Розробка композиції та моделювання властивостей біополімерної системи для гелевих космецевтичних засобів з пролонгованою дією
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.341368Ключові слова:
біополімерна система, пролонгована доставка, кінетика вивільнення, структурно-механічні властивості, поліелектролітний комплексАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження є властивості біополімерної системи для пролонгованої доставки космецевтичних активних інгредієнтів на основі природних полісахаридів (гіалуронату натрію та хітозану)
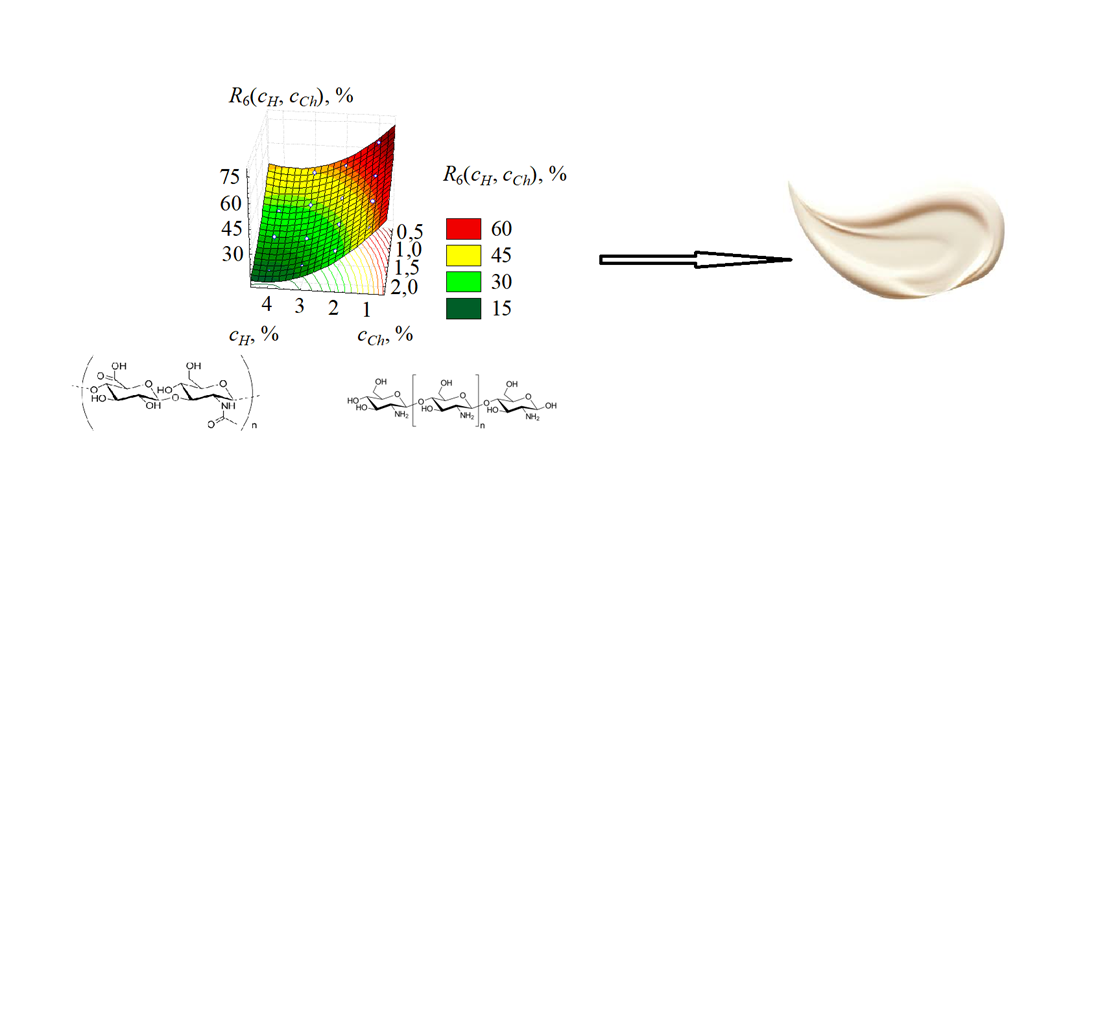
У роботі вирішується проблема відсутності методології для прогнозування властивостей біополімерної системи на етапі проектування. Ця методологія має зв'язувати її компонентний склад із функціональними та структурно-механічними характеристиками. Критерієм оптимізації має бути досягнення контрольованого профілю вивільнення гідрофільного активу (декспантенолу) без початкового «вибухового» ефекту. Встановлено, що оптимальним є співвідношення 2,5% гіалуронату натрію та 1,2% хітозану, що забезпечує вивільнення 30–35% декспантенолу за 6 год. та 60–65% – за 24 год. Структурно-механічний аналіз підтвердив формування стабільного гелю з в'язкістю 9800 ± 250 мПа·с і модулем зберігання 325 Па. Це пояснюється утворенням щільної поліелектролітної мережі за рахунок електростатичних взаємодій між аніонними групами гіалуронату натрію.
Результати дослідження біополімерної системи включають розробку апроксимаційних моделей. Ці моделі прогнозують профіль вивільнення декспантенолу на основі концентрації полімерів і оцінюють структурно-механічні властивості біополімерної системи. Отримані результати можуть бути використані у космецевтичній промисловості для створення гелевих засобів із пролонгованою дією. Ефективність системи підтверджена in vitro у фосфатному буферному розчині (pH 7,4; 37°C). Критерієм ефективності виступило досягнення контрольованого профілю вивільнення: 30–35% активної речовини за 6 годин та 60-65% за 24 години, що забезпечує тривалу дію без початкового «вибухового» ефекту.
Посилання
- Putyatin, B., Bliznjuk, O., Masalitina, N., Bezpal’ko, V., Zhukova, L., Filenko, O. et al. (2024). Identifying the influence of the concentration of surfactants on the technological indicators of aerosol emulsion. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (6 (132)), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.317819
- Felix-Sagaste, K. G., Garcia-Carrasco, M., Picos-Corrales, L. A., Gonzalez-Ruelas, T., Rodriguez-Mercado, J. A. (2023). Plant-animal extracts and biocompatible polymers forming oil-in-water emulsions: Formulations for food and pharmaceutical industries. Hybrid Advances, 3, 100072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hybadv.2023.100072
- Kunitsia, E., Popov, M., Gontar, T., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Stepankova, G. et al. (2024). Determination of the influence of hemp oil-based emulsion systems composition on the oxidation products content during storage. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (6 (129)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.304466
- Varanasi, S., Henzel, L., Mendoza, L., Prathapan, R., Batchelor, W., Tabor, R., Garnier, G. (2018). Pickering Emulsions Electrostatically Stabilized by Cellulose Nanocrystals. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00409
- Oleksy, M., Dynarowicz, K., Aebisher, D. (2023). Advances in Biodegradable Polymers and Biomaterials for Medical Applications – A Review. Molecules, 28 (17), 6213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176213
- Bhattacharjee, A., Chakraborty, A., Mukhopadhyay, G. (2018). Double emulsions – A review with emphasis on updated stability enhancement perspective. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7 (6), 475–493.
- Tang, J., He, H., Wan, R., Yang, Q., Luo, H., Li, L., Xiong, L. (2021). Cellulose Nanocrystals for Skin Barrier Protection by Preparing a Versatile Foundation Liquid. ACS Omega, 6 (4), 2906–2915. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05257
- Thy, L. T. M., Duy, H. K., Dat, N. M. (2025). Applications of lecithin in emulsion stabilization and advanced delivery systems in cosmetics: A mini-review. Results in Surfaces and Interfaces, 19, 100543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsurfi.2025.100543
- Leonida, M. D., Kumar, I., Song, J., Ocampo, A., Philip, S., Brazuna, R. P., Belbekhouche, S. (2025). Green ethanol-free antisolvent synthesis of zein–chitosan–gum arabic nanocomposites for controlled release of lupulone in topical antioxidant applications. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 726, 137817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2025.137817
- Aydin, T., Gok, B., Budama-Kilinc, Y., Kartal, M. (2025). Obtaining carvacrol from Origanum onites L. essential oil and developing carvacrol-loaded nanoformulation for use in cosmetics. Industrial Crops and Products, 226, 120652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2025.120652
- Millao, S., Iturra, N., Contardo, I., Morales, E., Quilaqueo, M., Rubilar, M. (2023). Structuring of oils with high PUFA content: Evaluation of the formulation conditions on the oxidative stability and structural properties of ethylcellulose oleogels. Food Chemistry, 405, 134772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134772
- Pawar, V. U., Dessai, A. D., & Nayak, U. Y. (2024). Oleogels: Versatile Novel Semi-Solid System for Pharmaceuticals. AAPS PharmSciTech, 25 (6). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-024-02854-2
- Liu, C., Zheng, Z., Liu, Y. (2022). Effects of natural waxes on the interfacial behavior, structural properties and foam stabilization of aerated emulsions. Food & Function, 13 (17), 8860–8870. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2fo01670b
- Tamarkin, D., Gazal, E., Papiashvili, I., Hazot, Y., Schuz, D., Keynan, R. (2015). Surfactant-free water-free foamable compositions, breakable foams and gels and their uses (U.S. Patent No. US10238746B2). U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
- Faria-Silva, C., Scavone, D., Marto, J., Carvalheiro, M., Simões, S. (2025). Topical foams containing natural saponins: a world of opportunities in pharmaceutical and cosmetic sciences. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 109, 106988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2025.106988
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Bogdan Putyatin, Olga Bliznjuk, Volodymyr Panasenko, Anna Belinska, Yana Svishchova, Olena Zolotukhina, Natalia Ashtaeva, Nataliia Masalitina, Inna Zabrodina, Tetiana Kovalova

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









