Удосконалення методу визначення координат розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату малобазовою мережею двох Software-Defined Radio приймачів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.341735Ключові слова:
безпілотний літальний апарат, малобазова мережа, Software-Defined Radio приймач, пеленгАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження є процес визначення координат розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату. Проблема, що вирішувалась, полягала у визначенні координат розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату малобазовою мережею мобільних пристроїв пасивної локації.
Удосконалено метод визначення координат розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату, який, на відміну від відомих, передбачає:
– визначення пеленгів на розвідувальний безпілотний літальний апарат;
– використання тріангуляційного методу.
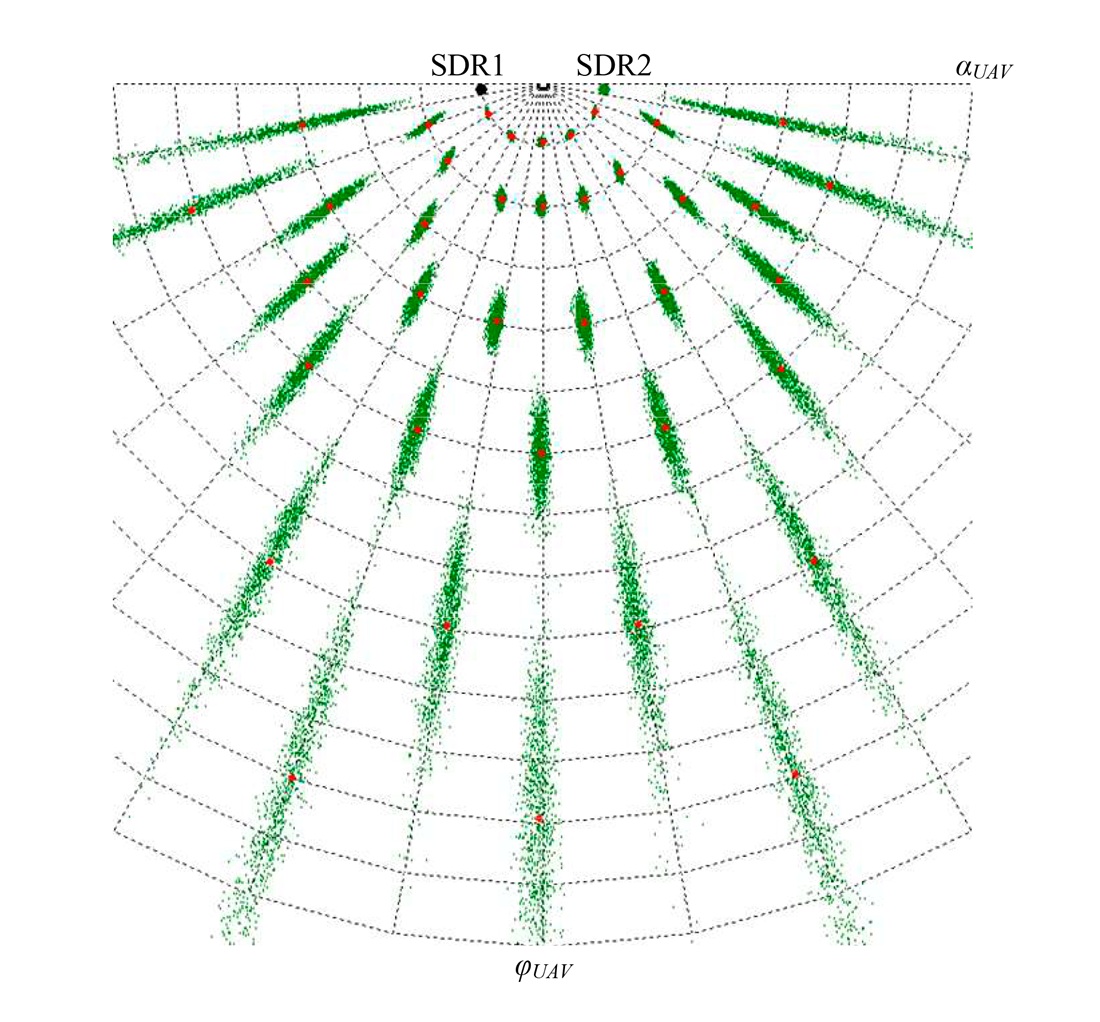
Проведено оцінювання точності визначення координат розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату малобазовою мережею двох Software-Defined Radio приймачів. Встановлено, що форма та орієнтація еліпсів похибок залежить від положення розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату відносно Software-Defined Radio приймачів. Точність визначення координат суттєво погіршується у випадках, коли полярний кут спостереження з центру бази наближається до 0° або 180°. Найвища точність визначення координат досягається тоді, коли розвідувальний безпілотний літальний апарат знаходиться на траверзі до середини бази.
Встановлено, що для малих баз спостерігається більш виражена нерівномірність залежності точності від положення розвідувального безпілотного літального апарату у порівнянні з більшими базами. На великих дальностях похибки при малих базах різко зростають. Встановлено, що зі зменшенням довжини бази площа еліпсів похибок зростає, що свідчить про погіршення потенційних характеристик точності системи та збільшення середньої кругової похибки. При цьому геометричні особливості зберігаються, орієнтація еліпсів та характер їхнього розташування відносно лінії бази залишаються сталими
Посилання
- Goldstein, L., Waechter, N. (2023). Chinese Strategists Evaluate the Use of 'Kamikaze' Drones in the Russia-Ukraine War. Rand. Available at: https://www.rand.org/pubs/commentary/2023/11/chinese-strategists-evaluate-the-use-ofkamikaze-drones.html
- Grigore, L., Cristescu, C. (2024). The Use of Drones in Tactical Military Operations in the Integrated and Cybernetic Battlefield. Land Forces Academy Review, 29 (2), 269–273. https://doi.org/10.2478/raft-2024-0029
- Riabukha, V. P. (2020). Radar Surveillance of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Review). Radioelectronics and Communications Systems, 63 (11), 561–573. https://doi.org/10.3103/s0735272720110011
- Hrudka, O. (2024). Russian drone manufacturer ‘Orlan-10’ ramps up production despite sanctions, Inform Napalm reports. Available at: https://euromaidanpress.com/2024/01/13/russian-drone-manufacturer-orlan-10-ramps-up-production-despite-sanctions-inform-napalm-reports/
- British intelligence: Russian radar destroyed in missile attack on Belbek in Crimea (2024). Available at: https://mind.ua/en/news/20269399-british-intelligence-russian-radar-destroyed-in-missile-attack-on-belbek-in-crimea
- Khudov, H., Makoveichuk, O., Kostyria, O., Butko, I., Poliakov, A., Kozhushko, Y. et al. (2024). Devising a method for determining the coordinates of an unmanned aerial vechicle via a network of portable spectrum analyzers. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (132)), 97–107. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.318551
- Khudov, H., Kostianets, O., Kovalenko, O., Maslenko, O., Solomonenko, Y. (2023). Using Software-Defined radio receivers for determining the coordinates of low-visible aerial objects. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (9 (124)), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286466
- Boussel, P. (2024). The Golden Age of Drones: Military UAV Strategic Issues and Tactical Developments. Available at: https://trendsresearch.org/insight/the-golden-age-of-drones-military-uav-strategic-issues-and-tactical-developments/?srsltid=AfmBOoptC41niCzbAJGHOTcUhRGJpWEW_y7hHLkJ_5hkabW_fIBS5sZ
- Melvin, W. L., Scheer, J. (2012). Principles of Modern Radar: Advanced techniques. The Institution of Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1049/sbra020e
- Melvin, W. L., Scheer, J. A. (2013). Principles of Modern Radar: Volume 3: Radar Applications. The Institution of Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1049/sbra503e
- Lishchenko, V., Kalimulin, T., Khizhnyak, I., Khudov, H. (2018). The Method of the organization Coordinated Work for Air Surveillance in MIMO Radar. 2018 International Conference on Information and Telecommunication Technologies and Radio Electronics (UkrMiCo), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ukrmico43733.2018.9047560
- Neyt, X., Raout, J., Kubica, M., Kubica, V., Roques, S., Acheroy, M., Verly, J. G. (2006). Feasibility of STAP for Passive GSM-Based Radar. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, 546–551. https://doi.org/10.1109/radar.2006.1631853
- Willis, N. J. (2004). Bistatic Radar. The Institution of Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1049/sbra003e
- Semenov, S., Jian, Y., Jiang, H., Chernykh, O., Binkovska, A. (2025). Mathematical model of intelligent UAV flight path planning. Advanced Information Systems, 9 (1), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2025.1.06
- Ruban, I., Khudov, H., Lishchenko, V., Pukhovyi, O., Popov, S., Kolos, R. et al. (2020). Assessing the detection zones of radar stations with the additional use of radiation from external sources. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (108)), 6–17. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.216118
- Multilateration (MLAT). Concept of Use. Available at: https://www2023.icao.int/APAC/Documents/edocs/mlat_concept.pdf
- Luo, D., Wen, G. (2024). Distributed Phased Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Radars for Early Warning: Observation Area Generation. Remote Sensing, 16 (16), 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163052
- Kalkan, Y. (2024). 20 Years of MIMO Radar. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 39 (3), 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1109/maes.2023.3349228
- Barabash, O., Kyrianov, A. (2023). Development of control laws of unmanned aerial vehicles for performing group flight at the straight-line horizontal flight stage. Advanced Information Systems, 7 (4), 13–20. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2023.4.02
- Khudov, H., Hryzo, A., Oleksenko, O., Repilo, I., Lisohorskyi, B., Poliakov, A. et al. (2025). Devising a method for determining the coordinates of an air object by a network of two SDR receivers. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (133)), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.323336
- Weber, C., Peter, M., Felhauer, T. (2015). Automatic modulation classification technique for radio monitoring. Electronics Letters, 51 (10), 794–796. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2015.0610
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Igor Ruban, Hennadii Khudov, Yelyzaveta Biernik, Oleksandr Makoveichuk, Volodymyr Maliuha, Serhii Yarovyi, Rostyslav Khudov, Vladyslav Khudov, Leonid Poberezhnyi, Olena Goncharenko

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









