Determining an approach to iris recognition depending on shooting conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325517Keywords:
iris recognition, Hamming Distance, HMI systems, DenseNet, CLAHE, Equalization HistogramAbstract
The object of this study is the development and evaluation of image processing and analysis methods for iris recognition, which can be integrated into human-machine interaction (HMI) systems based on biometric data or other contactless interaction approaches.
Enabling high accuracy and reliability of biometric iris recognition systems under variable imaging conditions remains an open scientific challenge. One of the primary difficulties is the impact of changing lighting conditions, head tilt, and partial eye openness on identification results.
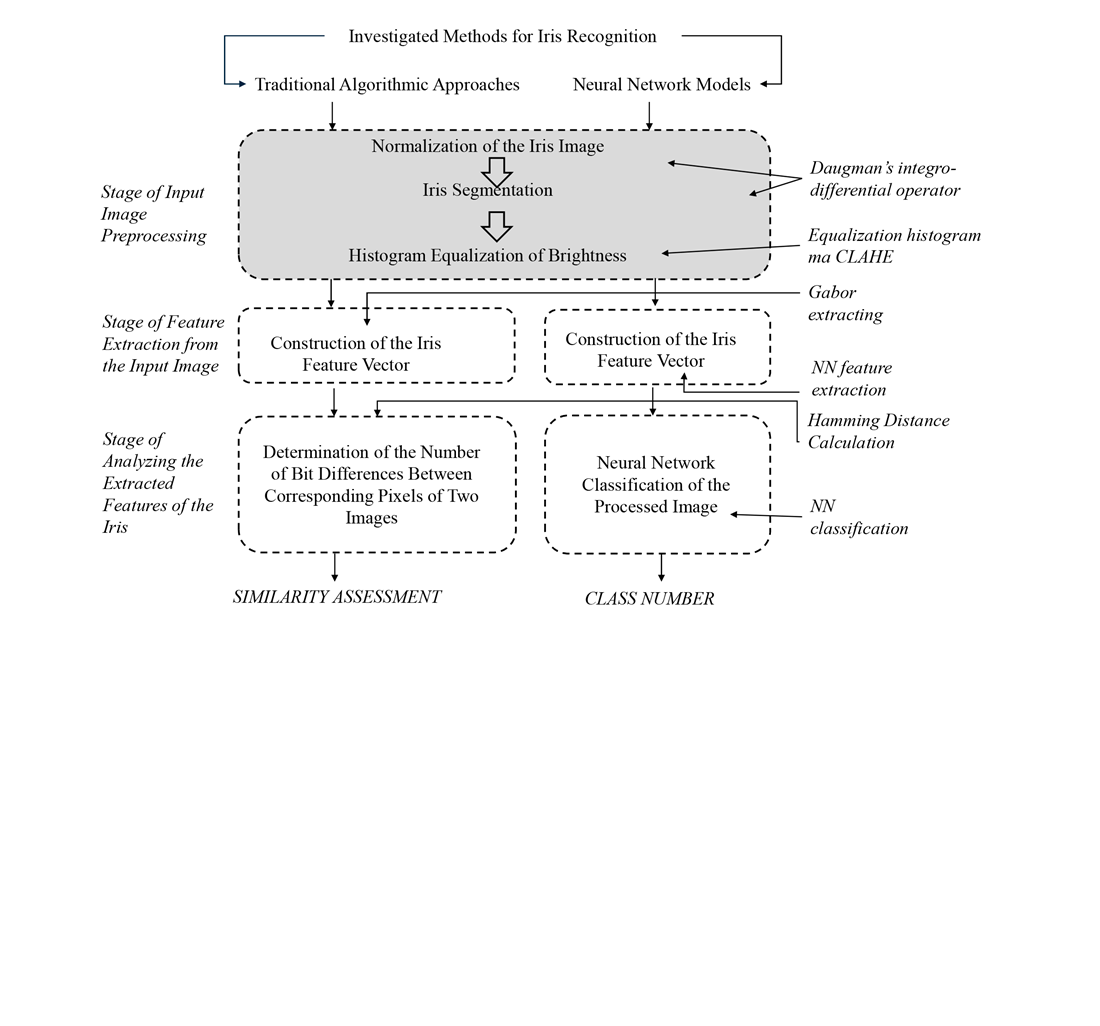
This study assesses the effect of preprocessing methods (Equalization Histogram, CLAHE) on iris image quality and compares the algorithmic method (Hamming Distance) with neural network models (CNN, DenseNet) based on key metrics, including accuracy, False Match Rate, False Non-Match Rate, and Equal Error Rate. Additionally, the influence of training dataset structure and neural network hyperparameters on classification performance was analyzed.
The results demonstrate that the Hamming Distance method (HD = 0.35) achieves 95.5 % accuracy, making it a competitive alternative to neural networks. It was established that combining CLAHE and Equalization Histogram effectively reduces noise and enhances segmentation accuracy. Furthermore, it was determined that the DenseNet-201 neural network achieves an accuracy of 99.93 % when using an optimal dataset split (70 %:15 %:15 %). The study confirms that preprocessing techniques such as normalization and adaptive contrast enhancement significantly reduce recognition errors under varying lighting conditions.
The proposed solution holds significant potential for assistive technologies for individuals with visual impairments, the automotive industry, as well as security systems
References
- Mourtzis, D., Angelopoulos, J., Panopoulos, N. (2023). The Future of the Human-Machine Interface (HMI) in Society 5.0. Future Internet, 15 (5), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15050162
- Zhou, H., Wang, D., Yu, Y., Zhang, Z. (2023). Research Progress of Human-Computer Interaction Technology Based on Gesture Recognition. Electronics, 12 (13), 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132805
- Ban, S., Lee, Y. J., Yu, K. J., Chang, J. W., Kim, J.-H., Yeo, W.-H. (2023). Persistent Human-Machine Interfaces for Robotic Arm Control Via Gaze and Eye Direction Tracking. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 5 (7). https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202200408
- Desmarais, Y., Mottet, D., Slangen, P., Montesinos, P. (2021). A review of 3D human pose estimation algorithms for markerless motion capture. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 212, 103275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2021.103275
- Malgheet, J. R., Manshor, N. B., Affendey, L. S. (2021). Iris Recognition Development Techniques: A Comprehensive Review. Complexity, 2021 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6641247
- Barkovska, O., Liapin, Y., Muzyka, T., Ryndyk, I., Botnar, P. (2024). Gaze direction monitoring model in computer system for academic performance assessment. Information Technologies and Learning Tools, 99 (1), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.33407/itlt.v99i1.5503
- Barkovska, O., Axak, N., Rosinskiy, D., Liashenko, S. (2018). Application of mydriasis identification methods in parental control systems. 2018 IEEE 9th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), 459–463. https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert.2018.8409177
- Perea-García, J. O., Danel, D. P., Monteiro, A. (2021). Diversity in Primate External Eye Morphology: Previously Undescribed Traits and Their Potential Adaptive Value. Symmetry, 13 (7), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13071270
- Sunilkumar, M., Rudresh, D. R., Prakash, H., Santosh, P., Jambukesh, H. J., Harakannanavar, S. S. (2023). Development of iris recognition model using transform domain approaches with Hamming distance classifier. International Journal of Advances in Engineering and Management, 5 (5), 459–469. Available at: https://ijaem.net/issue_dcp/Development%20of%20iris%20recognition%20model%20using%20transform%20domain%20approaches%20with%20Hamming%20distance%20classifier.pdf
- Xiong, Q., Zhang, X., He, S., Shen, J. (2022). Data Augmentation for Small Sample Iris Image Based on a Modified Sparrow Search Algorithm. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44196-022-00173-7
- Hapsari, R. K., Utoyo, M. I., Rulaningtyas, R., Suprajitno, H. (2020). Comparison of Histogram Based Image Enhancement Methods on Iris Images. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1569 (2), 022002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1569/2/022002
- Hassan, R., Kasim, S., Wan Chek Jafery, W. A. Z., Ali Shah, Z. (2017). Image Enhancement Technique at Different Distance for Iris Recognition. International Journal on Advanced Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 7 (4-2), 1510. https://doi.org/10.18517/ijaseit.7.4-2.3392
- Kintonova, A., Povkhan, I., Mussaif, M., Gabdreshov, G. (2022). Improvement of iris recognition technology for biometric identification of a person. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (120)), 60–69. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269948
- Venkatesh, P., Shyam, G. K., Alam, S. (2024). Enhancement of detection accuracy for preventing iris presentation attack. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), 14 (4), 4376. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v14i4.pp4376-4385
- Nguyen, K., Proença, H., Alonso-Fernandez, F. (2024). Deep Learning for Iris Recognition: A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 56 (9), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1145/3651306
- Damayanti, F. A., Andri Asmara, R., Prasetyo, G. B. (2024). Residual Network Deep Learning Model with Data Augmentation Effects in the Implementation of Iris Recognition. International Journal of Frontier Technology and Engineering, 2 (2), 79–86. https://doi.org/10.33795/ijfte.v2i2.6223
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Olesia Barkovska, Igor Ruban, Yuri Romanenkov, Pavlo Botnar, Anton Havrashenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









