A method for synthesizing a recursive-type neural element has been devised, which, due to the use of the basic structure, enables mechanisms for matching the time of receipt of weight coefficients and input data with the time of calculating the output, thus ensuring its implementation for specific applications. Considering ways to minimize equipment costs ensures the construction of a neural element with minimal hardware costs.
The synthesized neural element for a data depth of 16 bits with an increase in the number of bits that are simultaneously processed in a group, from 2 to 8, provides a decrease in the processing time by 2.8 times with a reduction in the efficiency of using the equipment of the neural element by no more than 1.6 times
References
- Leigh, A. J., Heidarpur, M., Mirhassani, M. (2022). A Low-Resource Digital Implementation of the Fitzhugh-Nagumo Neuron. 2022 17th Conference on Ph.D Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), 369–372. https://doi.org/10.1109/prime55000.2022.9816797
- Renteria-Cedano, J., Rivera, J., Sandoval-Ibarra, F., Ortega-Cisneros, S., Loo-Yau, R. (2019). SoC Design Based on a FPGA for a Configurable Neural Network Trained by Means of an EKF. Electronics, 8 (7), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8070761
- Tsmots, I. G., Opotyak, Yu. V., Shtohrinets, B. V., Mamchur, T. B., Oliinyk, O. O. (2024). Operational basis of artificial neural networks and evaluation of hardware characteristics for its implementation. Ukrainian Journal of Information Technology, 6 (2), 125–138. https://doi.org/10.23939/ujit2024.02.125
- Kundu, S., Banerjee, S., Raha, A., Basu, K. (2022). Special Session: Effective In-field Testing of Deep Neural Network Hardware Accelerators. 2022 IEEE 40th VLSI Test Symposium (VTS), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/vts52500.2021.9794227
- Wu, J., Zhao, B., Wen, H., Zhao, Q. (2022). Design of Neural Network Accelerator Based on In-Memory Computing Theory. 2022 4th International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICNLP), 547–551. https://doi.org/10.1109/icnlp55136.2022.00100
- Sarg, M., Khalil, A. H., Mostafa, H. (2021). Efficient HLS Implementation for Convolutional Neural Networks Accelerator on an SoC. 2021 International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/icm52667.2021.9664920
- Nouacer, R., Hussein, M., Espinoza, H., Ouhammou, Y., Ladeira, M., Castiñeira, R. (2020). Towards a framework of key technologies for drones. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 77, 103142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103142
- Saini, S., Lata, K., Sinha, G. R. (2021). VLSI and Hardware Implementations Using Modern Machine Learning Methods. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003201038
- Davies, M., Srinivasa, N., Lin, T.-H., Chinya, G., Cao, Y., Choday, S. H. et al. (2018). Loihi: A Neuromorphic Manycore Processor with On-Chip Learning. IEEE Micro, 38 (1), 82–99. https://doi.org/10.1109/mm.2018.112130359
- Hager, G., Wellein, G. (2010). Introduction to High Performance Computing for Scientists and Engineers. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/ebk1439811924
- Tsmots, I., Teslyuk, V., Kryvinska, N., Skorokhoda, O., Kazymyra, I. (2022). Development of a generalized model for parallel-streaming neural element and structures for scalar product calculation devices. The Journal of Supercomputing, 79 (5), 4820–4846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04838-0
- Liu, W., Wang, Z., Liu, X., Zeng, N., Liu, Y., Alsaadi, F. E. (2017). A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing, 234, 11–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.038
- Tsmots, I. G., Opotyak, Y. V., Shtohrinets, B. V., Mamchur, T. B., Holubets, V. M. (2024). Model, structure and synthesis method of matrix-type neural element. Scientific Bulletin of UNFU, 34 (4), 68–77. https://doi.org/10.36930/40340409
- Tsmots, I., Skorokhoda, O., Ignatyev, I., Rabyk, V. (2017). Basic vertical-parallel real time neural network components. 2017 12th International Scientific and Technical Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies (CSIT), 344–347. https://doi.org/10.1109/stc-csit.2017.8098801
- Leigh, A. J., Mirhassani, M., Muscedere, R. (2020). An Efficient Spiking Neuron Hardware System Based on the Hardware-Oriented Modified Izhikevich Neuron (HOMIN) Model. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 67 (12), 3377–3381. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2020.2984932
- Pi, X., Lin, X. (2022). An FPGA-based Piecewise Linear Spiking Neuron for Simulating Bursting Behavior. 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), 0415–0420. https://doi.org/10.1109/ccwc54503.2022.9720886
- Wang, G., Fu, D. (2024). Spike Neural Network with Delayed Propagation Characteristics and Hardware Implementation. 2024 6th International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Informatics (EEI), 1181–1185. https://doi.org/10.1109/eei63073.2024.10696338
- Ramirez-Morales, R. R., Ponce-Ponce, V. H., Molina-Lozano, H., Sossa-Azuela, H., Islas-García, O., Rubio-Espino, E. (2024). Analog Implementation of a Spiking Neuron with Memristive Synapses for Deep Learning Processing. Mathematics, 12 (13), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12132025
- Xu, Q., Ding, S., Bao, H., Chen, M., Bao, B. (2022). Piecewise-Linear Simplification for Adaptive Synaptic Neuron Model. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 69 (3), 1832–1836. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2021.3124666
- Bao, B., Zhu, Y., Li, C., Bao, H., Xu, Q. (2020). Global multistability and analog circuit implementation of an adapting synapse-based neuron model. Nonlinear Dynamics, 101 (2), 1105–1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05831-z
- Tsmots, I. H., Shtohrinets, B. V., Kazymyra, I. Y., Lytvyn, A. A. (2023). Model and method for synthesis of neural element of parallel-streaming type. Scientific Bulletin of UNFU, 33 (2), 92–100. https://doi.org/10.36930/40330213
- Tsmots, I. H., Skorokhoda, O. V., Medykovskyi, M. O. (2017). Pat. No. 118596 UA. Prystriy dlia obchyslennia skaliarnoho dobutku. No. a201700835; declareted: 30.01.2017; declareted: 11.02.2019.
- Tsmots, I. H., Tesliuk, V. M., Lukashchuk, Yu. A., Kazymyra, I. Ya. (2021). Pat. No. 127774 UA. Prystriy dlia obchyslennia skaliarnoho dobutku. No. a202104653; declareted: 12.08.2021; declareted: 28.12.2023.
- Shymkovych, V., Doroshenko, A., Mamedov, T., Yatsenko, O. (2022) Automated design of an artificial neuron for field-programmable gate arrays based on an Algebra-Algorithmic approach. International Scientific Technical Journal "Problems of Control and Informatics", 67 (5), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.34229/2786-6505-2022-5-6
- Tsmots, I., Opotyak, Y., Shtohrinets, B. (2023). Method of Synthesis of Devices for Parallel Stream Calculation of Scalar Product in Real Time. Vìsnik Nacìonalʹnogo Unìversitetu “Lʹvìvsʹka Polìtehnìka”. Serìâ Ìnformacìjnì Sistemi Ta Merežì, 14, 248–266. https://doi.org/10.23939/sisn2023.14.248
- Lin, X., Lu, H., Pi, X., Wang, X. (2020). An FPGA-based Implementation Method for Quadratic Spiking Neuron Model. 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), 0621–0627. https://doi.org/10.1109/uemcon51285.2020.9298029
- Zi, H., Zhao, K., Zhang, W. (2024). Designing and Accelerating Spiking Neural Network Based on High-Level Synthesis. 2024 Conference of Science and Technology for Integrated Circuits (CSTIC), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/cstic61820.2024.10531920
- Hassantabar, S., Wang, Z., Jha, N. K. (2022). SCANN: Synthesis of Compact and Accurate Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 41 (9), 3012–3025. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcad.2021.3116470
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ivan Tsmots, Vasyl Teslyuk, Yurii Opotyak, Taras Mamchur, Oleksandr Oliinyk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








