Automated real-time electrocardiogram diagnosis based on the modified Pan-Tompkins algorithm for long-term monitoring systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.336172Keywords:
electrocardiogram, Holter monitoring, automated analysis, Pan-Tompkins algorithm, ESP32, QRS complexAbstract
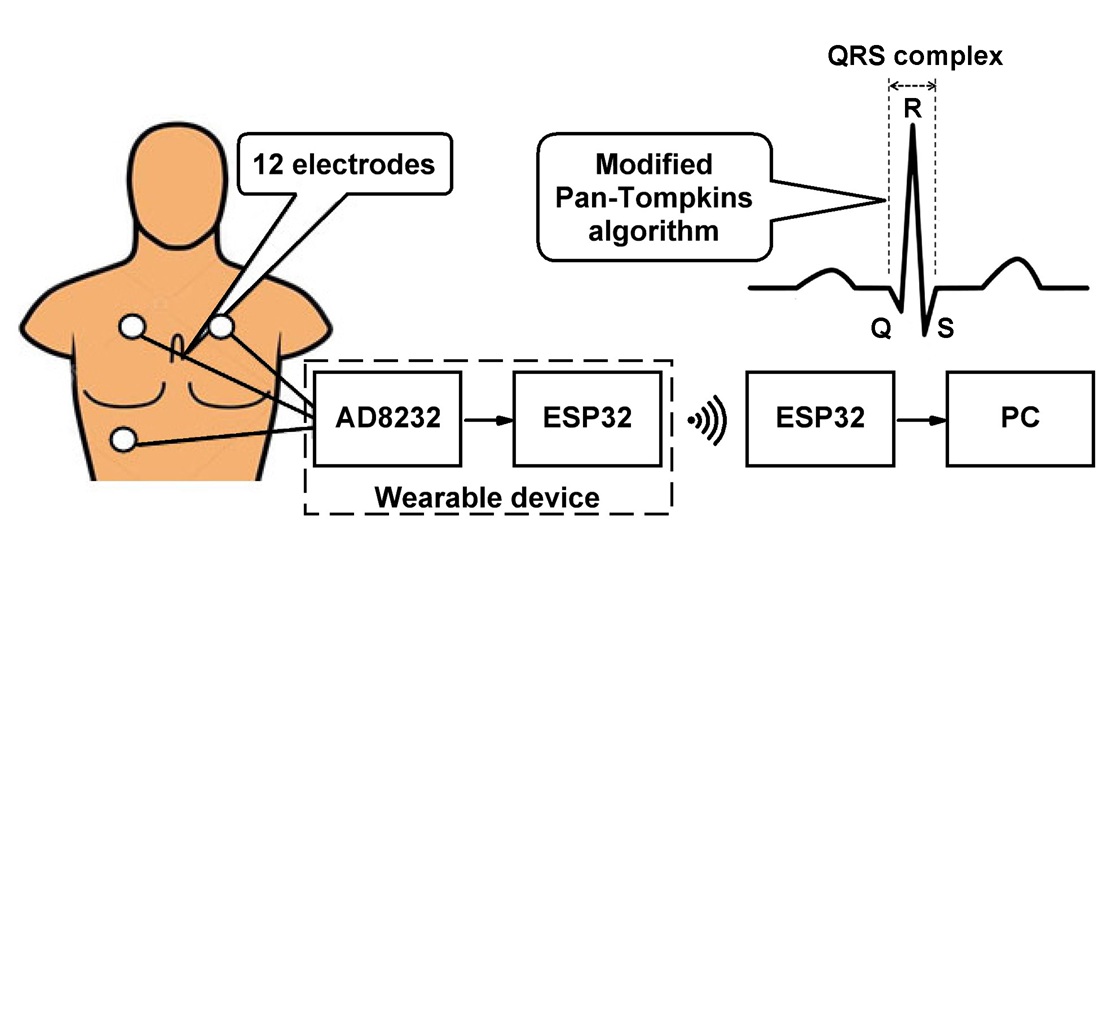
The object of this study is the process of automated analysis of the electrocardiographic signal (ECS) during long-term monitoring in real time, carried out by mobile wireless systems.
The study considers the problem related to the insufficient accuracy of automated diagnostics during long-term monitoring of the electrocardiogram (ECG) under conditions of limited computing resources and the presence of noise.
A modified Pan-Tompkins algorithm for determining the boundaries of the QRS system has been developed. Based on this algorithm, the PCard software module for the hardware and software system was implemented, enabling high-quality automated diagnostics both under the standard mode and during long-term ECG monitoring in 12 leads in real time. The PCard software module allows for ECG registration, digital filtering, measurement and calculation of electrocardiographic parameters, automatic determination of diagnostic criteria and diagnostic conclusions, formation of a general diagnostic conclusion of ECG, as well as medical processing of ECG.
The high quality of the diagnostic analysis was confirmed by the obtained accuracy rates of the algorithm for determining normal complexes – 99.99%, for determining ventricular complexes – 99.90%, for determining various pathologies – 98.43%. The ECG processing time was about 4.7 seconds for a 40-minute record. The proposed method for determining the boundaries of QRS complexes is based on the finite difference method, which distinguishes it from common methodologies using spectral analysis, wavelet transforms, or Fourier transforms. This methodology simplifies determining the parameters of the basic ECG elements and significantly reduces the amount of calculations, which generally increases the processing time and reduces the required volume of system resources
References
- Global Effect of Modifiable Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality (2023). New England Journal of Medicine, 389 (14), 1273–1285. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2206916
- Setiawidayat, S. (2023). Discrete electrocardiogram T amplitude detection based on cycle duration. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (9 (123)), 94–105. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.282759
- Liu, F., Liu, C., Jiang, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Wei, S. (2018). Performance Analysis of Ten Common QRS Detectors on Different ECG Application Cases. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2018, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9050812
- Attia, Z. I., Noseworthy, P. A., Lopez-Jimenez, F., Asirvatham, S. J., Deshmukh, A. J., Gersh, B. J. et al. (2019). An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: a retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. The Lancet, 394 (10201), 861–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31721-0
- Havranek, S., Stekla, B., Vesela, M., Holub, J., Miksova, L., Kvasnickova, K. et al. (2025). Artificial intelligence in resting ecg: higher accuracy in the interpretation of rhythm abnormalities. Europace, 27. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euaf085.029
- So-In, C., Phaudphut, C., Rujirakul, K. (2015). Real-Time ECG Noise Reduction with QRS Complex Detection for Mobile Health Services. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 40 (9), 2503–2514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1658-1
- Xiang, Y., Lin, Z., Meng, J. (2018). Automatic QRS complex detection using two-level convolutional neural network. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 17 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-018-0441-4
- He, R., Liu, Y., Wang, K., Zhao, N., Yuan, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, H. (2021). Automatic Detection of QRS Complexes Using Dual Channels Based on U-Net and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 25 (4), 1052–1061. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2020.3018563
- QRS Detection Based on Discrete Wavelet Transform for ECG Signal with Motion Artifacts (2024). Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 40 (1), 118–128. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.40.1.118128
- Khan, N., Imtiaz, M. N. (2023). Pan-Tompkins++: A Robust Approach to Detect R-peaks in ECG Signals. https://doi.org/10.32920/22734308
- Abd Al-Jabbar, E. Y., Al-Hatab, M. M. M., Qasim, M. A., Fathel, W. R., Fadhil, M. A. (2023). Clinical Fusion for Real-Time Complex QRS Pattern Detection in Wearable ECG Using the Pan-Tompkins Algorithm. Fusion: Practice and Applications, 12 (2), 172–184. https://doi.org/10.54216/fpa.120214
- Fariha, M. A. Z., Ikeura, R., Hayakawa, S., Tsutsumi, S. (2020). Analysis of Pan-Tompkins Algorithm Performance with Noisy ECG Signals. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1532 (1), 012022. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1532/1/012022
- Félix, R. A., Ochoa-Brust, A., Mata-López, W., Martínez-Peláez, R., Mena, L. J., Valdez-Velázquez, L. L. (2023). Fast Parabolic Fitting: An R-Peak Detection Algorithm for Wearable ECG Devices. Sensors, 23 (21), 8796. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23218796
- Belkadi, M., Daamouche, A. (2020). Swarm Intelligence Approach to QRS Detection. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, 17 (4), 480–487. https://doi.org/10.34028/iajit/17/4/6
- Zhao, K., Li, Y., Wang, G., Pu, Y., Lian, Y. (2021). A robust QRS detection and accurate R-peak identification algorithm for wearable ECG sensors. Science China Information Sciences, 64 (8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3150-2
- Ribeiro, L., Rosa, M. M. A., Soares, R., Costa, E. (2024). Exploring Approximate Adders for an Energy-Efficient Pre-Processing Pan-Tompkins Algorithm VLSI Design. 2024 37th SBC/SBMicro/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Circuits and Systems Design (SBCCI), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/sbcci62366.2024.10703995
- Waleed, R. (2024). Real-time processing stages of electrocardiogram signal: a review. Journal of Modern Technology and Engineering, 9 (1), 39–54. https://doi.org/10.62476/jmte9139
- Gerasimova, Y., Ivel, V., Moldakhmetov, S., Petrov, P. (2024). Hardware-software implementation of a local Wi-Fi network for the transmission of biomedical signals. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (9 (130)), 34–43. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.309387
- Ivel, V. P., Gerasimova, Y. V., Moldakhmetov, S. S., Petrov, P. A., Gerasimov, I. A., Zainchkovskaya, K. V. (2019). Wireless three-channel Holter monitoring system. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 537 (3), 032090. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/537/3/032090
- Database ROHMINE. ROHMINE. Available at: http://rohmine.org/baza-dannykh-rokhmine/
- LeVeque, R. J. (2007). Finite difference methods for ordinary and partial differential equations: steady-state and time-dependent problems. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM).
- Manikandan, M. S., Soman, K. P. (2012). A novel method for detecting R-peaks in electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 7 (2), 118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2011.03.004
- Hossain, M. B., Bashar, S. K., Walkey, A. J., McManus, D. D., Chon, K. H. (2019). An Accurate QRS Complex and P Wave Detection in ECG Signals Using Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise Approach. IEEE Access, 7, 128869–128880. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2939943
- Arzeno, N. M., Deng, Z.-D., Poon, C.-S. (2008). Analysis of First-Derivative Based QRS Detection Algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 55 (2), 478–484. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2007.912658
- Benitez, D., Gaydecki, P. A., Zaidi, A., Fitzpatrick, A. P. (2001). The use of the Hilbert transform in ECG signal analysis. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 31 (5), 399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-4825(01)00009-9
- Li, Q., Liu, Y., Zhao, N., Yuan, Y., He, R. (2023). A Novel ECG QRS Complex Detection Algorithm Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network. https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.22791089
- Lai, D., Zhang, F., Wang, C. (2015). A real-time QRS complex detection algorithm based on differential threshold method. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), 129–133. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdsp.2015.7251844
- Neri, L., Oberdier, M. T., Augello, A., Suzuki, M., Tumarkin, E., Jaipalli, S. et al. (2023). Algorithm for Mobile Platform-Based Real-Time QRS Detection. Sensors, 23 (3), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031625
- Gradl, S., Kugler, P., Lohmuller, C., Eskofier, B. (2012). Real-time ECG monitoring and arrhythmia detection using Android-based mobile devices. 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2452–2455. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2012.6346460
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yuliya Gerasimova, Fatimah Sidi, Victor Ivel, Vladimir Avdeyev, Lili Nurliyana Abdullah, Sayat Moldakhmetov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








