Devising a production technology and assessing the quality of gluten-free energy bars with a gelled layer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329265Keywords:
energy bars, functional food products, response surface methodology, fruit puree, antioxidant activityAbstract
The object of this study is the production of energy bars. The subject of the research is the production technology of gluten-free functional energy bars with a gelled layer based on millet flour, fruit puree, and functional additives. The task addressed is to select optimal ratios of components, providing stable organoleptic and textural characteristics of the product while preserving functional properties and the possibility of industrial scaling.
In designing the research plan, special attention was given to selecting optimal ingredient ratios and processing parameters to achieve a stable and high-quality product.
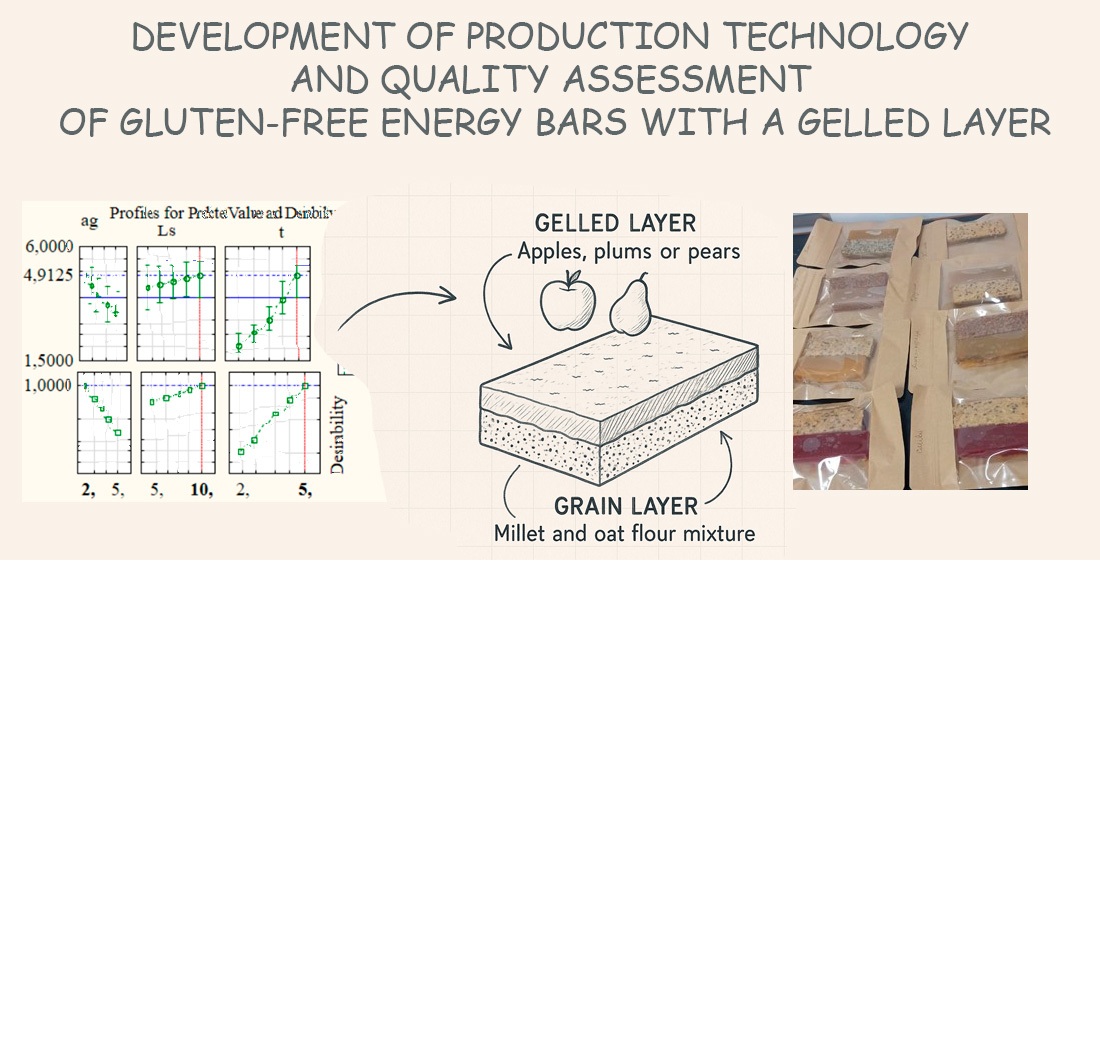
The development of energy bars involved the use of the following ingredients: a blend of oat and millet flour, fruit purée (apple, pear, plum) with the addition of agar-agar, cinnamon, mint, and ginger. Recipe optimization was carried out using the Response Surface Methodology (RSM), which allows for the identification of the best ingredient ratios.
Sensory analysis revealed that the most appealing taste characteristics were observed in bars containing cinnamon and mint. These samples received the highest scores for aroma, flavor, and texture. The highest antioxidant activity levels were recorded in samples containing cinnamon and apple (up to 82.8 %). This is attributed to the high content of phenolic compounds in cinnamon, known for their strong antioxidant properties. Optimal texture parameters were achieved with a layer height of 12 mm – ensuring a balanced structure, a syrup content of 5 % – preventing excessive stickiness, and a protein content of 7 % – improving product firmness and elasticity. The samples with mint and cinnamon exhibited the lowest water activity (aw=0.68–0.72), making them more resistant to microbial spoilage and extending their shelf life.
The application of multi-criteria analysis methods and statistical experimental design allowed for the identification of key parameters influencing product quality
References
- Wei, X., Yao, J., Wang, F., Wu, D., Zhang, R. (2022). Extraction, isolation, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from elderberry fruit. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.947706
- Dżugan, M., Pizoń, A., Tomczyk, M., Kapusta, I. (2019). A New Black Elderberry Dye Enriched in Antioxidants Designed for Healthy Sweets Production. Antioxidants, 8 (8), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080257
- Li, M., He, P., Zhao, Z., Liu, J., Liu, H., Ma, S. et al. (2023). Effect of temperature on betacyanins synthesis and the transcriptome of Suaeda salsa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1203089
- Ju, C., Lv, J., Wu, A., Wang, Y., Zhu, Y., Chen, J. (2022). Effect of pH on betalain-anthocyanin mixture in bayberry juice: influences on pigments, colour, and antioxidant capacity. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 57 (6), 3556–3566. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15680
- Monteiro, S. S., Santos, N. C., Almeida, R. L. J., de Lima, T. L. B., Tomé, A. E. S., Morais, S. K. Q. et al. (2025). Evaluation of sapodilla pulp as a matrix for probiotic fermentation: Physicochemical changes, antioxidant potential, and in vitro digestibility during storage. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 435, 111175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2025.111175
- Khuzaimah, S. (2018). Uji Aktivitas Antioksidan Hasil Ekstraksi Zat Warna Alami Dari Kulit Buah Naga (Hylocereus undatus). Ratih: Jurnal Rekayasa Teknologi Industri Hijau, 3 (2). Available at: https://ejournal.unugha.ac.id/index.php/ratih/article/view/432/
- Sholika Sari, T., Kusumawati, I., Isnaeni. (2023). Color Stability and Antioxidant Activity of Red Roselle (Hibiscus Sabdariffa L.) Calyx Infuse. Berkala Ilmiah Kimia Farmasi, 10 (2), 42–47. https://doi.org/10.20473/bikfar.v10i2.51706
- Chen, W., Ma, X., Wang, X., Chen, S., Rogiewicz, A., Slominski, B. et al. (2019). Establishment of a rapeseed meal fermentation model for iturin A production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CX‐20. Microbial Biotechnology, 12 (6), 1417–1429. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13483
- Liu, H., Ni, Y., Yu, Q., Fan, L. (2023). Evaluation of co-fermentation of L. plantarum and P. kluyveri of a plant-based fermented beverage: Physicochemical, functional, and sensory properties. Food Research International, 172, 113060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113060
- Fortin, G. A., Asnia, K. K. P., Ramadhani, A. S., Maherawati, M. (2021). Minuman fungsional serbuk instan kaya antioksidan dari bahan nabati. Agrointek : Jurnal Teknologi Industri Pertanian, 15 (4), 984–991. https://doi.org/10.21107/agrointek.v15i4.8977
- Van Vliet, T., Primo‐Martín, C. (2011). Interplay between product characteristics, oral physiology and texture perception of cellular brittle foods. Journal of Texture Studies, 42 (2), 82–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4603.2010.00273.x
- Cristea, E., Sturza, R., Jauregi, P., Niculaua, M., Ghendov‐Moșanu, A., Patras, A. (2019). Influence of pH and ionic strength on the color parameters and antioxidant properties of an ethanolic red grape marc extract. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 43 (4), e12788. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12788
- Kim, J. H., Kim, Y. S., Kim, T. I., Li, W., Mun, J.-G., Jeon, H. D. et al. (2020). Unripe Black Raspberry (Rubus coreanus Miquel) Extract and Its Constitute, Ellagic Acid Induces T Cell Activation and Antitumor Immunity by Blocking PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction. Foods, 9 (11), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111590
- Delić, J., Ikonić, P., Jokanović, M., Peulić, T., Ikonić, B., Banjac, V. et al. (2023). Sustainable snack products: Impact of protein- and fiber-rich ingredients addition on nutritive, textural, physical, pasting and color properties of extrudates. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 87, 103419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2023.103419
- Saleena, P., Jayashree, E., Neethu, K. C., Bhuvaneswari, S., Alfiya, P. V., Anees, K. (2024). Optimization of vacuum impregnated nutmeg rind candy using RSM modeling: effect on functional and nutritional properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 61 (11), 2121–2132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-024-05982-6
- Kuzembayeva, G., Kuzembayev, K., Tlevlessova, D. (2023). Optimization of the method of hydrothermal treatment of mogar grain for production of food concentrate "Talkan". Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (11 (125), 16–25. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289235
- Draszanowska, A., Starowicz, M., Czarnowska‐Kujawska, M., Olszewska, M. A. (2024). Effects of different spices on the bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity, and sensory qualities of kale crisps. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 59 (6), 3851–3859. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.17132
- Boasiako, T. A., Hua, F., YuQing, X., Boateng, I. D., Ma, Y. (2024). Enzymatic catalytic dynamics of lactic-acetic acid co-fermentation: Effect of cellulase on the physicochemical, phytochemicals, volatiles, and antioxidant activity of jujube puree extracts. Industrial Crops and Products, 222, 119590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.119590
- Dana, H., Sonia, A. (2024). Physicochemical Properties of Apple Purees and Peel Extract for Potential Use in Pastry Products. Applied Sciences, 14 (5), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052011
- Goraya, R. K., Singla, M., Kaura, R., Singh, C. B., Singh, A. (2024). Exploring the impact of high pressure processing on the characteristics of processed fruit and vegetable products: a comprehensive review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2024.2373390
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Farah Saleena Taip, Dinara Tlevlessova, Barna Khamitova, Sanavar Azimova, Gaukhar Kuzembayeva, Kanash Kuzembayev, Aizhan Ablayeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








