Defining supply chain resilience during wartime
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.272877Keywords:
supply chain resilience, civil logistics, russia-Ukraine war, logistics landscape, Futures-WheelAbstract
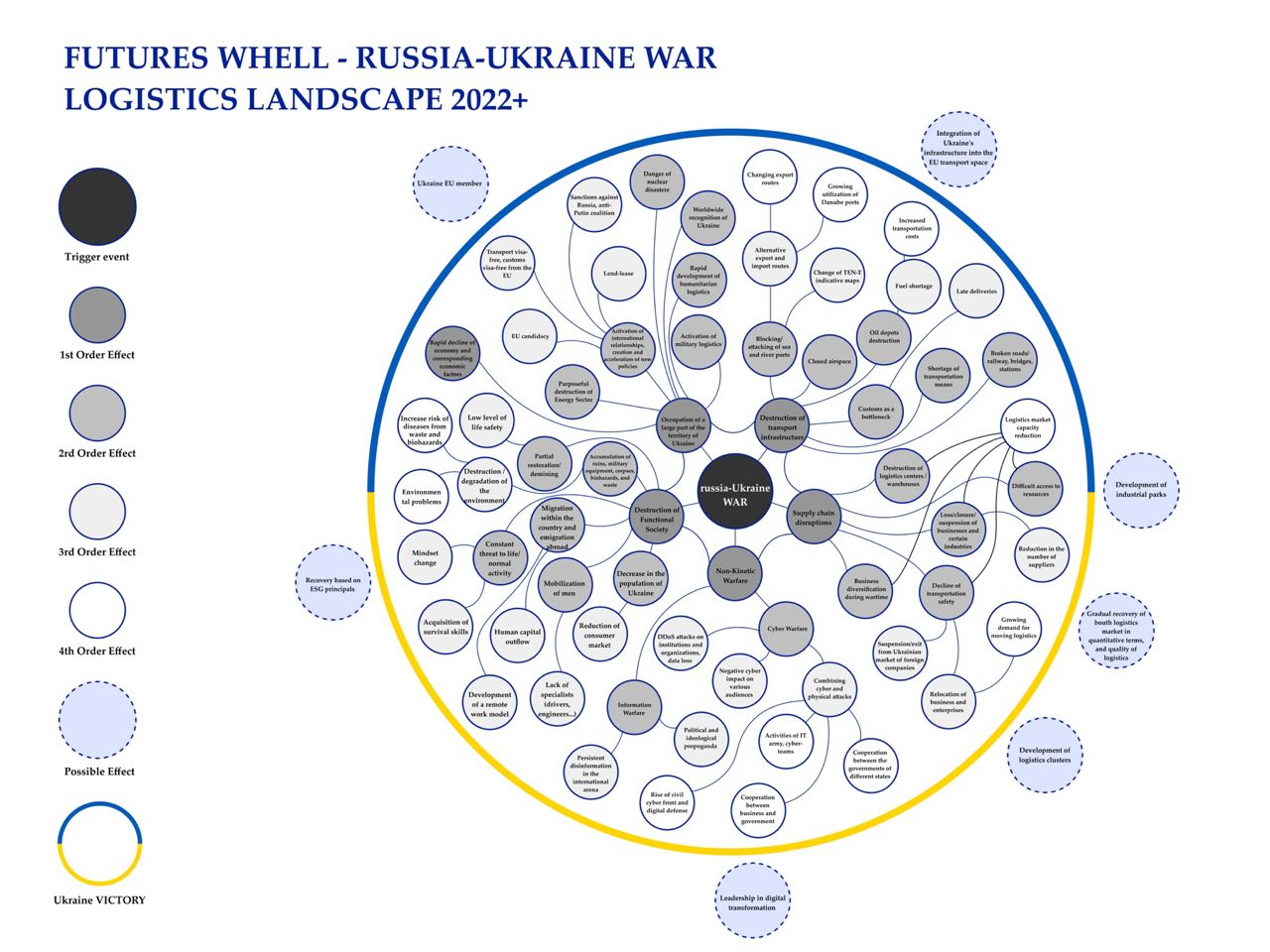
Russia's full-scale military invasion of Ukraine led to the occupation of a large part of the territory of Ukraine, active warfare in the East and South parts of Ukraine, activation of military logistics, rapid development of humanitarian logistics. At the same time, non-kinetic warfare, destruction of functional society, attack on the logistics infrastructure and supply chain disruptions are observed. Civil Logistics and Supply Chains acquired the specifics of working in wartime conditions – constant danger, brittle, anxious, nonlinear, incomprehensible. The following two research questions were asked in the paper. First – how was it possible to ensure the functioning of the supply chains, overcoming logistics obstacles. Second – how are the events unfolding and what strategic consequences will the war have for Ukraine's logistics landscape. To answer the first research question, the focus group method was used (the representativeness of which was ensured by top managers of logistics companies). The answer to the second research question was obtained by the method of summarizing and systematizing figures and facts about the events that have a direct impact on the logistics industry of Ukraine, supplemented by the method for graphical visualization of research results – Futures-Wheel. As a result, the highlighted strategies that were used in managing supply chains when facing logistics obstacles caused by war can potentially be useful in other crises. Futures-Wheel presents an overall picture of the impact of war on the logistics landscape of Ukraine as well as a vision of the future
References
- DHL resilience 360. Turning a potential disruption into competitive advantage. DHL. Available at: https://tapcrowdstatic-ie.s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/5544/confbagfiles/event/10890/CSI_DHL_Resilience360_1474895712_1507195876.pdf
- Katsaliaki, K., Galetsi, P., Kumar, S. (2021). Supply chain disruptions and resilience: a major review and future research agenda. Annals of Operations Research, 319 (1), 965–1002. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03912-1
- Golan, M. S., Jernegan, L. H., Linkov, I. (2020). Trends and applications of resilience analytics in supply chain modeling: systematic literature review in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Environment Systems and Decisions, 40 (2), 222–243. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-020-09777-w
- Marcucci, G., Mazzuto, G., Bevilacqua, M., Ciarapica, F. E., Urciuoli, L. (2022). Conceptual model for breaking ripple effect and cycles within supply chain resilience. Supply Chain Forum: An International Journal, 23 (3), 252–271. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/16258312.2022.2031275
- Wieteska, G. (2020). The Impact of Supplier Involvement in Product Development on Supply Chain Risks and Supply Chain Resilience. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 13 (4), 359–374. doi: https://doi.org/10.31387/oscm0430276
- Zavala-Alcívar, A., Verdecho, M.-J., Alfaro-Saiz, J.-J. (2020). A Conceptual Framework to Manage Resilience and Increase Sustainability in the Supply Chain. Sustainability, 12 (16), 6300. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166300
- Robb, C., Kang, M., Stephens, A. (2022). The effects of dynamism, relational capital, and ambidextrous innovation on the supply chain resilience of U.S. firms amid COVID-19. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 15 (1), 1–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.31387/oscm0480326
- Spieske, A., Birkel, H. (2021). Improving supply chain resilience through industry 4.0: A systematic literature review under the impressions of the COVID-19 pandemic. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 158, 107452. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107452
- Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Childe, S. J., Fosso Wamba, S., Roubaud, D., Foropon, C. (2019). Empirical investigation of data analytics capability and organizational flexibility as complements to supply chain resilience. International Journal of Production Research, 59 (1), 110–128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1582820
- Singagerda, F. S., Fauzan, A. T., Desfiandi, A. (2022). The role of supply chain visibility, supply chain flexibility, supplier development on business performance of logistics companies. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 10 (2), 463–470. doi: https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2021.12.005
- Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Bryde, D. J., Dwivedi, Y. K., Papadopoulos, T. (2020). Blockchain technology for enhancing swift-trust, collaboration and resilience within a humanitarian supply chain setting. International Journal of Production Research, 58 (11), 3381–3398. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1722860
- Tarigan, Z. J. H., Siagian, H., Jie, F. (2021). Impact of Internal Integration, Supply Chain Partnership, Supply Chain Agility, and Supply Chain Resilience on Sustainable Advantage. Sustainability, 13 (10), 5460. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105460
- Grzybowska, K., Tubis, A. A. (2022). Supply Chain Resilience in Reality VUCA – An International Delphi Study. Sustainability, 14 (17), 10711. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710711
- Nikolopoulos, K., Punia, S., Schäfers, A., Tsinopoulos, C., Vasilakis, C. (2021). Forecasting and planning during a pandemic: COVID-19 growth rates, supply chain disruptions, and governmental decisions. European Journal of Operational Research, 290 (1), 99–115. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2020.08.001
- Aigbogun, O., Xing, M., Fawehinmi, O., Ibeabuchi, C., Ehido, A., Ahmad, R. B., Abdullahi, M. S. (2022). A supply chain resilience model for business continuity: The way forward for highly regulated industries. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 10 (1), 1–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2021.11.001
- Singh, S., Kumar, R., Panchal, R., Tiwari, M. K. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on logistics systems and disruptions in food supply chain. International Journal of Production Research, 59 (7), 1993–2008. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1792000
- Belhadi, A., Kamble, S., Jabbour, C. J. C., Gunasekaran, A., Ndubisi, N. O., Venkatesh, M. (2021). Manufacturing and service supply chain resilience to the COVID-19 outbreak: Lessons learned from the automobile and airline industries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 163, 120447. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120447
- Ozdemir, D., Sharma, M., Dhir, A., Daim, T. (2022). Supply chain resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic. Technology in Society, 68, 101847. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101847
- Herold, D. M., Nowicka, K., Pluta-Zaremba, A., Kummer, S. (2021). COVID-19 and the pursuit of supply chain resilience: reactions and “lessons learned” from logistics service providers (LSPs). Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 26 (6), 702–714. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/scm-09-2020-0439
- Chiappetta Jabbour, C. J., Sobreiro, V. A., Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A. B., de Souza Campos, L. M., Mariano, E. B., Renwick, D. W. S. (2017). An analysis of the literature on humanitarian logistics and supply chain management: paving the way for future studies. Annals of Operations Research, 283 (1-2), 289–307. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2536-x
- Altay, N., Kovács, G., Spens, K. (2021). The evolution of humanitarian logistics as a discipline through a crystal ball. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management, 11 (4), 577–584. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/jhlscm-06-2021-0056
- Glenn, J. (2021). The Futures Wheel. Chap. 6. In Futures Research Methodology 3.0. The Millennium Project. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349335014_THE_FUTURES_WHEEL
- «My v stani enerhetychnoi viyny z Rosieiu», kazhut v YeS, hotuiuchy dii u vidpovid. Voice of America. Available at: https://ukrainian.voanews.com/a/6737830.html
- Zelenskyi: ZSU zvilnyly ponad 6000 kv. km, rukh viysk tryvaie. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.pravda.com.ua/news/2022/09/12/7367187/
- Ukraina 2022. Yak ne vtratyty sviy shans staty sylnoiu derzhavoiu. Ukrainskyi instytut maibutnoho. Available at: https://uifuture.org/publications/ukrayina-2022-yak-ne-vtratyty-svij-shans-staty-sylnoyu-derzhavoyu/
- Svitova ekonomika tsoho roku vtratyt trylion dolariv cherez vtorhnennia rf – The Economist. Slovo i dilo. Available at: https://www.slovoidilo.ua/2022/08/05/novyna/ekonomika/svitova-ekonomika-czoho-roku-vtratyt-tryljon-dolariv-cherez-vtorhnennya-rf-the-economist
- U Bilomu domi poiasnyly, koly pochnut vykorystovuvaty prohramu lend-lizu dlia Ukrainy. Slovo i dilo. Available at: https://www.slovoidilo.ua/2022/07/14/novyna/bezpeka/bilomu-domi-poyasnyly-koly-pochnut-vykorystovuvaty-prohramu-lend-lizu-ukrayiny
- Zbytky vid blokuvannia portiv v Ukraini sklaly miliardy dolariv. Interviu iz zastupnykom holovy AMPU. Suspilne. Available at: https://suspilne.media/262222-zbitki-vid-blokuvanna-portiv-v-ukraini-sklali-milardi-dolariv-intervu-iz-zastupnikom-golovi-ampu/
- Ukraina otrymala status kandydata na vstup v YeS. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.pravda.com.ua/news/2022/06/23/7354307/
- Ukraina otrymala transportnyi "bezviz" z krainamy YeS. Chomu tse vazhlyvo? Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.epravda.com.ua/columns/2022/07/6/688923/
- Mizhnarodna humanitarna dopomoha dlia Ukrainy: peremohy ta vyklyky. LB.ua. Available at: https://lb.ua/blog/oleksandra_vasylenko/525144_mizhnarodna_gumanitarna_dopomoga.html
- Osoblyvosti ukrainskoi lohistyky humanitarnykh vantazhiv cherez Rumuniyu v umovakh viyny. Logist. Available at: https://logist.today/uk/osoboe_mnenie/2022-09-02/osobennosti-ukrainskoj-logistiki-gumanitarnyh-gruzov-cherez-rumyniyu-v-usloviyah-vojny/
- From disruption to reinvention. Accenture. Available at: https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-177/Accenture-Disruption-Reinvention.pdf
- Cherez viynu Ukraina vtratyla 23% zaliznychnoi merezhi. Yunian. Available at: https://www.unian.ua/economics/transport/ukrajina-vtratila-23-zaliznichnoji-merezhi-viyna-z-rosiyeyu-2022-novini-ukrajina-11826117.html
- Vartist zaliznychnykh perevezen zbilshylas na 70%. Landlord. Available at: https://landlord.ua/news/vartist-zaliznychnykh-perevezen-zbilshylas-na-70/
- liutoho - 24 serpnia 2022: shist misiatsiv viyny dlia infrastruktury i transportu Ukrainy. Tsentr transportnykh stratehiy. Available at: https://cfts.org.ua/articles/24_lyutogo_24_serpnya_2022_shist_misyatsiv_viyni_dlya_infrastrukturi_i_transportu_ukrani_1920
- Lohistychni shliakhy Ukrainy staly chastynoiu Transievropeiskoi transportnoi merezhi. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.epravda.com.ua/news/2022/07/27/689709/
- Ekspert prohnozuie, shcho do kintsia lita bahato inozemnykh kompaniy vidnovliat robotu v Ukraini. Khmarochos. Available at: https://hmarochos.kiev.ua/2022/07/25/ekspert-prognozuye-shho-do-kinczya-lita-bagato-inozemnyh-kompanij-vidnovlyat-robotu-v-ukrayini/
- U Minfini povidomyly, yaka chastka biznesu v Ukraini pryzupynyla svoiu diyalnist cherez viynu. Slovo i dilo. Available at: https://www.slovoidilo.ua/2022/06/01/novyna/biznes/minfini-povidomyly-yaka-chastka-biznesu-ukrayini-pryzupynyla-svoyu-diyalnist-cherez-vijnu
- % maloho i serednoho biznesu vtratyly ponad $100 tysiach cherez viinu – opytuvannia. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.epravda.com.ua/news/2022/08/16/690482/
- Relokatsiya biznesu: skilky pidpryiemstv uzhe ponovyly robotu. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.epravda.com.ua/news/2022/08/17/690505/
- Ukraintsi stvoryly ponad 150 tysiach biznesiv za chas viiny. Dniprovske investytsiine ahenstvo. Available at: https://dia.dp.gov.ua/ukra%d1%97nci-stvorili-ponad-150-tisyach-biznesiv-za-chas-vijni/
- Microsoft rozpovila pro kiberataky y kibervplyv Rosiyi na Ukrainu ta yii soiuznykiv. Ukrainska pravda. Available at: https://www.pravda.com.ua/news/2022/06/23/7354192/
- Predstavnyk Google u Radbezi OON: Meta kiberatak rosiyi - vypravdannia voiennykh zlochyniv. Ukrinform. Available at: https://www.ukrinform.ua/rubric-technology/3512169-predstavnik-google-u-radbezi-oon-meta-kiberatak-rosii-vipravdanna-voennih-zlociniv.html
- Viyna rosiyi proty Ukrainy suprovodzhuietsia spleskom kiberatak u sviti – YeS. Ukrinform. Available at: https://www.ukrinform.ua/rubric-world/3533103-vijna-rosii-proti-ukraini-suprovodzuetsa-spleskom-kiberatak-u-sviti-es.html
- Za piv roku viyny postrazhdala tretyna lisovoho fondu Ukrainy, zbytky perevyshchuiut 180 mlrd hrn – holova Minpryrody. Interfaks Ukraina. Available at: https://ua.interfax.com.ua/news/general/855884.html
- Ukraine: civilian casualty update 12 September 2022. United National Human Rights. Available at: https://www.ohchr.org/en/news/2022/09/ukraine-civilian-casualty-update-12-september-2022
- Ukraine Situation Flash Update #30 (16 September 2022). Reliefweb provided by OCHA. Available at: https://reliefweb.int/report/ukraine/ukraine-situation-flash-update-30-16-september-2022
- Ukraine Refugee Situation. Operational Data Portal (ODP). Available at: https://data.unhcr.org/en/situations/ukraine
- Rynok pratsi v umovakh viyny: osnovni tendentsiyi ta napriamy stabilizatsiyi. Razumkov centre. Available at: https://razumkov.org.ua/images/2022/07/18/2022-ANALIT-ZAPIS-PISHULINA-2.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yevhen Krykavskyy, Nataliya Chornopyska, Oksana Dovhun, Nataliya Hayvanovych, Sofiya Leonova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








