Надійна оптимізація для динамічних рішень постачальників та завдань розподілу обсягів постачання у галузі мультироздрібної торгівлі
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.305111Ключові слова:
дистрибуція, мультироздрібний, галузь, інфраструктура, математичні моделіАнотація
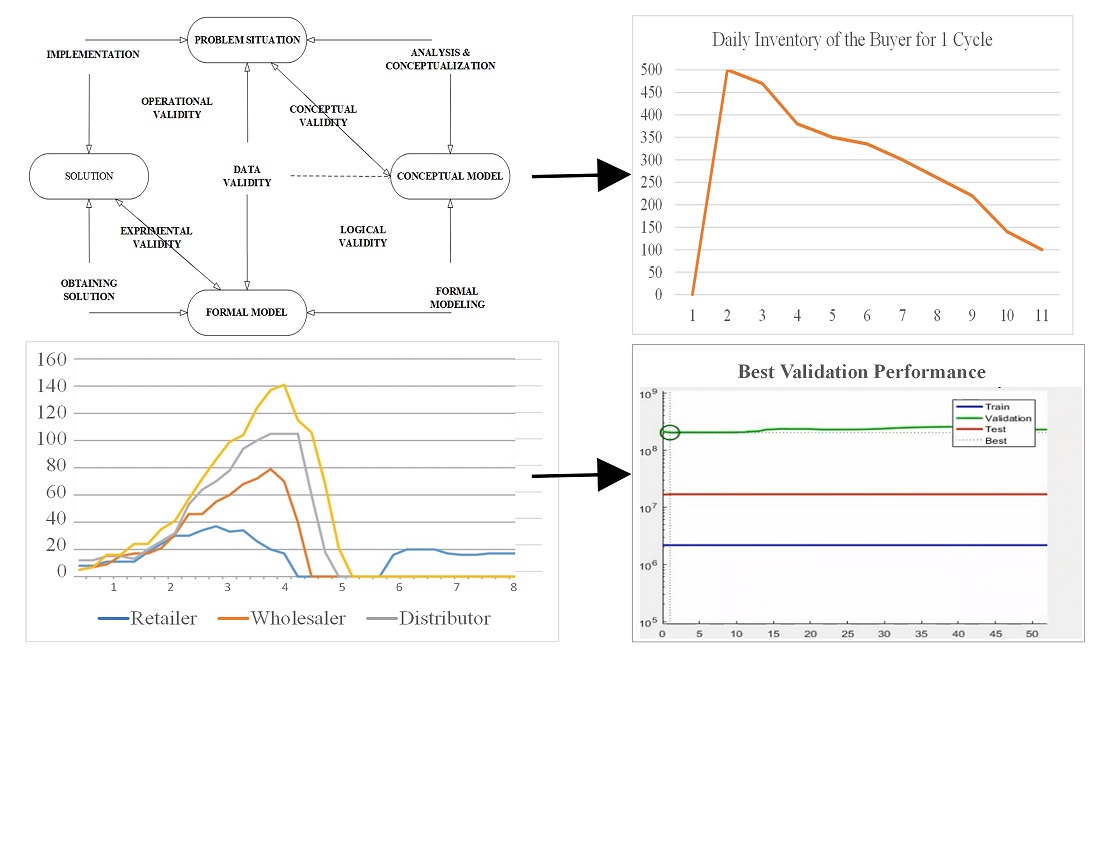
Дослідження зосереджено на мультироздрібній дистрибуції зі стратегічною мережею розподілу. Серед викликів – гостра конкуренція, логістичні та транспортні складності, що вимагають надійної інфраструктури, такої як склади та ефективне управління ланцюгами постачання, а також недоліки в операційній діяльності та витрати на розподіл. Для вирішення цих проблем застосовується модель прийняття стратегічних рішень, таких як визначення необхідної кількості споруд для мінімізації загальних операційних витрат мережі ланцюга постачання та інфраструктури для роздрібної торгівлі. В результаті отримано модель, що пропонує новий підхід до підвищення ефективності ланцюга постачання від виробництва до розподілу, тим самим зменшуючи системні витрати, включаючи витрати на замовлення та обробку запасів. Витрати, що виникають від залишкової продукції, можуть бути мінімізовані за умови врахування мереж, кількох постачальників, кількох складів, Центрів Дистрибуції (ЦД), кількох роздрібних торговців та кількох товарів, з урахуванням відстаней між спорудами в мережі. В подальшому має бути проведене комплексне тестування параметрів інспекції, розподілу та роздрібної торгівлі з акцентом на конкретні періоди та типи товарів. При застосуванні цієї моделі необхідно врахувати певні характеристики щодо важливості вибору ефективних постачальників товарів, такі як закупівлі, покращення продуктивності та кількість ланцюгів постачання та систем ланцюга постачання. Дане дослідження пропонує нововведення в методах виробництва, які можуть призвести до збільшення задоволення клієнтів, обсягу продажів, ринкової частки, маржі прибутку, більш ефективного брендування та підвищення доходів. У цьому процесі дослідження проходить процес навчання, тестування та валідації для створення стратегічної моделі мультироздрібної мережі розподілу, що охоплює 52 епохи. В результаті цього процесу точність навчання досягає 90 %, тестування – 92 % та валідації – 94 %
Посилання
- José Alem, D., Morabito, R. (2012). Production planning in furniture settings via robust optimization. Computers & Operations Research, 39 (2), 139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2011.02.022
- Maranesi, C., De Giovanni, P. (2020). Modern Circular Economy: Corporate Strategy, Supply Chain, and Industrial Symbiosis. Sustainability, 12 (22), 9383. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12229383
- van Hoek, R. (2021). Lessons from CSCMP Supply Chain Hall of Famer Henry Ford and the research that they call for in modern supply chains. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 52 (1), 88–102. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijpdlm-10-2020-0315
- De, A., Singh, S. P. (2021). Analysis of fuzzy applications in the agri-supply chain: A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 283, 124577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124577
- Teodorescu, M., Korchagina, E. (2021). Applying Blockchain in the Modern Supply Chain Management: Its Implication on Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7 (1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010080
- Luo, L., Sheng, Y., Song, Y. (2023). A Historical Review on Omni Channel Retailing Consumer Research. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 16 (4), 435–449. https://doi.org/10.31387/oscm0550402
- Pawlicka, K., Bal, M. (2021). Supply chain finance and challenges of modern supply chains. Logforum, 17 (1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.17270/j.log.2021.525
- Chen, B., Chao, X. (2020). Dynamic Inventory Control with Stockout Substitution and Demand Learning. Management Science, 66 (11), 5108–5127. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2019.3474
- Stevenson, M., Cole, R. (2018). Modern slavery in supply chains: a secondary data analysis of detection, remediation and disclosure. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 23 (2), 81–99. https://doi.org/10.1108/scm-11-2017-0382
- Zimmer, K., Fröhling, M., Schultmann, F. (2015). Sustainable supplier management – a review of models supporting sustainable supplier selection, monitoring and development. International Journal of Production Research, 54 (5), 1412–1442. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2015.1079340
- Shah, N. K., Ierapetritou, M. G. (2012). Integrated production planning and scheduling optimization of multisite, multiproduct process industry. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 37, 214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.08.007
- Caiado, R. G. G., Scavarda, L. F., Gavião, L. O., Ivson, P., Nascimento, D. L. de M., Garza-Reyes, J. A. (2021). A fuzzy rule-based industry 4.0 maturity model for operations and supply chain management. International Journal of Production Economics, 231, 107883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107883
- Trautrims, A., Schleper, M. C., Cakir, M. S., Gold, S. (2020). Survival at the expense of the weakest? Managing modern slavery risks in supply chains during COVID-19. Journal of Risk Research, 23 (7-8), 1067–1072. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2020.1772347
- Ruiz-Torres, A. J., Mahmoodi, F., Ohmori, S. (2019). Joint determination of supplier capacity and returner incentives in a closed-loop supply chain. Journal of Cleaner Production, 215, 1351–1361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.146
- Jeng, D. J.-F. (2015). Generating a causal model of supply chain collaboration using the fuzzy DEMATEL technique. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 87, 283–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2015.05.007
- Kalkanci, B., Plambeck, E. L. (2020). Reveal the Supplier List? A Trade-off in Capacity vs. Responsibility. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 22 (6), 1251–1267. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2019.0795
- Staquicini, D. I., Tang, F. H. F., Markosian, C., Yao, V. J., Staquicini, F. I., Dodero-Rojas, E. et al. (2021). Design and proof of concept for targeted phage-based COVID-19 vaccination strategies with a streamlined cold-free supply chain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118 (30). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2105739118
- Chen, Y., Chen, I. J. (2019). Mediated power and sustainable supplier management (SSM). International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 49 (8), 861–878. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijpdlm-12-2018-0393
- Ras, I., Gregoriou, C. (2019). The Quest to End Modern Slavery: Metaphors in corporate modern slavery statements. Anti-Trafficking Review, 13, 100–118. https://doi.org/10.14197/atr.201219137
- Olivella-Rosell, P., Lloret-Gallego, P., Munné-Collado, Í., Villafafila-Robles, R., Sumper, A., Ottessen, S. et al. (2018). Local Flexibility Market Design for Aggregators Providing Multiple Flexibility Services at Distribution Network Level. Energies, 11 (4), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040822
- Qu, T., Huang, T., Nie, D., Fu, Y., Ma, L., Huang, G. Q. (2022). Joint Decisions of Inventory Optimization and Order Allocation for Omni-Channel Multi-Echelon Distribution Network. Sustainability, 14 (10), 5903. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105903
- Thevenin, S., Ben-Ammar, O., Brahimi, N. (2022). Robust optimization approaches for purchase planning with supplier selection under lead time uncertainty. European Journal of Operational Research, 303 (3), 1199–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2022.03.029
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Solly Aryza, Syahril Efendi, Poltak Sihombing, Sawaluddin

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









