Forecasting anomalies in network traffic
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326779Keywords:
Network anomaly, telecommunication traffic, network traffic prediction, long short-term memory (LSTM), semi-supervised learningAbstract
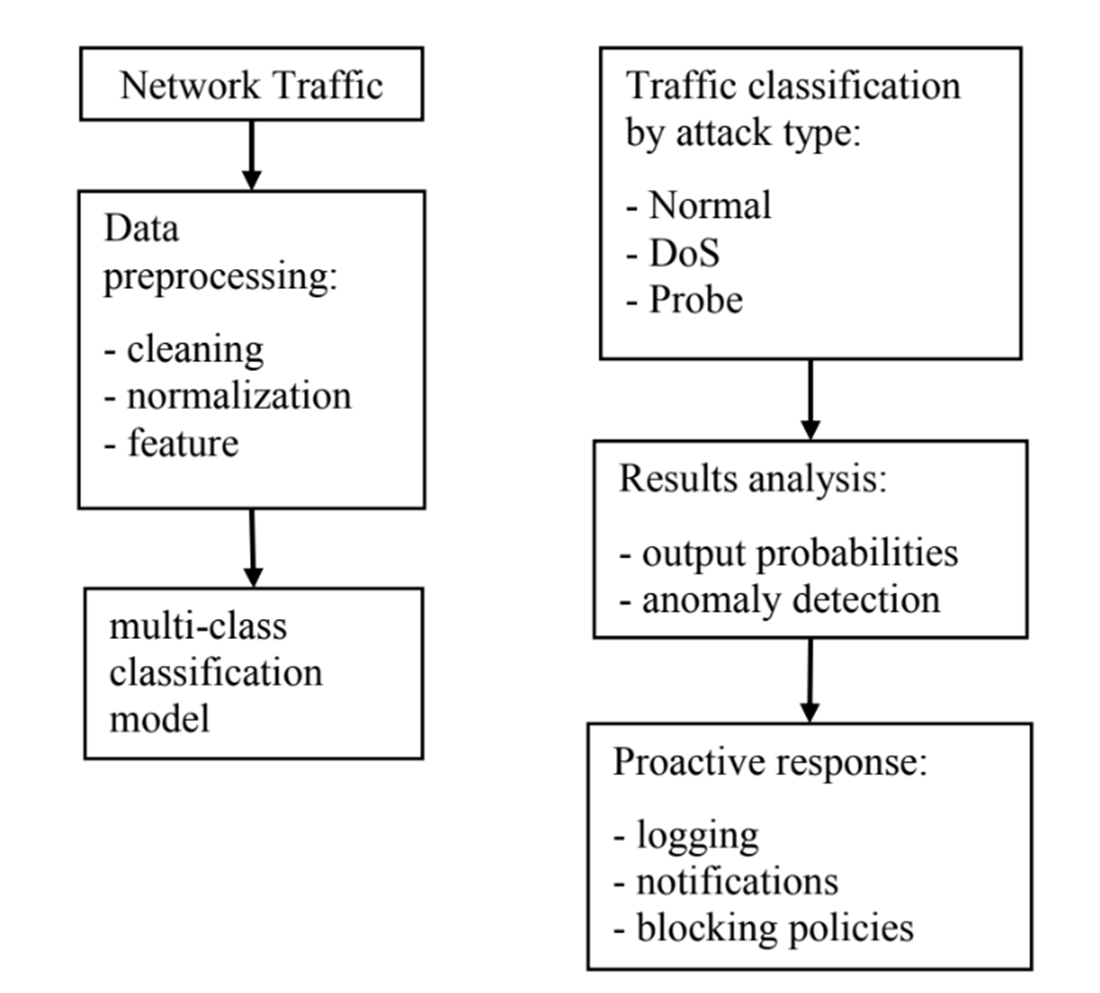
The increasing volume of traffic, growing number of connections in telecommunication networks, and rising number of mobile devices place significant demands on network providers. These challenges can lead to congestion, latency issues, and security vulnerabilities. However, they can be mitigated or even prevented by identifying network failures in advance. Anomaly detection plays a crucial role in proactively addressing these issues, enabling network operators to optimize network performance, enhance security, and improve the overall user experience.
In this paper, a method for predicting anomalies based on machine learning has been implemented. The LSTM-SMOTE model, which was trained and tested on the KDD-NLS dataset, was considered and the results of the forecasting model were analyzed. Developing the multi-classification model proved to be a challenging task, primarily due to the limited number of attack types. SMOTE is designed to address such difficulties. Imbalanced datasets present a major challenge in predictive modeling, especially when solving classification problems. The four main types of attacks include Denial of service (DoS) attacks, Probe attacks, Privilege attacks, and Access attacks. In this work, three neural network models were developed, including: binary classification, four-class classification, multi-class classification. It is observed that the prediction model retrained again showed the best results, then the model trained with new anomalous data. The LSTM-SMOTE multiclass model achieved the highest performance, with its predictive accuracy rising from 75 % to 99 % across iterations, underscoring its strong dependence on the quality and quantity of data. Practical application of the results obtained can be applied for optimizing network performance
References
- Cheng, Y., Liu, Q., Wang, J., Wan, S., Umer, T. (2018). Distributed Fault Detection for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Support Vector Regression. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4349795
- Muriira, L. M., Zhao, Z., Min, G. (2018). Exploiting Linear Support Vector Machine for Correlation-Based High Dimensional Data Classification in Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors, 18 (9), 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092840
- Latif, Z., Umer, Q., Lee, C., Sharif, K., Li, F., Biswas, S. (2022). A Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Prediction Service for Software-Defined Networks. Sensors, 22 (21), 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218434
- Song, W., Beshley, M., Przystupa, K., Beshley, H., Kochan, O., Pryslupskyi, A. et al. (2020). A Software Deep Packet Inspection System for Network Traffic Analysis and Anomaly Detection. Sensors, 20 (6), 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061637
- Oliveira, T. P., Barbar, J. S., Soares, A. S. (2016). Computer network traffic prediction: a comparison between traditional and deep learning neural networks. International Journal of Big Data Intelligence, 3 (1), 28. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbdi.2016.073903
- Alkasassbeh, M. (2018). A Novel Hybrid Method for Network Anomaly Detection Based on Traffic Prediction and Change Point Detection. Journal of Computer Science, 14 (2), 153–162. https://doi.org/10.3844/jcssp.2018.153.162
- Khan, I. A., Pi, D., Khan, Z. U., Hussain, Y., Nawaz, A. (2019). HML-IDS: A Hybrid-Multilevel Anomaly Prediction Approach for Intrusion Detection in SCADA Systems. IEEE Access, 7, 89507–89521. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2925838
- Bhatia, R., Benno, S., Esteban, J., Lakshman, T. V., Grogan, J. (2019). Unsupervised machine learning for network-centric anomaly detection in IoT. Proceedings of the 3rd ACM CoNEXT Workshop on Big DAta, Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Data Communication Networks, 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359992.3366641
- Nurzhaubayeva, G., Haris, N., Chezhimbayeva, K. (2024). Design of the Wearable Microstrip Yagi-Uda Antenna for IoT Applications. International Journal on Communications Antenna and Propagation (IRECAP), 14 (1), 24. https://doi.org/10.15866/irecap.v14i1.24315
- Chezhimbayeva, K., Konyrova, M., Kumyzbayeva, S., Kadylbekkyzy, E. (2021). Quality assessment of the contact center while implementation the IP IVR system by using teletraffic theory. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (3 (114)), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.244976
- Mukhamejanova, A. D., Grabs, E. A., Tumanbayeva, K. K., Lechshinskaya, E. M. (2022). Traffic simulation in the LoRaWAN network. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 11 (2), 1117–1125. https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v11i2.3484
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Inkar Zhumay, Kymyssay Tumanbayeva, Katipa Chezhimbayeva, Kuat Kalibek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









