Розробка моделей навчання на основі машинного навчання з квантовим відпалом для оптимізації навчання в цифрову еру
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.333721Ключові слова:
машинне навчання, налаштування гіперпараметрів, складність квантового відпалу, оптимізація цифрової трансформаціїАнотація
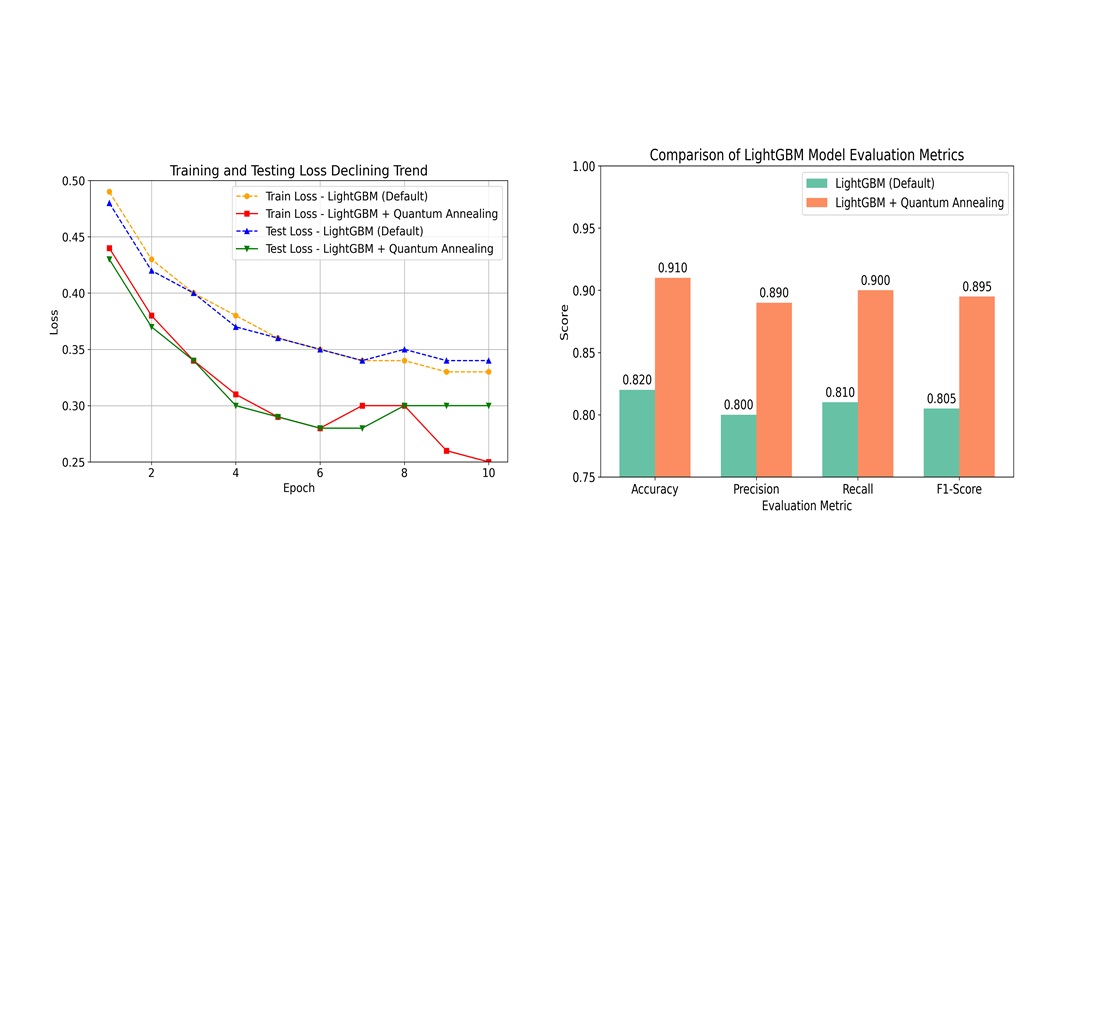
Об'єктом цього дослідження є прогнозування успішності цифрового навчання. Проблеми, що вирішуються в цьому дослідженні, полягають у низькій точності та ефективності моделі прогнозування, спричиненій складністю навчальних даних, та обмеженнями традиційних методів налаштування, таких як пошук по сітці та випадковий пошук, які не здатні оптимально орієнтуватися в широкому та нелінійному просторі параметрів. Отримані результати показують, що інтеграція квантового відпалу в процес оптимізації гіперпараметрів може значно покращити продуктивність моделі. Точність моделі зросла з 82% до 91%, з постійним покращенням точності, повноти та F1-оцінки. Модель також продемонструвала швидшу збіжність та менші втрати як на навчальних, так і на тестових даних, що свідчить про кращі можливості узагальнення на нові дані. З інтерпретації цих результатів можна зробити висновок, що квантовий відпал може ефективно орієнтуватися в просторі параметрів, досліджуючи комбінації значень, які недоступні традиційними методами. Головною особливістю та характеристикою цих результатів є їхня здатність поєднувати обчислювальну ефективність LightGBM з дослідженням складних рішень за допомогою квантових методів, що робить її дуже придатною для задач динамічного навчання. Сфера застосування та умови практичного використання розробленої моделі включають цифрові системи управління навчанням, адаптивні навчальні платформи. Ці висновки є актуальними для застосування в розробці освітніх систем на основі штучного інтелекту, які підтримують персоналізацію в сучасну епоху цифрової трансформації
Посилання
- Yulianti, L. P., Surendro, K. (2022). Implementation of Quantum Annealing: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access, 10, 73156–73177. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3188117
- Salloum, H., Aldaghstany, H. S., Orabi, O., Haidar, A., Bahrami, M. R., Mazzara, M. (2024). Integration of Machine Learning with Quantum Annealing. Advanced Information Networking and Applications, 338–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57870-0_30
- Nath, R. K., Thapliyal, H., Humble, T. S. (2021). A Review of Machine Learning Classification Using Quantum Annealing for Real-World Applications. SN Computer Science, 2 (5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00751-0
- Salloum, H., Sabbagh, K., Savchuk, V., Lukin, R., Orabi, O., Isangulov, M., Mazzara, M. (2025). Performance of Quantum Annealing Machine Learning Classification Models on ADMET Datasets. IEEE Access, 13, 16263–16287. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2025.3531391
- Jooya, A., Keshavarz, B., Dimopoulos, N., Oberoi, J. S. (2017). Accelerating Neural Network Ensemble Learning Using Optimization and Quantum Annealing Techniques. Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Post Moores Era Supercomputing, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1145/3149526.3149528
- Zielewski, M., Takahashi, K., Shimomura, Y., Takizawa, H. (2023). Efficient Pause Location Prediction Using Quantum Annealing Simulations and Machine Learning. IEEE Access, 11, 104285–104294. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3317698
- Wang, H., Wang, W., Liu, Y., Alidaee, B. (2022). Integrating Machine Learning Algorithms With Quantum Annealing Solvers for Online Fraud Detection. IEEE Access, 10, 75908–75917. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3190897
- Panizza, V., Hauke, P., Micheletti, C., Faccioli, P. (2024). Protein Design by Integrating Machine Learning with Quantum Annealing and Quantum-inspired Optimization. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.07177
- Pranjic, D., Mummaneni, B. C., Tutschku, C. (2024). Quantum Annealing based Feature Selection in Machine Learning. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2411.19609
- Yoon, B., Chang, C. C., Kenyon, G. T., Nguyen, N. T. T., Rrapaj, E. (2022). Prediction and compression of lattice QCD data using machine learning algorithms on quantum annealer. Proceedings of The 38th International Symposium on Lattice Field Theory — PoS(LATTICE2021), 143. https://doi.org/10.22323/1.396.0143
- Yulianti, L. P., Trisetyarso, A., Santoso, J., Surendro, K. (2023). A hybrid quantum annealing method for generating ensemble classifiers. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 35 (10), 101831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101831
- Setiadi, D. R. I. M., Susanto, A., Nugroho, K., Muslikh, A. R., Ojugo, A. A., Gan, H.-S. (2024). Rice Yield Forecasting Using Hybrid Quantum Deep Learning Model. Computers, 13 (8), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13080191
- Felefly, T., Roukoz, C., Fares, G., Achkar, S., Yazbeck, S., Meyer, P. et al. (2023). An Explainable MRI-Radiomic Quantum Neural Network to Differentiate Between Large Brain Metastases and High-Grade Glioma Using Quantum Annealing for Feature Selection. Journal of Digital Imaging, 36 (6), 2335–2346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-023-00886-x
- Okey, O. D., Maidin, S. S., Lopes Rosa, R., Toor, W. T., Carrillo Melgarejo, D., Wuttisittikulkij, L. et al. (2022). Quantum Key Distribution Protocol Selector Based on Machine Learning for Next-Generation Networks. Sustainability, 14 (23), 15901. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315901
- Samà, M., D’Ariano, A., D’Ariano, P., Pacciarelli, D. (2017). Scheduling models for optimal aircraft traffic control at busy airports: Tardiness, priorities, equity and violations considerations. Omega, 67, 81–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2016.04.003
- Jamili, A. (2017). A robust mathematical model and heuristic algorithms for integrated aircraft routing and scheduling, with consideration of fleet assignment problem. Journal of Air Transport Management, 58, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2016.08.008
- Zhang, L., Li, Z., Królczyk, G., Wu, D., Tang, Q. (2019). Mathematical modeling and multi-attribute rule mining for energy efficient job-shop scheduling. Journal of Cleaner Production, 241, 118289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118289
- Correa Issi, G., Linfati, R., Escobar, J. W. (2020). Mathematical Optimization Model for Truck Scheduling in a Distribution Center with a Mixed Service-Mode Dock Area. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8813372
- Hammad, A. W., Grzybowska, H., Sutrisna, M., Akbarnezhad, A., Haddad, A. (2019). A novel mathematical optimisation model for the scheduling of activities in modular construction factories. Construction Management and Economics, 38 (6), 534–551. https://doi.org/10.1080/01446193.2019.1682174
- Aly, M. (2024). Revolutionizing online education: Advanced facial expression recognition for real-time student progress tracking via deep learning model. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 84 (13), 12575–12614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-19392-5
- Rizwan, S., Nee, C. K., Garfan, S. (2025). Identifying the Factors Affecting Student Academic Performance and Engagement Prediction in MOOC Using Deep Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access, 13, 18952–18982. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2025.3533915
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Irfan Dahnial, Al-Khowarizmi Al-Khowarizmi, Karina Winda

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









