Identifying areas for improving management accounting tools in the food industry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322429Keywords:
accounting, food industry, innovation processes, dataflow automation, cost managementAbstract
The object of the research is the individual elements of management accounting in the food industry.
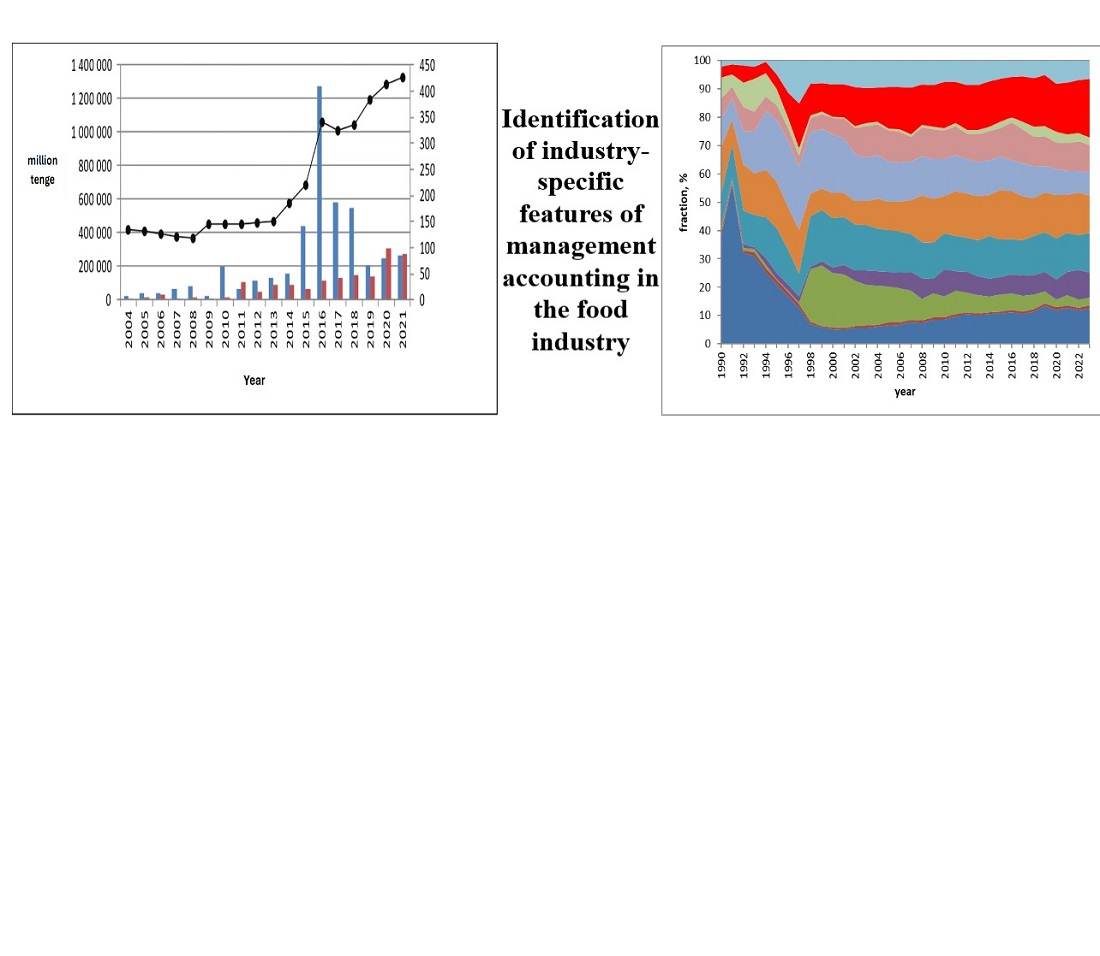
The study examines the key challenges faced by food industry organizations, which operate under the influence of numerous diverse factors and have their own industry-specific characteristics. This necessitates the use of modern administrative tools and unconventional solutions based on management accounting principles. Exploring the capabilities of the food industry management accounting system, it was found that the final stage can be extended to obtain data that enable cash flow monitoring, net profit assessment, and the identification of key allocation directions.
The findings highlight the need to implement the direct costing system in the country's food industry, as it best aligns with the operational specifics of these production sectors. This approach optimizes the tax burden on enterprises by focusing on variable costs, which are particularly significant in the food industry. The adoption of ERP systems, big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and accounting methods such as ABC costing, target costing, and standard costing enables more precise cost allocation, efficient capacity utilization, and real-time resource management. This contributes to increased profitability and competitiveness of food industry enterprises. The industry-specific features of management accounting in the food sector are closely linked to production structure analysis, accounting for seasonal fluctuations, utilization of average annual capacity, and tracking specific costs such as quality control and compliance expenses
References
- Sisaye, S., Birnberg, J. G. (2014). Sociological Approaches to Organizational Learning: Applications to Process Innovations in Management Accounting Systems. Advances in Management Accounting, 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1108/s1474-787120140000023001
- Syzdykbayeva, N., Turysbekova, R., Abdykalyk, S., Bastaubayev, A. (2021). Factors and key areas of modernization of the agro-industrial complex of Kazakhstan. Economics: The Strategy and Practice, 16 (2), 116–133. https://doi.org/10.51176/1997-9967-2021-2-116-133
- Abed, R. A., Kareem, A. H., Jabbar, A. K., Zwaid, J. G., Hasan, H. F. (2023). The implementation of accounting information systems on the stock return and financial performance based on information technology (IT). Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (13 (125)), 57–64. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289424
- Syrtseva, S., Cheban, Y. (2021). Accounting compliance: an institutional approach to ensure the quality of accounting information of the enterprise. Baltic Journal of Economic Studies, 7 (2), 210–218. https://doi.org/10.30525/2256-0742/2021-7-2-210-218
- Osato, O., Wilhelmina, A., Chinwe, O., Adedoyin, O., Onyeka, O., Chinonye, U. (2024). The role of accounting in mitigating food supply chain risks and food price volatility. International Journal of Science and Research Archive, 11 (1), 2557–2565. https://doi.org/10.30574/ijsra.2024.11.1.0340
- Hadachek, J., Ma, M., Sexton, R. J. (2023). Market structure and resilience of food supply chains under extreme events. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 106 (1), 21–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12393
- Dautkanov, N., Dautkanova, D., Mussayeva, S. (2022). Analysis of risks and safety indicators of raw materials and products of the sugar industry of Kazakhstan. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (11 (118)), 105–112. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.263130
- Sjah, T., Zainuri, Z. (2020). Agricultural Supply Chain and Food Security. Zero Hunger. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95675-6_82
- Bhat, S. A., Huang, N.-F., Sofi, I. B., Sultan, M. (2021). Agriculture-Food Supply Chain Management Based on Blockchain and IoT: A Narrative on Enterprise Blockchain Interoperability. Agriculture, 12 (1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010040
- Zatsu, V., Shine, A. E., Tharakan, J. M., Peter, D., Ranganathan, T. V., Alotaibi, S. S. et al. (2024). Revolutionizing the food industry: The transformative power of artificial intelligence-a review. Food Chemistry: X, 24, 101867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101867
- Abdullah, A. A. H., Almaqtari, F. A. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0 on transforming accounting and auditing practices. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10 (1), 100218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joitmc.2024.100218
- Mauina, G. M., Chertkova, E. A., Aitimova, U. Zh., Nukusheva, S. A. (2020). A heuristic approach to the choice of management solutions for agricultural enterprises in Northern Kazakhstan. Bulletin of Science of S. Seifullin Kazakh Agrotechnical Research University, 4 (107), 177–191.
- Otraslevaia statistika. Biuro natcionalnoi statistiki Agentstva po strategicheskomu planirovaniiu i reformam Respubliki Kazakhstan. Available at: https://stat.gov.kz/ru/industries/
- Alajdarkyzy, K., Alaydar, J., Nazarova, V. L., Dauzova, A. M. (2019). International experience of cost accounting in the system "direct costing" and "standard-cost». Statistics, Account and Audit, 2 (73), 14–20.
- Baimukhanova, S. B., Nurmaganbetova, A. Z., Dildabekov, A. N., Omar, K. B. (2020). Introduction of the latest cost calculation systems of cost on Kazakhstan enterprises. Statistics, Account and Audit, 4 (79), 35–40.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Aigul Amirgaliyeva, Yelena Kaliyeva, Korlan Kadyrova, Nazym Nurpeisova, Karlygash Bolshekbaeva, Perizat Beisekova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








