Optimizing permanent magnet synchronous motor control: a comparative study of MPCC-based techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.331895Keywords:
PMSM, MPCC, ANFIS, ANN, THD, industrial drives, electric vehiclesAbstract
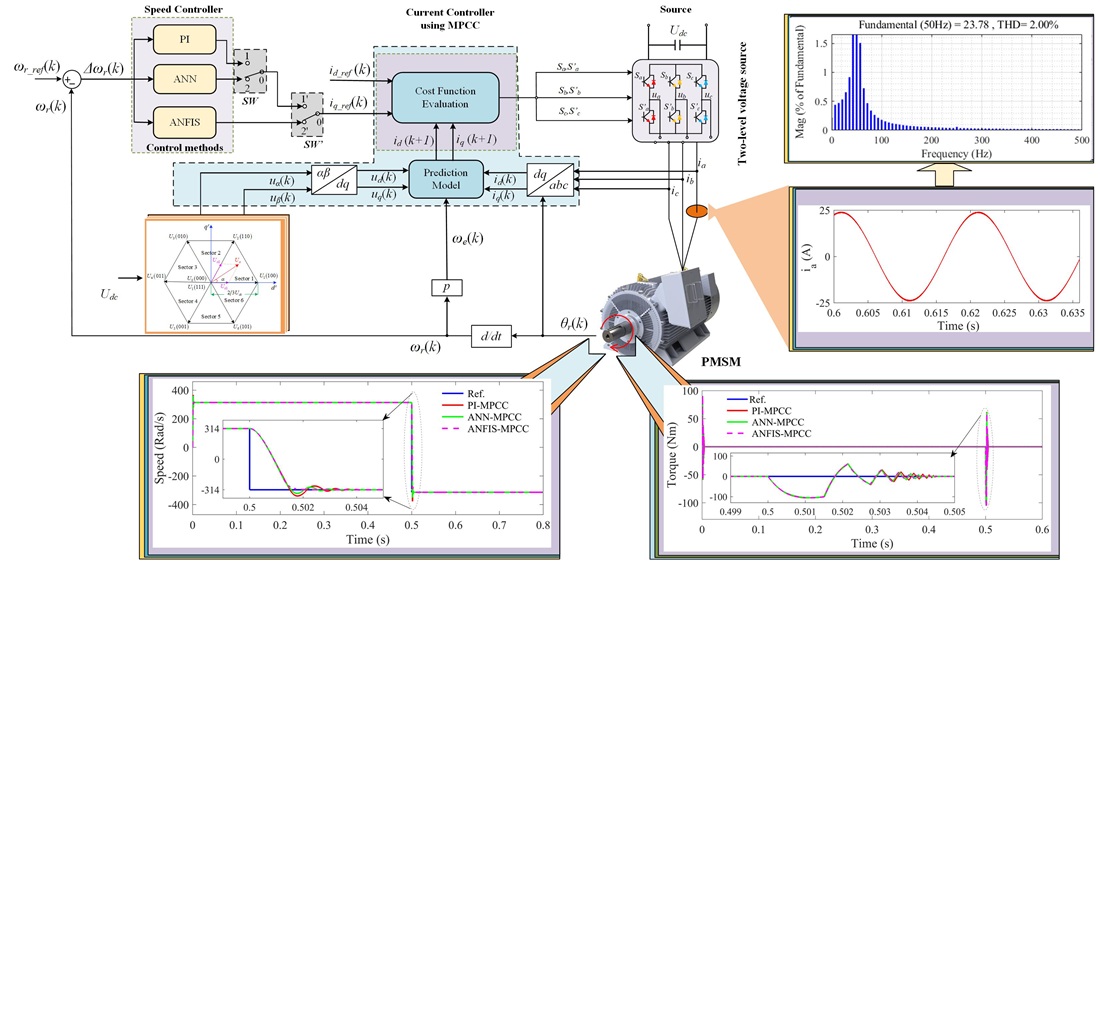
This study focuses on optimizing the control of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) by introducing a new model predictive current control (MPCC) strategy, integrated with the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), referred to as ANFIS-MPCC. The main problem addressed in this research is the challenge of improving the dynamic response of PMSMs under varying operating conditions, particularly under rapid load and speed variations. Traditional control methods like proportional-integral MPCC (PI-MPCC) and artificial neural network MPCC (ANN-MPCC) are compared with the proposed ANFIS-MPCC method to evaluate its effectiveness in solving issues such as overshoot reduction, settling time minimization, and harmonic distortion (THD) suppression. The results show that ANFIS-MPCC significantly outperforms the traditional methods, with overshoot reduced to 0.015%, a settling time of 0.00147 seconds, and THD minimized to 2.0% at rated speed and 2.02% at low speed. These improvements demonstrate that ANFIS-MPCC is highly effective in controlling PMSMs, particularly in systems exposed to rapid load changes and dynamic speed variations. The method's key advantage lies in its integration of fuzzy logic and neural networks, allowing superior handling of nonlinearities and dynamic load conditions. The results suggest that ANFIS-MPCC is especially beneficial for industrial motor control systems and electric vehicles, where fast response, stability, and low harmonic distortion are crucial
References
- Fu, R., Cao, Y. (2021). Hybrid flux predictor‐based predictive flux control of permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IET Electric Power Applications, 16 (4), 472–482. https://doi.org/10.1049/elp2.12168
- Hu, J., Fu, Z., Xu, R., Jin, T., Feng, Z., Wang, S. (2024). Low-Complexity Model Predictive Control for Series-Winding PMSM with Extended Voltage Vectors. Electronics, 14 (1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010127
- Pang, S., Zhang, Y., Huangfu, Y., Li, X., Tan, B., Li, P. et al. (2024). A Virtual MPC-Based Artificial Neural Network Controller for PMSM Drives in Aircraft Electric Propulsion System. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 60 (2), 3603–3612. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2023.3338605
- Wen, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. (2023). Three‐vector model‐free predictive control for permanent magnet synchronous motor. IET Power Electronics, 16 (16), 2754–2768. https://doi.org/10.1049/pel2.12599
- Wang, H., Wu, X., Zheng, X., Yuan, X. (2023). Model Predictive Current Control of Nine-Phase Open-End Winding PMSMs With an Online Virtual Vector Synthesis Strategy. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 70 (3), 2199–2208. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2022.3174241
- Sangar, B., Singh, M., Sreejeth, M. (2024). An improved ANFIS model predictive current control approach for minimizing torque and current ripples in PMSM-driven electric vehicle. Electrical Engineering, 106 (5), 5897–5907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-024-02346-3
- Alitasb, G. K. (2024). Integer PI, fractional PI and fractional PI data trained ANFIS speed controllers for indirect field oriented control of induction motor. Heliyon, 10 (18), e37822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37822
- Rodriguez, C. A., Ponce, P., Molina, A. (2016). ANFIS and MPC controllers for a reconfigurable lower limb exoskeleton. Soft Computing, 21 (3), 571–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2321-9
- Bouguenna, I. F., Tahour, A., Kennel, R., Abdelrahem, M. (2021). Multiple-Vector Model Predictive Control with Fuzzy Logic for PMSM Electric Drive Systems. Energies, 14 (6), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14061727
- Dianov, A., Tinazzi, F., Calligaro, S., Bolognani, S. (2022). Review and Classification of MTPA Control Algorithms for Synchronous Motors. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 37 (4), 3990–4007. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpel.2021.3123062
- Gade, C. R., W, R. S. (2022). Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using MPC–MTPA Control for Deployment in Electric Tractor. Sustainability, 14 (19), 12428. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912428
- Yu, H., Wang, J., Xin, Z. (2022). Model Predictive Control for PMSM Based on Discrete Space Vector Modulation with RLS Parameter Identification. Energies, 15 (11), 4041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15114041
- Dai, L., Tung, D. (2017). Modeling for Development of Simulation Tool: A Case Study of Grid Connected Doubly Fed Induction Generator Based on Wind Energy Conversion System. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 12 (11), 2981–2996.
- Utomo, W. M., Muhammad Zin, N., Haron, Z. A., Sim, S. Y., Bohari, A. A. et al. (2014). Speed Tracking of Field Oriented Control Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Neural Network. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS), 4 (3). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v4i3.5941
- Jang, J.-S. R. (1993). ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 23 (3), 665–685. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Doan Van Hoa, Huynh Hoang Bao Nghia, Le Van Dai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









