Підвищення швидкості біноміального стиснення на основі двійкових біноміальних чисел
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.335729Ключові слова:
адаптивне стиснення, біноміальні числа, вибір кодування, біноміально-векторний метод, час стисненняАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження є адаптивне стиснення двійкових послідовностей загального виду на основі двійкових біноміальних чисел.
Проблема, що вирішується, – забезпечення високої швидкості стиснення двійкової інформації на основі біноміальних чисел за умови невизначеності характеристик двійкових послідовностей, що стискаються.
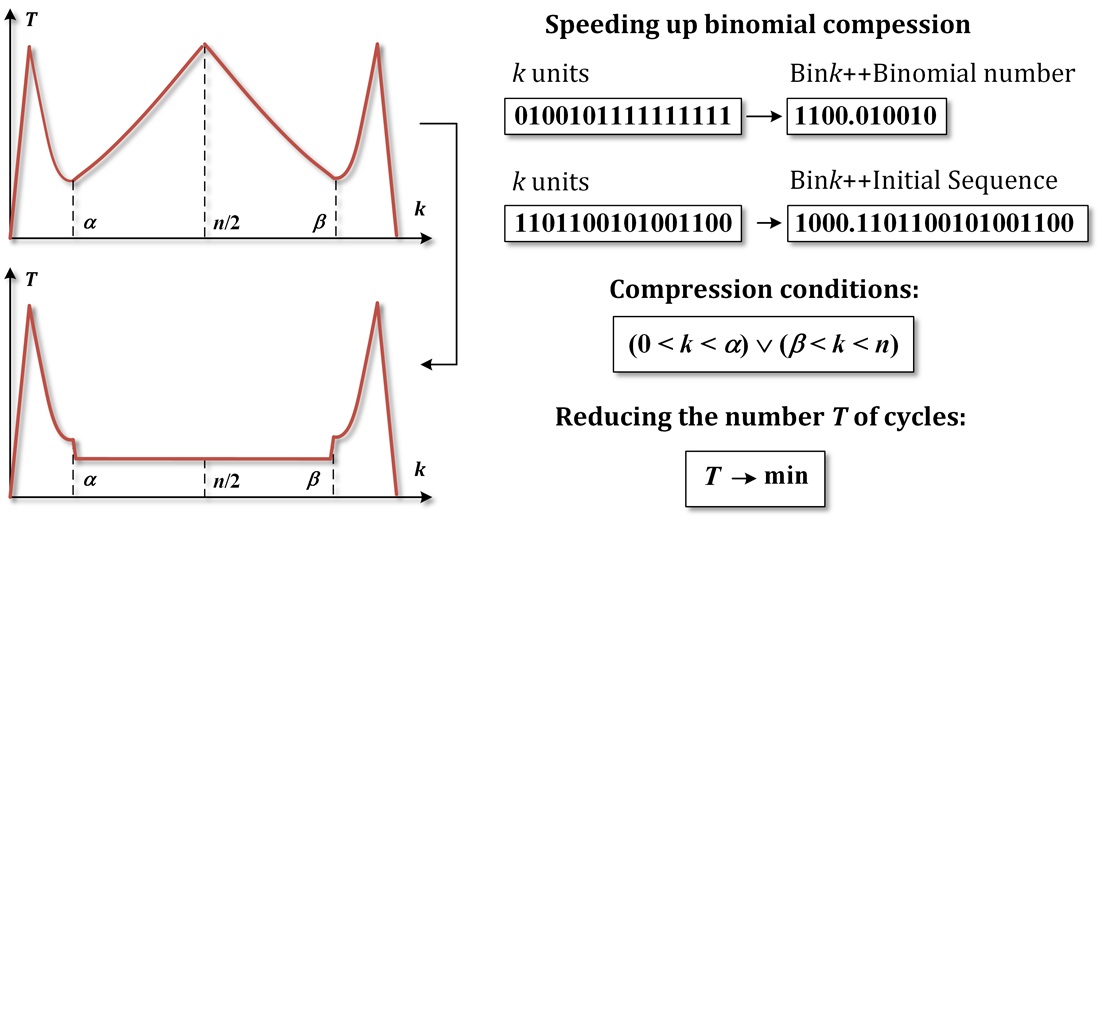
Одним з факторів, що знижують ефективність біноміального стиснення, є неконтрольовані переходи кількостей одиниць комбінацій до області неефективного використання, найгірших коефіцієнтів стиснення.
У зв'язку з цим в роботі застосований адаптивний підхід до біноміального стиснення, заснований на виборі способу кодування залежно від числа одиниць оброблюваної послідовності.
Даний підхід забезпечує наступний результат: у кілька разів скорочення обсягу часових витрат при обробці двійкових комбінацій, що не стискаються. Як наслідок, це призводить до збільшення середньої швидкості біноміального стиснення при невеликому, до трьох-п'яти відсотків, зниженні ступеня стиснення.
До моделі процесу адаптивного стиснення включені етапи порівняння обчислених кількостей двійкових одиниць з умовами стиснення та вибору техніки кодування на основі двійкових біноміальних чисел. Якщо поточне значення числа одиниць виходить за межи умов стиснення, то обчислення кількості одиниць припиняється, а оброблювана послідовність залишається без змін. Тим самим усуваються невиправдані витрати часу, коли коефіцієнт стиснення стає менше за одиницю.
На практиці адаптивний підхід до стиснення на основі двійкових біноміальних чисел є ефективним у випадку, коли двійкові послідовності, що стискаються, мають невизначені характеристики, а їх попереднє оцінювання є неможливим або ускладненим.
Посилання
- Jerzy, S. A. (2013). Information Systems and Data Compression. Springer, 494. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-585-27999-2_6
- Routray, S. K., Javali, A., Sharmila, K. P., Semunigus, W., Pappa, M., Ghosh, A. D. (2020). Lossless Compression Techniques for Low Bandwidth Networks. 2020 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Sustainable Systems (ICISS), 823–828. https://doi.org/10.1109/iciss49785.2020.9315936
- Salomon, D. (2010). Handbook of Data Compression. Springer, 1383. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84882-903-9
- Li, Z.-N., Drew, M. S., Liu, J. (2021). Fundamentals of Multimedia. Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 824. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62124-7
- Duda, J., Tahboub, K., Gadgil, N. J., Delp, E. J. (2015). The use of asymmetric numeral systems as an accurate replacement for Huffman coding. 2015 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1109/pcs.2015.7170048
- Mrudula, S. T., Srinivasa Murthy, K. E., Prasad, M. N. G. (2022). Optimized Context-Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coder in Video Compression Standard Without Probability Estimation. Mathematical Modelling of Engineering Problems, 9 (2), 458–462. https://doi.org/10.18280/mmep.090222
- Stakhov, A. (2016). Fibonacci p-codes and Codes of the “Golden” p-proportions: New Informational and Arithmetical Foundations of Computer Science and Digital Metrology for Mission-Critical Applications. British Journal of Mathematics & Computer Science, 17 (1), 1–49. https://doi.org/10.9734/bjmcs/2016/25969
- Borysenko, O. A., Horiachev, O. Ye., Serdiuk, V. V., Yermakov, M. S. (2018). Information protection problems of factorial numbers. Ukrainian Scientific Journal of Information Security, 24 (3), 169–174. https://doi.org/10.18372/2225-5036.24.13069
- Borysenko, O., Matsenko, S., Bobrovs, V. (2021). Binomial Number System. Applied Sciences, 11 (23), 11110. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311110
- Luzhetskyi, V. A., Savytska, L. A. (2015). Development and research of adaptive data compression methods based on linear fibonacci form. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (73)), 16–22. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2015.37026
- Borysenko, A. A. (2004). Bynomyalnii schet. Teoryia y praktyka. Sumi: YTD «Unyversytetskaia knyha», 170. Available at: https://essuir.sumdu.edu.ua/handle/123456789/55161
- Borisenko, A. A., Kulik, I. A. (2010). Binomialnoe kodirovanie. Sumy: Izd-vo SumGU, 206.
- Schalkwijk, J. (1972). An algorithm for source coding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 18 (3), 395–399. https://doi.org/10.1109/tit.1972.1054832
- Cover, T. (1973). Enumerative source encoding. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 19 (1), 73–77. https://doi.org/10.1109/tit.1973.1054929
- Butler, J. T., Sasao, T. (2011). Fast constant weight codeword to index converter. 2011 IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/mwscas.2011.6026312
- Borysenko, O., Matsenko, S., Salgals, T., Spolitis, S., Bobrovs, V. (2022). The Lossless Adaptive Binomial Data Compression Method. Applied Sciences, 12 (19), 9676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199676
- Kulyk, I., Berezhna, O., Shevchenko, M. (2018). Development of data compressing coding methods on basis of binary binomial numbers. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 2 (2 (46)), 12–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2019.169897
- Kulyk, Y. A., Novhorodtsev, A. Y., Shevchenko, M. S. (2019). Method for borders estimation of compression on basis of binary binomial numbers. Systemy obrobky informatsii, 2 (157), 57–62. https://doi.org/10.30748/soi.2019.157.07
- Reingold, M. E., Nievegelt, J., Deo, N. (1977). Combinatorial Algorithms: Theory and Practice. Pearson College Div, 930.
- Kulyk, Y. A. (2004). O srednei dlyne dvoychnikh bynomyalnikh chysel. Visnyk Sumskoho derzhavnoho universytetu. Seriia «Tekhnichni nauky», 12 (71), 106–112.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Igor Kulyk, Maryna Shevchenko, Vitalii Grynenko, Maksim Hermes

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









