Розробка гібридної архітектури сіамської нейронної мережі та нейронної мережі прямого поширення для вимірювання семантичної подібності текстів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326956Ключові слова:
нейронна мережа прямого поширення, семантична текстова подібність, Sentence-BERT, сіамська нейронна мережаАнотація
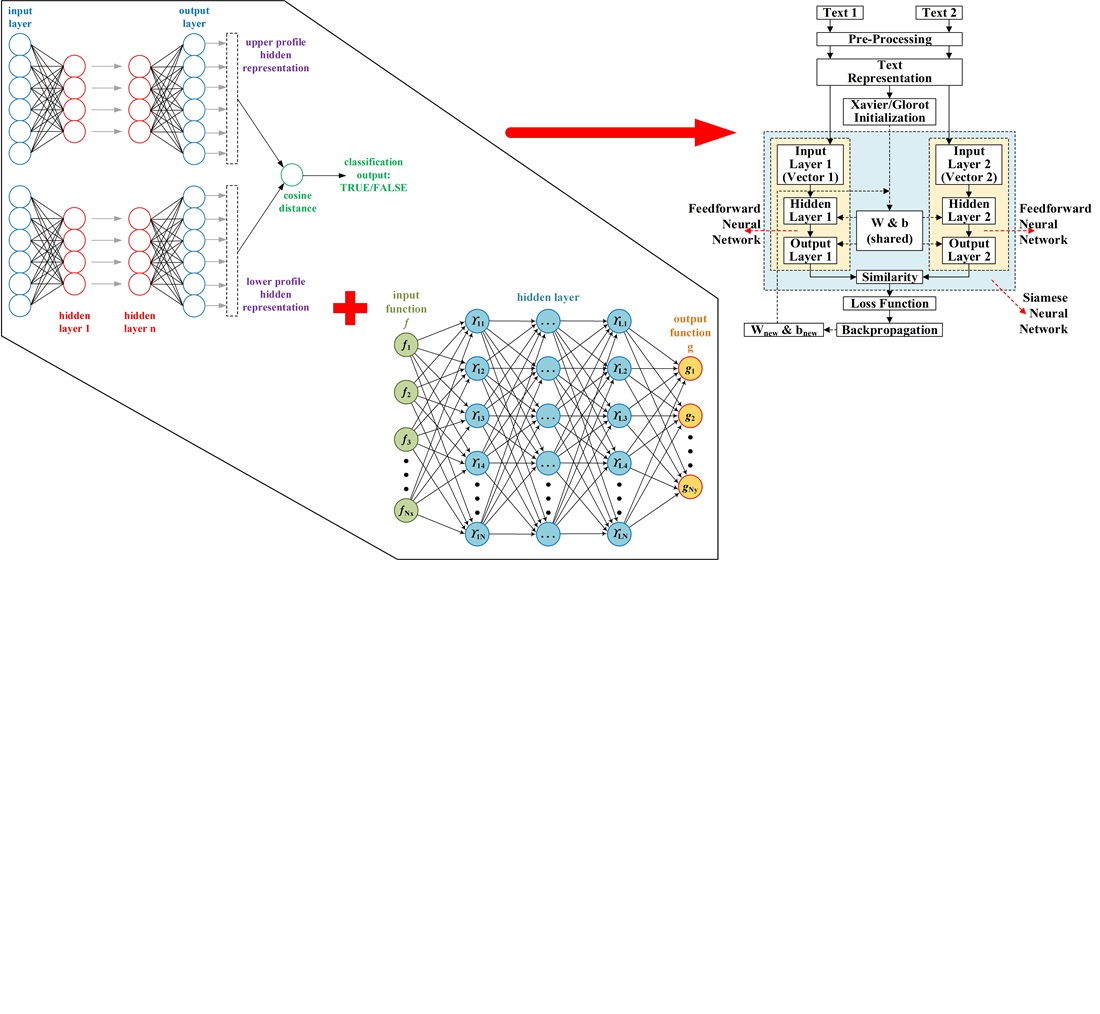
Об'єктом цього дослідження є семантична подібність між двома текстами. Це дослідження зосереджено на розробці гібридної архітектури, яка поєднує сіамську нейронну мережу (SNN) з нейронною мережею прямого поширення (FNN) для вимірювання семантичної подібності тексту, з представленням тексту за допомогою методу Sentence-BERT. Розглядається проблема виявлення глибоких семантичних зв'язків між двома текстами, чого важко досягти традиційними методами, такими як метод частоти термінів та зворотної частоти документів (TF-IDF) або Word2Vec. Це дослідження спрямоване на подолання цих недоліків шляхом об'єднання двох архітектур у більш потужну гібридну систему. Результати тестування показують найвищу точність 87,82 % на наборі даних Semantic Textual Simility (STS) з використанням моделі SBERT “all-MiniLM-L6-v2”, 76,72 % на наборі даних Quora Question Pairs (QQP) з використанням моделі “multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1” та 73,79 % на наборі даних Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus (MSRP) з використанням моделі “paraphrase-MiniLM-L12-v2”. Оптимальні параметри для кількості епох коливалися від 300 до 700, а оптимальний коефіцієнт навчання – від 0,01 до 0,5. Моделі SBERT, такі як “paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2” та “paraphrase-MiniLM-L12-v2”, дали найкращі результати на відповідних наборах даних. Гнучкість моделі «multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1» також показує, що модель, розроблена для завдань запитань і відповідей, може бути використана в області виявлення перефраз. Унікальною особливістю моделі є інтеграція SBERT як текстового представлення, що призводить до багатшого семантичного вектора, ніж традиційні методи. Модель має потенціал для широкого застосування в різних областях, таких як виявлення плагіату, юридичні документи та системи запитань і відповідей. Однак, реалізація вимагає уваги до вибору параметрів, таких як швидкість навчання та кількість епох, щоб уникнути надмірного або недостатнього налаштування
Посилання
- Jinarat, S., Pruengkarn, R. (2024). Enhancing Short Text Semantic Similarity Measurement Using Pretrained Word Embeddings and Big Data. 2024 5th International Conference on Big Data Analytics and Practices (IBDAP), 63–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/ibdap62940.2024.10689695
- Abdalgader, K., Matroud, A. A., Hossin, K. (2024). Experimental study on short-text clustering using transformer-based semantic similarity measure. PeerJ Computer Science, 10, e2078. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2078
- Alnajem, N. A., Binkhonain, M., Shamim Hossain, M. (2024). Siamese Neural Networks Method for Semantic Requirements Similarity Detection. IEEE Access, 12, 140932–140947. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3469636
- Fan, A., Wang, S., Wang, Y. (2024). Legal Document Similarity Matching Based on Ensemble Learning. IEEE Access, 12, 33910–33922. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3371262
- Bao, W., Dong, J., Xu, Y., Yang, Y., Qi, X. (2024). Exploring Attentive Siamese LSTM for Low-Resource Text Plagiarism Detection. Data Intelligence, 6 (2), 488–503. https://doi.org/10.1162/dint_a_00242
- Goltaji, M., Abbaspour, J., Jowkar, A., Fakhrahmad, S. M. (2023). Comparison of text-based and linked-based metrics in terms of estimating the similarity of articles. Journal of Librarianship and Information Science, 56 (3), 760–772. https://doi.org/10.1177/09610006231165759
- Korade, N. B., Salunke, M. B., Bhosle, A. A., Kumbharkar, P. B., Asalkar, G. G., Khedkar, R. G. (2024). Strengthening Sentence Similarity Identification Through OpenAI Embeddings and Deep Learning. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 15 (4). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2024.0150485
- Reimers, N., Gurevych, I. (2019). Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/d19-1410
- Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805
- Altamimi, A., Umer, M., Hanif, D., Alsubai, S., Kim, T.-H., Ashraf, I. (2024). Employing Siamese MaLSTM Model and ELMO Word Embedding for Quora Duplicate Questions Detection. IEEE Access, 12, 29072–29082. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3367978
- Li, R., Cheng, L., Wang, D., Tan, J. (2023). Siamese BERT Architecture Model with attention mechanism for Textual Semantic Similarity. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82 (30), 46673–46694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15509-4
- Chicco, D. (2020). Siamese Neural Networks: An Overview. Artificial Neural Networks, 73–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0826-5_3
- Wong, K., Dornberger, R., Hanne, T. (2022). An analysis of weight initialization methods in connection with different activation functions for feedforward neural networks. Evolutionary Intelligence, 17 (3), 2081–2089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-022-00795-y
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Lydia, M. S., Efendi, S. (2023). A novel approach to the development of neural network architecture based on metaheuristic protis approach. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (124)), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281986
- Han, S., Shi, L., Tsui, F. (Rich). (2025). Enhancing semantical text understanding with fine-tuned large language models: A case study on Quora Question Pair duplicate identification. PLOS ONE, 20 (1), e0317042. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0317042
- Faseeh, M., Khan, M. A., Iqbal, N., Qayyum, F., Mehmood, A., Kim, J. (2024). Enhancing User Experience on Q&A Platforms: Measuring Text Similarity Based on Hybrid CNN-LSTM Model for Efficient Duplicate Question Detection. IEEE Access, 12, 34512–34526. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3358422
- Abdalla, H. I., Amer, A. A. (2021). Boolean logic algebra driven similarity measure for text based applications. PeerJ Computer Science, 7, e641. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.641
- Xue, Y., Tong, Y., Neri, F. (2022). An ensemble of differential evolution and Adam for training feed-forward neural networks. Information Sciences, 608, 453–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.06.036
- Hemeida, A. M., Hassan, S. A., Mohamed, A.-A. A., Alkhalaf, S., Mahmoud, M. M., Senjyu, T., El-Din, A. B. (2020). Nature-inspired algorithms for feed-forward neural network classifiers: A survey of one decade of research. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 11 (3), 659–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.01.007
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Effendi, S., Lidya, M. S. (2021). Prediction Using A Neural Network Algorithm Approach (A Review). 2021 International Conference on Software Engineering & Computer Systems and 4th International Conference on Computational Science and Information Management (ICSECS-ICOCSIM), 325–330. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsecs52883.2021.00066
- Saini, J. R., Vaidya, S. (2024). A Novel Page Similarity Classification Algorithm for Healthcare Web URL Classification. Proceedings of Third International Conference on Computing and Communication Networks, 291–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-2671-4_22
- Diamzon, J., Venturi, D. (2025). Uncertainty Propagation in Feed-Forward Neural Network Models. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5201857
- Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press. Available at: https://www.deeplearningbook.org/
- Shen, Y., Lin, Z. (2024). PatentGrapher: A PLM-GNNs Hybrid Model for Comprehensive Patent Plagiarism Detection Across Full Claim Texts. IEEE Access, 12, 182717–182725. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3508762
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Ng Poi Wong, Tengku Henny Febriana Harumy, Syahril Efendi

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









