Parameter evaluation of complex maneuvering targets using Kalman fitering and multi-model adaptation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.335274Keywords:
guidance law, missile, homing, maneuvers, estimateAbstract
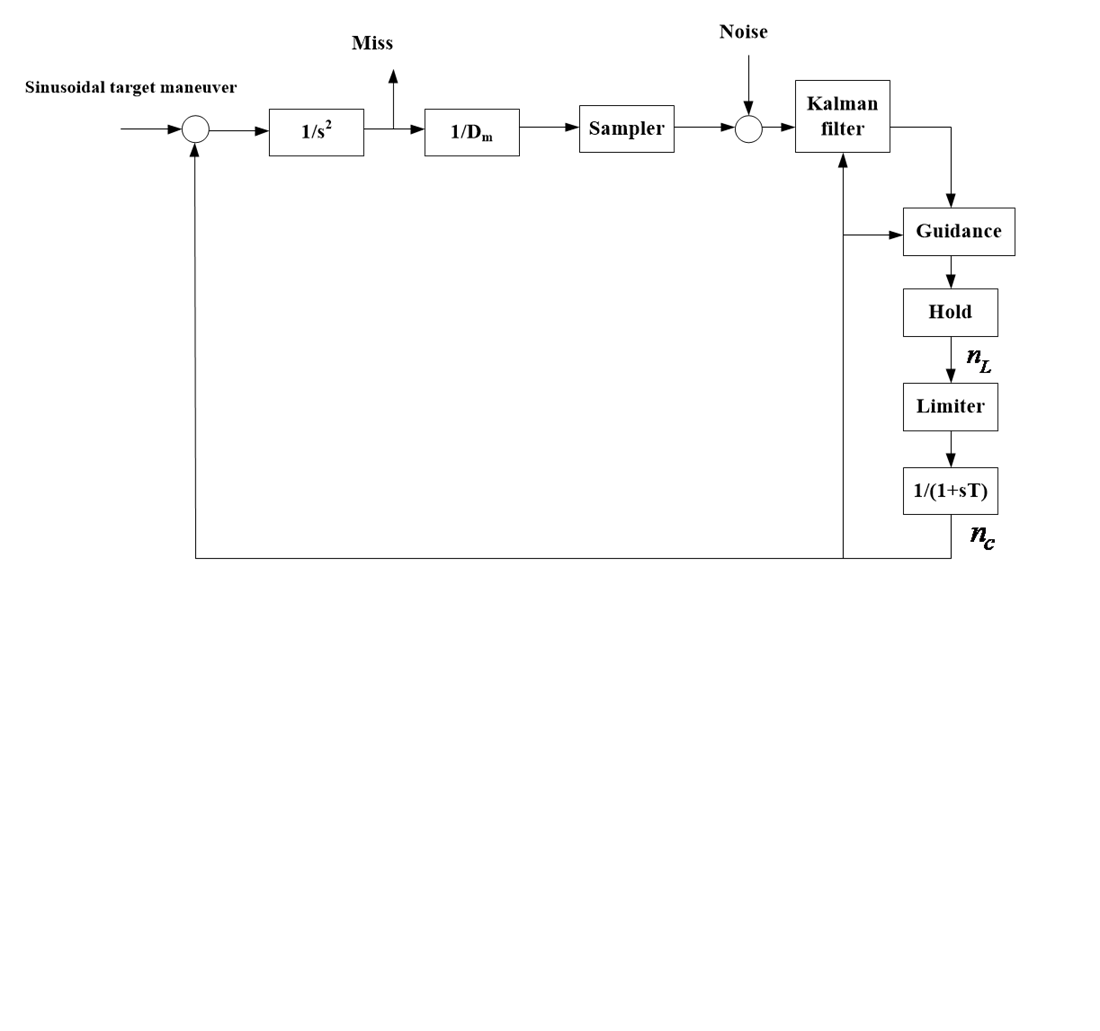
The object of research is the system determines the target angular coordinates on the missile’s homing head. Current target coordinate determination systems employed in seekers often operate under significant limitations. When a target’s actual motion deviates from the simplified, hypothetical model used to synthesize the coordinate system, a critical issue arises: the errors in evaluating both the coordinates and their derivative components rapidly and significantly increase.
Problem that was solved is to evaluate complex maneuvering target parameters. But there is no need to know the target’s maneuver frequency.
This study presents a novel filtering algorithm that accurately estimates all parameters of complex maneuvering targets without prior knowledge of their maneuver frequency. The algorithm achieves a significant advantage, reducing estimation error by over 95% within the first 5 seconds. With its simple structure, high stability, and fast convergence, this robust solution is essential for modern guidance systems, greatly enhancing the effectiveness of tracking unpredictable threats.
A key strength of the proposed algorithm lies in its simple structure. Furthermore, it demonstrates high convergence rates and exceptional stability, crucial attributes for real-time applications. Its design also ensures ease of practical implementation, making it a viable solution for contemporary guidance systems.
The algorithm is built on modern control techniques, combining extended Kalman filtering with interactive multi-models. It is necessary to accurately evaluate the target’s position, velocity, acceleration, and acceleration derivative without needing to know in advance the target’s maneuver frequency
References
- Tuan, N. N., Thi, N. D., Van Bang, N., Van Tuyen, T. (2021). Synthesis of Remote Control Law When Taking into Dynamics and Nonlinear of the Missile Stage. Intelligent Systems and Networks, 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2094-2_22
- Nguen, V. B., Dang, K. Vy., Trin', K. F., Nguen, N. T. (2021). Synthesis of the maneuver target acceleration determines algorithm. Estestvennye i Tekhnicheskie Nauki, 3 (154). https://doi.org/10.25633/etn.2021.02.07
- Hsueh, M.-H., Huang, C.-I., Fu, L.-C. (2007). A Differential Game Based Guidance Law for the Interceptor Missiles. IECON 2007 - 33rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 665–670. https://doi.org/10.1109/iecon.2007.4460196
- Li, X.-R., Jilkov, V. P. (2004). A survey of maneuvering target tracking: approximation techniques for nonlinear filtering. SPIE Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.553357
- Jiyuan, L., Jun, Z., Yingying, L. (2018). Applying auto-adaptation filter to tracking of maneuvering target in special relative navigation. J. Northwest, Polytech. Univ., 4, 013.
- Liu, L., Wang, X., Yang, X., Liu, H., Li, J., Wang, P. (2023). Path planning techniques for mobile robots: Review and prospect. Expert Systems with Applications, 227, 120254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120254
- Kabir, H., Tham, M.-L., Chang, Y. C. (2023). Internet of robotic things for mobile robots: Concepts, technologies, challenges, applications, and future directions. Digital Communications and Networks, 9 (6), 1265–1290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2023.05.006
- Martin, J. G., Muros, F. J., Maestre, J. M., Camacho, E. F. (2023). Multi-robot task allocation clustering based on game theory. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 161, 104314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2022.104314
- Kanoon, Z. E., Al-Araji, A. S., Abdullah, M. N. (2022). Enhancement of Cell Decomposition Path-Planning Algorithm for Autonomous Mobile Robot Based on an Intelligent Hybrid Optimization Method. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 15 (3), 161–175. Available at: https://inass.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/2022063014-2.pdf
- Zhang, H., Peng, Q. (2022). PSO and K-means-based semantic segmentation toward agricultural products. Future Generation Computer Systems, 126, 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.06.059
- Salama, O. A. A., Eltaib, M. E. H., Mohamed, H. A., Salah, O. (2021). RCD: Radial Cell Decomposition Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning. IEEE Access, 9, 149982–149992. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3125105
- Trung, D., Tuan, N., Bang, N., Tuyen, T. (2021). Synthesis of Line of Sight Angle Coordinate Filter on the Basis of Interactive Multi-Model Evaluation Algorithm. Informatics and Automation, 20 (6), 1333–1367. https://doi.org/10.15622/ia.20.6.6
- Rafai, A. N. A., Adzhar, N., Jaini, N. I. (2022). A Review on Path Planning and Obstacle Avoidance Algorithms for Autonomous Mobile Robots. Journal of Robotics, 2022, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2538220
- Abdulsaheb, J. A., Kadhim, D. J. (2023). Classical and Heuristic Approaches for Mobile Robot Path Planning: A Survey. Robotics, 12 (4), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12040093
- Zhu, K., Zhang, T. (2021). Deep reinforcement learning based mobile robot navigation: A review. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 26 (5), 674–691. https://doi.org/10.26599/tst.2021.9010012
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nguyen Thi Dieu Linh, Dao Xuan Hien, Nguyen Van Bang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








