Development of machine learning for forecasting optimization implemented in morphology plant growth
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.331745Keywords:
forecasting optimization, plant morphology, machine learning, multilinear regression neural networkAbstract
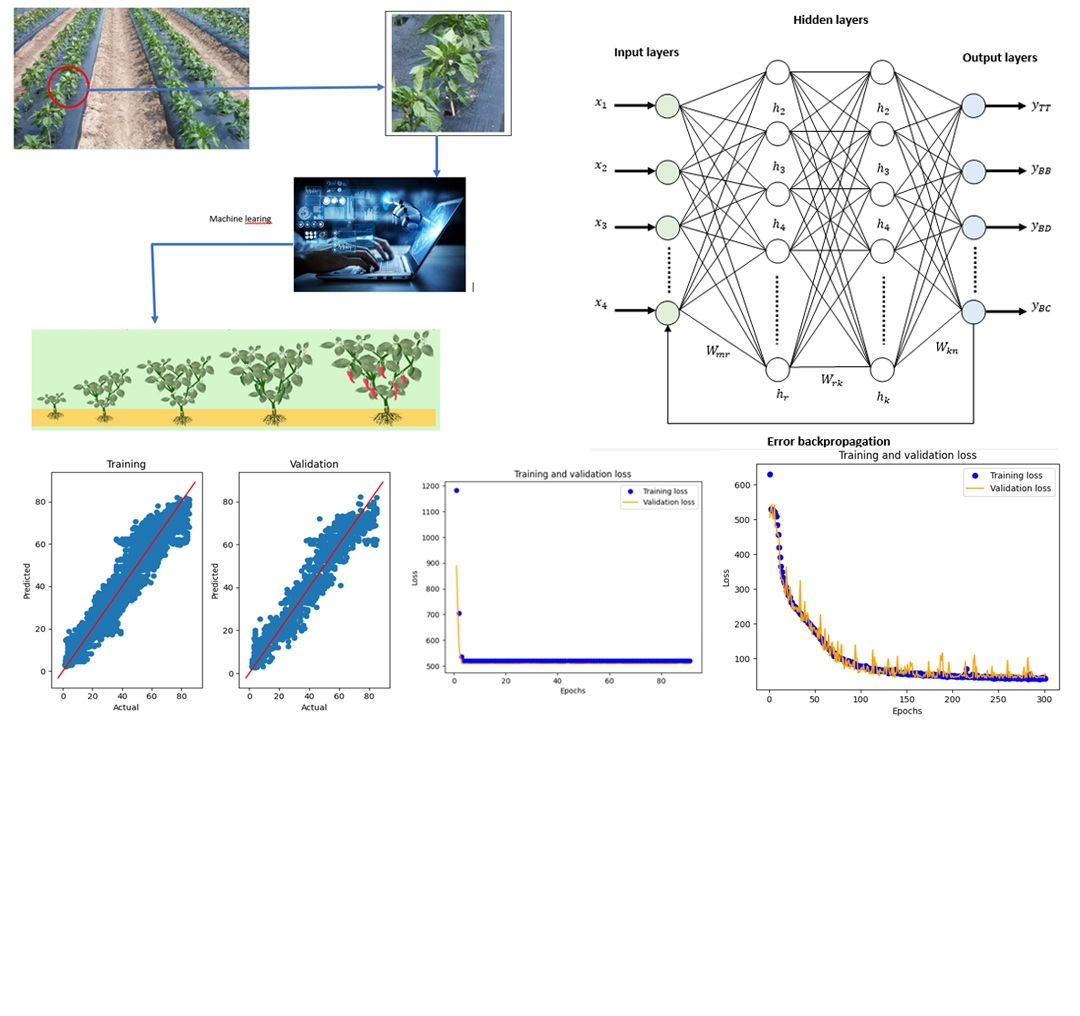
The object of the study is the forecasting and optimizing the plant growth rather. The data distribution at each iteration in the continuous optimization process tends to produce premature convergence because the optimum points are found at the beginning of the iteration, so that the actual optimum condition cannot be achieved. For this reason, a method is needed to see the optimum points at each iteration in the continuous optimization process. A multi-linear regression approach is used to predict the variables generated at each iteration, and then optimized using a neural network method approach for each optimum point found. This research is implemented and observed on the growth morphology of chili plants with a total sample of 100 stems, for 100 days of growth. The testing process consists of 5 different experimental scenarios based on the activation function, and the iteration process is carried out at 250, 500, and 1000 epochs. Furthermore, with a percentage of 70% training data and 30% testing data, the results obtained using the ReLU activation function have an ideal value compared to the Tanh, Softplus, Elu, and Sigmoid activation functions. Compared to the time series method with an MSE value of 4.62, this value is much better than the value of 8.6 for the time series. The RMSE and MAPE values of 16.36 and 36.53 are also excellent. Comparison of the level of forecasting accuracy of the results of continuous optimization carried out with the activation function ReLU and tanh compared to the time series method, the value with the activation function ReLU and tanh has a percentage value 46.36% and 46.86% and this value is a good value compared to using the time series method, which is exactly 67.39%
References
- Stein, O. (2024). Basic Concepts of Global Optimization. In Mathematics Study Resources. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-66240-3
- Zhigljavsky, A., Žilinskas, A. (2021). Bayesian and High-Dimensional Global Optimization. In SpringerBriefs in Optimization. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64712-4
- Marakumbi Prakash, R. (2020). Distributed Load Balancing algorithms for Cloud Computing-A Survey. International Journal of Progressive Research in Science and Engineering, 1 (6). Available at: https://www.ijprse.com/2020/Vol1_Iss6_September20/IJPRSE_V1I6_15.pdf
- Feng, L., Gupta, A., Tan, K. C., Ong, Y. S. (2023). Evolutionary Multi-Task Optimization. In Machine Learning: Foundations, Methodologies, and Applications. Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5650-8
- Cerf, M. (2023). 1.4 Global optimum. Optimization Techniques I, 37–48. https://doi.org/10.1051/978-2-7598-3162-3.c007
- Sariyildiz, İ., Köse Ulukök, M. (2023). Sayısal Global Optimum için Çift-Girişim Tabanlı İyileştirme Algoritmasının Yakınsama Analizi. Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.53070/bbd.1346673
- Zhang, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, H., Wang, J. (2024). A hybrid optimization algorithm for multi-agent dynamic planning with guaranteed convergence in probability. Neurocomputing, 592, 127764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127764
- Huang, C., Wu, D., Zhou, X., Song, Y., Chen, H., Deng, W. (2024). Competitive swarm optimizer with dynamic multi-competitions and convergence accelerator for large-scale optimization problems. Applied Soft Computing, 167, 112252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2024.112252
- Hu, R., Wen, S., Zeng, Z., Huang, T. (2017). A short-term power load forecasting model based on the generalized regression neural network with decreasing step fruit fly optimization algorithm. Neurocomputing, 221, 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.027
- Summary of Volume 2: Paradigms of Combinatorial Optimization (2014). Applications of Combinatorial Optimization, 415–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119005384.oth3
- Kadlec, M., Buhnova, B., Tomsik, J., Herman, J., Druzbikova, K. (2017). Weather forecast based scheduling for demand response optimization in smart grids. 2017 Smart City Symposium Prague (SCSP), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/scsp.2017.7973867
- Schupbach, J., Pryor, E., Webster, K., Sheppard, J. (2022). Combining Dynamic Bayesian Networks and Continuous Time Bayesian Networks for Diagnostic and Prognostic Modeling. 2022 IEEE AUTOTESTCON, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/autotestcon47462.2022.9984758
- Scutari, M., Denis, J.-B. (2021). The Continuous Case: Gaussian Bayesian Networks. Bayesian Networks, 37–62. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429347436-2
- Luo, X., Yan, R., Wang, S. (2023). Comparison of deterministic and ensemble weather forecasts on ship sailing speed optimization. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 121, 103801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2023.103801
- de Matos Sá, M., Correia da Fonseca, F. X., Amaral, L., Castro, R. (2024). Optimising O&M scheduling in offshore wind farms considering weather forecast uncertainty and wake losses. Ocean Engineering, 301, 117518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117518
- Keun Kim, M., Cremers, B., Fu, N., Liu, J. (2024). Predictive and correlational analysis of heating energy consumption in four residential apartments with sensitivity analysis using long Short-Term memory and Generalized regression neural network models. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 71, 103976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2024.103976
- Ait Lahoussine Ouali, H., Touili, S., Alami Merrouni, A., Moukhtar, I. (2024). Artificial neural Network-Based LCOH estimation for concentrated solar power plants for industrial process heating applications. Applied Thermal Engineering, 236, 121810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.121810
- Mizushima, Y., Inoue, H., Morikawa, S., Taira, S. (2023). Optimization of formworks shoring location as a continuous optimization problem. Structures, 56, 104949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2023.104949
- Wang, Y., Sun, S., Fathi, G., Eslami, M. (2024). Improving the Method of Short-term Forecasting of Electric Load in Distribution Networks using Wavelet transform combined with Ridgelet Neural Network Optimized by Self-adapted Kho-Kho Optimization Algorithm. Heliyon, 10 (7), e28381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28381
- Feng, J., Hou, S., Yu, L., Dimov, N., Zheng, P., Wang, C. (2020). Optimization of photovoltaic battery swapping station based on weather/traffic forecasts and speed variable charging. Applied Energy, 264, 114708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114708
- Ni, Y., Liu, W., Du, X., Xiao, R., Chen, G., Wu, Y. (2024). Evolutionary optimization approach based on heuristic information with pseudo-utility for the quadratic assignment problem. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 87, 101557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101557
- Sun, F., Liu, T., Song, B., Cui, Y., Nagy, Z. K., Findeisen, R. (2024). Multi-objective optimization based nonlinear model predictive control of seeded cooling crystallization process with application to β form L-glutamic acid. Chemical Engineering Science, 299, 120475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2024.120475
- Cadenas, J. M., Garrido, M. C., Martínez-España, R., Guillén-Navarro, M. A. (2020). Making decisions for frost prediction in agricultural crops in a soft computing framework. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 175, 105587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105587
- Wang, Y., Zhang, Y. (2021). Prediction of runway configurations and airport acceptance rates for multi-airport system using gridded weather forecast. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 125, 103049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2021.103049
- Barus, E. S., Zarlis, M., Nasution, Z., Sutarman. (2019). Forcasting Plant Growth Using Neural Network Time Series. 2019 International Conference of Computer Science and Information Technology (ICoSNIKOM), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/icosnikom48755.2019.9111503
- Matondang, D., Saogo, D., Sianturi, R., Dapit, S., Barus, E. (2023). Analisis Pemberian Nutrisi Menggunakan Metode Fuzzy Logic Studi Kasus Tanaman Cabai. Jurnal Teknik Informasi Dan Komputer (Tekinkom), 6 (2), 408–416. Available at: https://jurnal.murnisadar.ac.id/index.php/Tekinkom/article/view/929
- Barus, E. S., Sahputra (2023). Sistem Monitoring Pertumbuhan Tanaman Berbasis Internet of Things. Jurnal Ilmu Komputer Dan Sistem Informasi (JIKOMSI), 6 (1), 1–8. Available at: https://ejournal.sisfokomtek.org/index.php/jikom/article/view/849
- Huang, S., Wang, Z., Ge, Y., Wang, F. (2024). A coevolutionary estimation of distribution algorithm based on dynamic differential grouping for mixed-variable optimization problems. Expert Systems with Applications, 245, 123122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.123122
- Sahputra, S., Sembiring, D. C., Sipayung, I. H., Barus, E. S. (2024). Analisis Prediksi Hasil Produksi Tanaman Cabai Menggunakan Metode Multi Linier Regresi. Jurnal Teknik Informasi Dan Komputer (Tekinkom), 7 (2), 619. https://doi.org/10.37600/tekinkom.v7i2.1512
- Anand, V., Oinam, B., Wieprecht, S. (2024). Machine learning approach for water quality predictions based on multispectral satellite imageries. Ecological Informatics, 84, 102868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102868
- Senanayake, I. P., Hartmann, P., Giacomini, A., Huang, J., Thoeni, K. (2024). Prediction of rockfall hazard in open pit mines using a regression based machine learning model. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 177, 105727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2024.105727
- Liu, J., Zhu, C., Long, Z., Huang, H., Liu, Y. (2021). Low-rank tensor ring learning for multi-linear regression. Pattern Recognition, 113, 107753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107753
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ertina Sabarita Barus, Muhammad Zarlis, Zulkifli Nasution, Sutarman Sutarman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








