Проектування та оптимізація системи бічного керування на основі нечіткої логіки типу 2 для підвищення траєкторної стабільності в автономних транспортних засобах
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326193Ключові слова:
автономний транспортний засіб, НЛК типу 2, ПІД-керування, кут повороту керма, функція належності, маневриАнотація
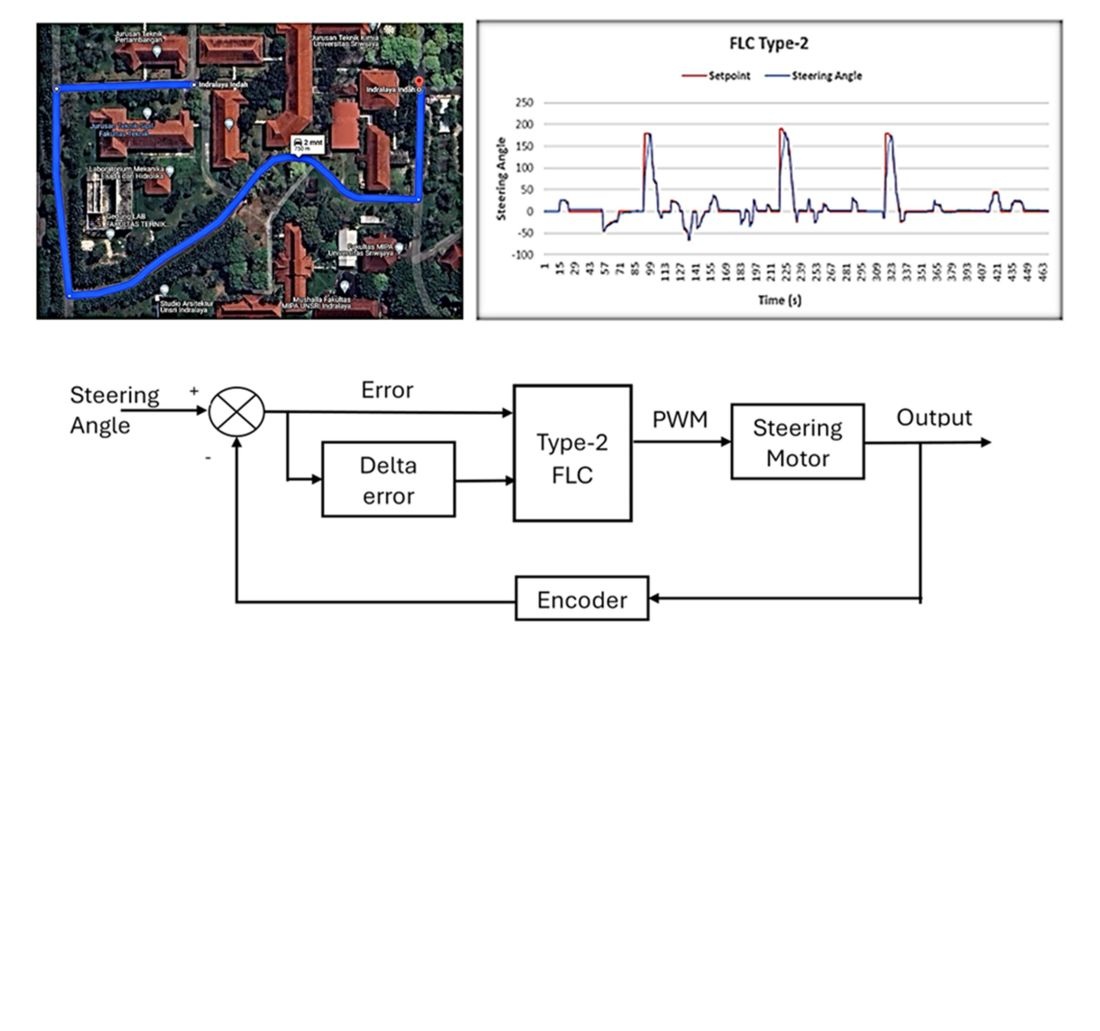
У цьому дослідженні основна увага приділяється системі бокового керування автономними транспортними засобами з використанням рульового керування. Головна мета полягає в тому, щоб забезпечити постійне утримання транспортного засобу на правильному шляху. Існуючі методи залишаються обмеженими, оскільки вони часто припускають ідеальні дорожні умови без перешкод або динамічних об’єктів. Щоб усунути це обмеження, в цьому дослідженні аналізується керування кутом повороту керма для автономних транспортних засобів у неструктурованих середовищах з потенційними перешкодами. У ньому зокрема аналізується застосування нечіткого логічного контролера типу 2 (НЛК типу 2) для керування кермом, використовуючи вхідні значення у вигляді похибки та дельта-помилки. Ці значення обчислюються з різниці між згенерованим виходом та кутом повороту керма, виміряним імпульсним енкодером, встановленим на кермі. НЛК типу 2 продемонстрував високу точність у тестах на уникнення перешкод: 1,54% (людина), 4,28% (один автомобіль), 1,2% (два об’єкти ліворуч) та 2,13% (два ліворуч, один праворуч). Натомість, ПІД-контролер показав вищі показники помилок: 2,19%, 3,49%, 1,12% та 3,49% відповідно. Повне тестування маршруту показало середню похибку прямого маршруту 8,87% для НЛК типу 2 та 12,35% для ПІД-контролера. На зворотному маршруті НЛК типу 2 зафіксував похибку 4,52%, тоді як ПІД-контролер показав 7,57%. Загалом, НЛК типу 2 досяг нижчого рівня похибок та кращої точності, ніж ПІД-контролер, особливо в динамічних умовах. Ці результати підкреслюють ефективність НЛК типу 2 у покращенні продуктивності автономного транспортного засобу та точності керування. Його низькі значення похибки вказують на чудові можливості відстеження шляху, що ефективно відповідає меті дослідження
Посилання
- Hussain, R., Zeadally, S. (2019). Autonomous Cars: Research Results, Issues, and Future Challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21 (2), 1275–1313. https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2018.2869360
- Fagnant, D. J., Kockelman, K. (2015). Preparing a nation for autonomous vehicles: opportunities, barriers and policy recommendations. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 77, 167–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2015.04.003
- Daily, M., Medasani, S., Behringer, R., Trivedi, M. (2017). Self-Driving Cars. Computer, 50 (12), 18–23. https://doi.org/10.1109/mc.2017.4451204
- Yaqoob, I., Khan, L. U., Kazmi, S. M. A., Imran, M., Guizani, N., Hong, C. S. (2020). Autonomous Driving Cars in Smart Cities: Recent Advances, Requirements, and Challenges. IEEE Network, 34 (1), 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1109/mnet.2019.1900120
- Parekh, D., Poddar, N., Rajpurkar, A., Chahal, M., Kumar, N., Joshi, G. P., Cho, W. (2022). A Review on Autonomous Vehicles: Progress, Methods and Challenges. Electronics, 11 (14), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142162
- Kuutti, S., Fallah, S., Katsaros, K., Dianati, M., Mccullough, F., Mouzakitis, A. (2018). A Survey of the State-of-the-Art Localization Techniques and Their Potentials for Autonomous Vehicle Applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5 (2), 829–846. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2018.2812300
- Hossain, T., Habibullah, H., Islam, R. (2022). Steering and Speed Control System Design for Autonomous Vehicles by Developing an Optimal Hybrid Controller to Track Reference Trajectory. Machines, 10 (6), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060420
- Kebbati, Y., Ait‐Oufroukh, N., Ichalal, D., Vigneron, V. (2022). Lateral control for autonomous wheeled vehicles: A technical review. Asian Journal of Control, 25 (4), 2539–2563. https://doi.org/10.1002/asjc.2980
- Filho, C. M., Wolf, D. F., Grassi, V., Osorio, F. S. (2014). Longitudinal and lateral control for autonomous ground vehicles. 2014 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, 588–593. https://doi.org/10.1109/ivs.2014.6856431
- Chebly, A., Talj, R., Charara, A. (2017). Coupled Longitudinal and Lateral Control for an Autonomous Vehicle Dynamics Modeled Using a Robotics Formalism. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 50 (1), 12526–12532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.2190
- Wang, J., Zhang, L., Huang, Y., Zhao, J., Bella, F. (2020). Safety of Autonomous Vehicles. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8867757
- Hasmitha, J., Shivani, M., Manasa, M., Chavan, A. (2020). Steering Control for Autonomous Vehicle using Model Predictive Controller. 2020 IEEE International Conference for Innovation in Technology (INOCON), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/inocon50539.2020.9298205
- Jung, C., Kim, H., Son, Y., Lee, K., Yi, K. (2014). Parameter adaptive steering control for autonomous driving. 17th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 1462–1467. https://doi.org/10.1109/itsc.2014.6957892
- Yuan, T., Zhao, R. (2022). LQR-MPC-Based Trajectory-Tracking Controller of Autonomous Vehicle Subject to Coupling Effects and Driving State Uncertainties. Sensors, 22 (15), 5556. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155556
- Emirler, M. T., Uygan, İ. M. C., Aksun Güvenç, B., Güvenç, L. (2014). Robust PID Steering Control in Parameter Space for Highly Automated Driving. International Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2014, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/259465
- Wang, X., Fu, M., Ma, H., Yang, Y. (2015). Lateral control of autonomous vehicles based on fuzzy logic. Control Engineering Practice, 34, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2014.09.015
- de Silva, C. W. (1995). Applications of fuzzy logic in the control of robotic manipulators. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 70 (2-3), 223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(94)00219-w
- Kodagoda, K. R. S., Wijesoma, W. S., Teoh, E. K. (2002). Fuzzy speed and steering control of an AGV. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 10 (1), 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1109/87.974344
- Liang, Q., Mendel, J. M. (2000). Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 8 (5), 535–550. https://doi.org/10.1109/91.873577
- Arifin, B., Suprapto, B. Y., Prasetyowati, S. A. D., Nawawi, Z. (2022). Steering Control in Electric Power Steering Autonomous Vehicle Using Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Control and PI Control. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 13 (3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj13030053
- Carreon-Ortiz, H., Valdez, F., Castillo, O. (2023). Comparative Study of Type-1 and Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems in Parameter Adaptation for the Fuzzy Discrete Mycorrhiza Optimization Algorithm. Mathematics, 11 (11), 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112501
- Rastelli, J. P., Peñas, M. S. (2015). Fuzzy logic steering control of autonomous vehicles inside roundabouts. Applied Soft Computing, 35, 662–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.06.030
- Naranjo, J. E., Gonzalez, C., Garcia, R., de Pedro, T. (2008). Lane-Change Fuzzy Control in Autonomous Vehicles for the Overtaking Maneuver. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 9 (3), 438–450. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2008.922880
- Ashraf, Z., Roy, M. L., Muhuri, P. K., Danish Lohani, Q. M. (2020). Interval type-2 fuzzy logic system based similarity evaluation for image steganography. Heliyon, 6 (5), e03771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03771
- Ginarsa, I. M., Muljono, A. B., Nrartha, I. M. A., Zebua, O. (2018). Desain Power System Stabilizer Berbasis Fuzzy Tipe-2 untuk Perbaikan Stabilitas Mesin Tunggal. Jurnal Rekayasa Elektrika, 14 (1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.17529/jre.v14i1.8464
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Bhakti Yudho Suprapto, Suci Dwijayanti, Muhammad Irvin Fadillah

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









